
In presence of strong bases, triple bonds will migrate within carbon skeletons by the:
(A) Removal of protons
(B) Addition of protons
(C) Removal and addition of protons
(D) Addition and removal of protons
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: The functional group that contains carbon-carbon triple bonds is called alkyne functional group and it is their characteristic that the C-H bonds that are \[\alpha \] with respect to alkyne will react in presence of strong base because of their acidic character.
Complete answer:
In the question, migration of triple bonds is carried out.
- When a carbon-carbon triple bond is present, this group is called the alkyne functional group and we know that the hydrogens attached to \[\alpha \]-carbon to the alkyne functional group is also acidic enough to react with a strong base.
- So, in presence of strong bases like Sodamide or Sodium-tert-butoxide, the \[\alpha \]-hydrogens of alkyne functional groups react and the compound gets deprotonated. The reaction is shown below.
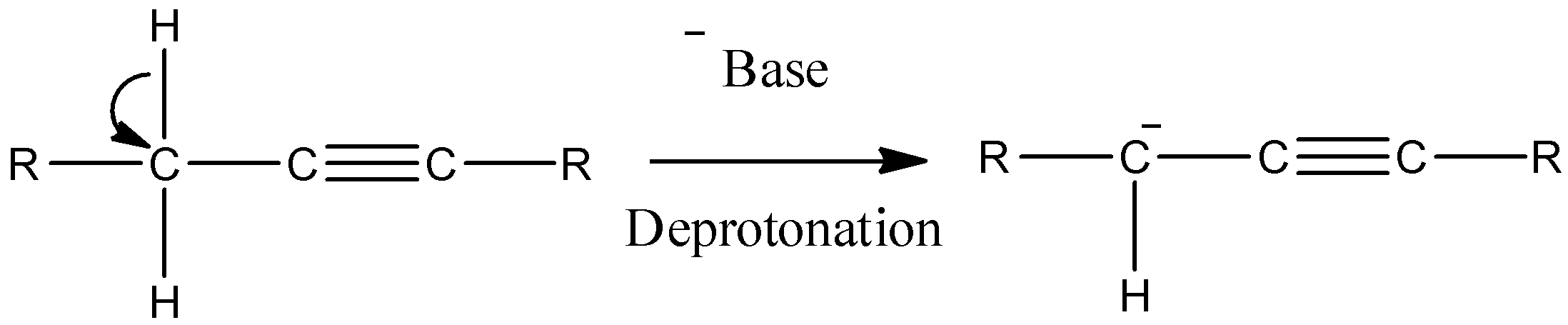
- After deprotonation, the carbanion formed can show resonance structures and will react with a Protonated base to produce allene.
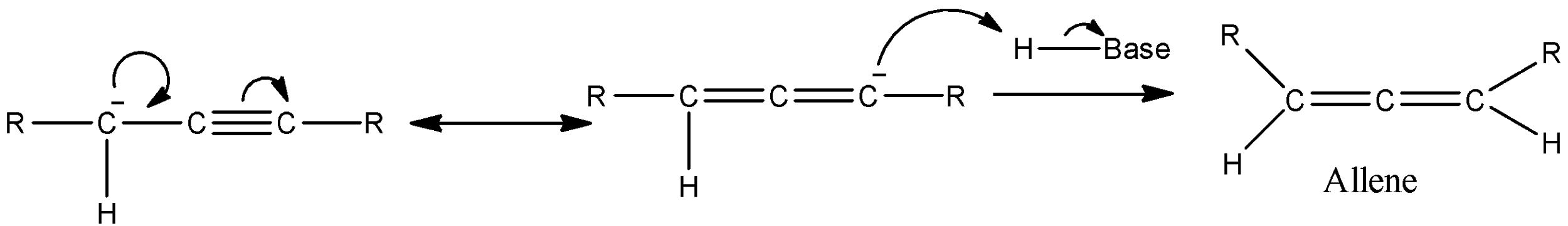
- Then protons of allenes are also acidic enough to react with the strong base in the system and will form a carbanion as shown below.
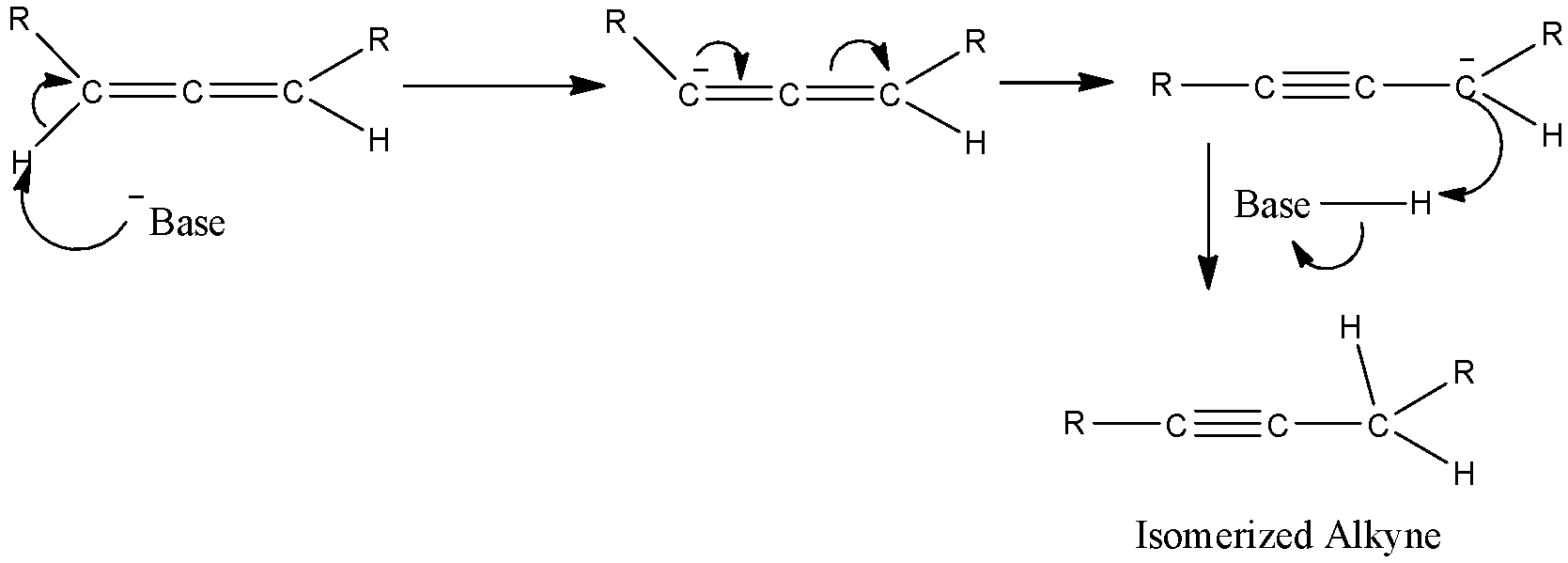
Hence as shown here, the carbanion formed will react with the protonated base and form an isomerized alkyne.
So, we can say that migration of triple bonds occurs by first deprotonation and then re-protonation. That means by removal and addition of protons.
So, correct answer for this reaction is (C) Removal and addition of protons
