
In $PC{l_2}{F_3}$, Fluorine is present at:
A.Axial position
B.Equatorial position
C.Axial as well as equatorial position
D.Cannot be predicted
Answer
544.8k+ views
Hint: To answer this question you must recall the concept of hybridization. Hybridization is the concept of mixing of atomic orbitals resulting into the formation of new hybrid orbitals that possess different shapes and energies as compared to the original parent atomic orbitals.
Complete step-by-step answer:We know that in $PC{l_2}{F_3}$, phosphorus undergoes a hybridization of $s{p^3}d$ and the geometry of the molecule is trigonal bipyramidal. Three bonds formed by $s{p^2}$ hybrid orbitals lie in one plane and are known as equatorial bonds while two bonds formed by the $pd$ hybrid orbitals lie perpendicular to the equatorial plane and are known as axial bonds.
Since the equatorial bonds have a higher $s - $character, and thus a higher electronegativity, thus, the more electronegative atoms prefer to occupy the less electronegative axial bonds. Whereas, the less electronegative atoms form equatorial bonds.
We know that fluorine is more electronegative than chlorine and thus two fluorine atoms occupy the axial positions while the third fluorine atom occupies an equatorial position alongside two chlorine atoms.
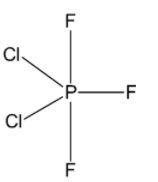
Thus, the correct answer is C.
Note: The Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR Theory) proposes that the hybridized orbitals in an atom arrange themselves in such a way so as to minimize the repulsion between them, hence specifying the geometry of a molecule on the basis of its hybridization. Hybrid orbitals are suitable for the formation of chemical bonds having equal energies. Also, since hybrid orbitals have lower energy than the unhybrid orbitals, hybridization of orbitals leads to the formation of more stable compounds.
Complete step-by-step answer:We know that in $PC{l_2}{F_3}$, phosphorus undergoes a hybridization of $s{p^3}d$ and the geometry of the molecule is trigonal bipyramidal. Three bonds formed by $s{p^2}$ hybrid orbitals lie in one plane and are known as equatorial bonds while two bonds formed by the $pd$ hybrid orbitals lie perpendicular to the equatorial plane and are known as axial bonds.
Since the equatorial bonds have a higher $s - $character, and thus a higher electronegativity, thus, the more electronegative atoms prefer to occupy the less electronegative axial bonds. Whereas, the less electronegative atoms form equatorial bonds.
We know that fluorine is more electronegative than chlorine and thus two fluorine atoms occupy the axial positions while the third fluorine atom occupies an equatorial position alongside two chlorine atoms.

Thus, the correct answer is C.
Note: The Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR Theory) proposes that the hybridized orbitals in an atom arrange themselves in such a way so as to minimize the repulsion between them, hence specifying the geometry of a molecule on the basis of its hybridization. Hybrid orbitals are suitable for the formation of chemical bonds having equal energies. Also, since hybrid orbitals have lower energy than the unhybrid orbitals, hybridization of orbitals leads to the formation of more stable compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




