
In peas, yellow seed (Y) is dominant over green seed (y). In this $F_2$ generation of a monohybrid cross that begins when a dominant homozygote is crossed with a recessive homozygote, you would expect.
a. Plants that produce three yellow seeds to every green seed
b. Plants with one yellow seed for every green seed
c. Only plants with the genotype Yy
d. Only plants that produces yellow seeds
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: The father of genetics, Gregor John Mendel had worked on pea plants and discovered fundamental laws of genetics. He established three laws of inheritance that are law of dominance, law of segregation and law of independent assortment.
Complete answer:
Let’s remember these three laws to achieve an answer.
• Law of dominance states that the dominant allele or trait expresses itself in both homozygous and heterozygous conditions.
• Law of segregation represents that a parent may have two different alleles for the same gene each on a set of two chromosomes. These two alleles get separated during the second cell division of meiosis.
• Law of independent assortment states that when two allele pairs get separated during meiosis it has nothing to do with how other allele pairs get separated.
Here to get an answer, we have to use the law of dominance and law of segregation. Here we first have to make cross over between dominant homozygous alleles and recessive homozygous alleles. In the given question, yellow colored seeds are dominant while green colored seeds are recessive. When the first crossover takes place between YY (yellow color allele) and yy (green color allele), the first $F_1$ generation produces heterozygous alleles (Yy). In which yellow is dominated, pea plants will produce yellow seeds. When self-crossed, that is Yy x Yy, $F_2$ generation will have three fourth plants that will produce yellow seeds and one fourth plants that will produce green seeds. We can see the pictorial representation below.
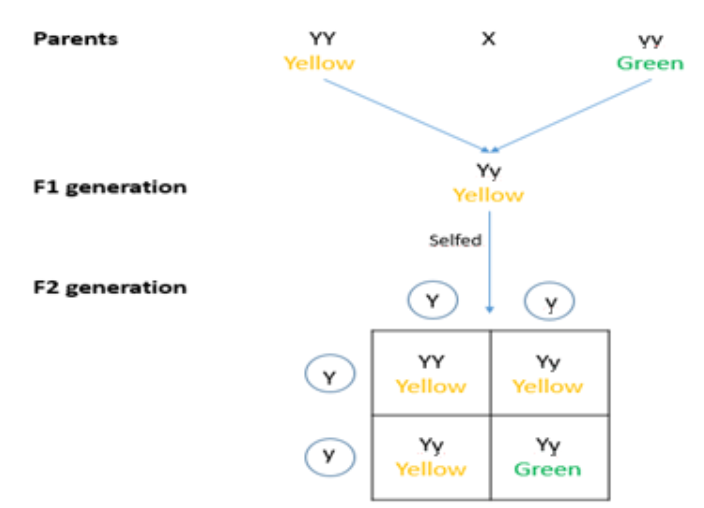
From the pictorial representation, we can conclude that $F_2$ generation shows phenotypic ratio as 3:1.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Mendel’s laws of dominance, segregation and independent assortment helps us identify the true identity of alleles. This law can be proven by practical examination. So many genetic disorders work on the basis of the law of dominance.
Complete answer:
Let’s remember these three laws to achieve an answer.
• Law of dominance states that the dominant allele or trait expresses itself in both homozygous and heterozygous conditions.
• Law of segregation represents that a parent may have two different alleles for the same gene each on a set of two chromosomes. These two alleles get separated during the second cell division of meiosis.
• Law of independent assortment states that when two allele pairs get separated during meiosis it has nothing to do with how other allele pairs get separated.
Here to get an answer, we have to use the law of dominance and law of segregation. Here we first have to make cross over between dominant homozygous alleles and recessive homozygous alleles. In the given question, yellow colored seeds are dominant while green colored seeds are recessive. When the first crossover takes place between YY (yellow color allele) and yy (green color allele), the first $F_1$ generation produces heterozygous alleles (Yy). In which yellow is dominated, pea plants will produce yellow seeds. When self-crossed, that is Yy x Yy, $F_2$ generation will have three fourth plants that will produce yellow seeds and one fourth plants that will produce green seeds. We can see the pictorial representation below.

From the pictorial representation, we can conclude that $F_2$ generation shows phenotypic ratio as 3:1.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Mendel’s laws of dominance, segregation and independent assortment helps us identify the true identity of alleles. This law can be proven by practical examination. So many genetic disorders work on the basis of the law of dominance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