Note: Do not think that initially protonation reaction occurs, because there is no suitable acid present in the reaction mixture. Remember that both the carbon atoms that have alkyl groups bonded with in allene, can undergo deprotonation reaction but in only one case, we will get different alkyne than the starting material.
Complete answer:
In the question, migration of triple bonds is carried out.
- When a carbon-carbon triple bond is present, this group is called the alkyne functional group and we know that the hydrogens attached to \[\alpha \]-carbon to the alkyne functional group is also acidic enough to react with a strong base.
- So, in presence of strong bases like Sodamide or Sodium-tert-butoxide, the \[\alpha \]-hydrogens of alkyne functional groups react and the compound gets deprotonated. The reaction is shown below.

- After deprotonation, the carbanion formed can show resonance structures and will react with a Protonated base to produce allene.

- Then protons of allenes are also acidic enough to react with the strong base in the system and will form a carbanion as shown below.

Hence as shown here, the carbanion formed will react with the protonated base and form an isomerized alkyne.
So, we can say that migration of triple bonds occurs by first deprotonation and then re-protonation. That means by removal and addition of protons.
So, correct answer for this reaction is (C) Removal and addition of protons
Note: Do not think that initially protonation reaction occurs, because there is no suitable acid present in the reaction mixture. Remember that both the carbon atoms that have alkyl groups bonded with in allene, can undergo deprotonation reaction but in only one case, we will get different alkyne than the starting material.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




