
In order to determine a focal length of a concave mirror by obtaining the image of the distant object on screen, the position of screen should be
A. parallel to plane of concave mirror
B. perpendicular to plane of concave mirror
C. inclined at 60 degree angle to plane of concave mirror
D. in any direction with respect to plane of concave mirror
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: In case of mirrors usually there are three types used. Plain mirror, concave mirror and convex mirror. All will serve different purposes. Properties of different mirrors are different. In case of convex mirrors they always form virtual images. While concave mirrors form both virtual and real images and plain mirrors form virtual images. Inverted image in the sense it is real.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
Complete answer:
Various positions of placing an object in front of a concave lens gives us various positions of images.
If an object is placed between the pole and focus of the concave mirror then image will be formed on the other side of the mirror. That image formed can be enlarged or diminished and virtual .
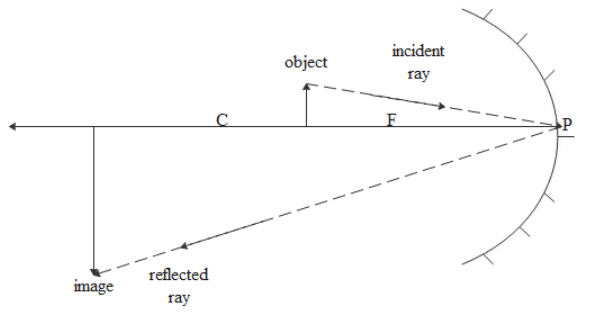
Now if we place the object between focus and center then the image is formed away from the center and the image will be real and inverted. The size of the image will be bigger than an object as shown in the diagram.
C is center and F is focus while P is the pole.
If we place the object away from the center then the image formed will be between center and focus. That image will be real and inverted and diminished.
We have mirror equation
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
Where ‘u’ is object distance and ‘v’ is the image distance and ‘f’ is focal length.
If rays coming from infinity i.e distant objects, image will be formed at the focal length as shown below.
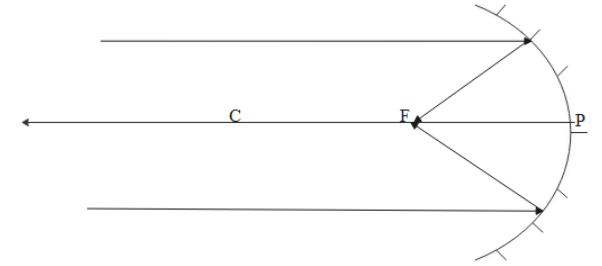
Hence the screen should be kept in a concave mirror.
So option A is correct.
Note:
Concave mirror can be analogous to convex lens. All the properties of image formed by the concave mirror will be possessed by the image formed due to convex lens. The only difference between the two images will be the side where images are formed. If images are formed on the object side in a concave mirror then images will be formed on the other side of the convex lens. Rest everything will be the same for the same position of objects in both the cases. Same can be applied for convex mirrors and concave lenses.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
Complete answer:
Various positions of placing an object in front of a concave lens gives us various positions of images.
If an object is placed between the pole and focus of the concave mirror then image will be formed on the other side of the mirror. That image formed can be enlarged or diminished and virtual .

Now if we place the object between focus and center then the image is formed away from the center and the image will be real and inverted. The size of the image will be bigger than an object as shown in the diagram.
C is center and F is focus while P is the pole.
If we place the object away from the center then the image formed will be between center and focus. That image will be real and inverted and diminished.
We have mirror equation
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
Where ‘u’ is object distance and ‘v’ is the image distance and ‘f’ is focal length.
If rays coming from infinity i.e distant objects, image will be formed at the focal length as shown below.

Hence the screen should be kept in a concave mirror.
So option A is correct.
Note:
Concave mirror can be analogous to convex lens. All the properties of image formed by the concave mirror will be possessed by the image formed due to convex lens. The only difference between the two images will be the side where images are formed. If images are formed on the object side in a concave mirror then images will be formed on the other side of the convex lens. Rest everything will be the same for the same position of objects in both the cases. Same can be applied for convex mirrors and concave lenses.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




