
In Kranz anatomy, the bundle sheath cells have-
(a)Thin walls, many intercellular spaces, and no chloroplast
(b)Thick walls, no intercellular spaces, and a large number of chloroplast
(c)Thin walls, no intercellular spaces, and several chloroplasts
(d)Thick walls, many intercellular spaces, and few chloroplasts
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Kranz means wreath (ring) and is a representation of the cells' arrangement. These cells are distinguished by a large number of agranal chloroplasts, thick walls, and no spaces that are impervious to gaseous exchange.
Complete answer:
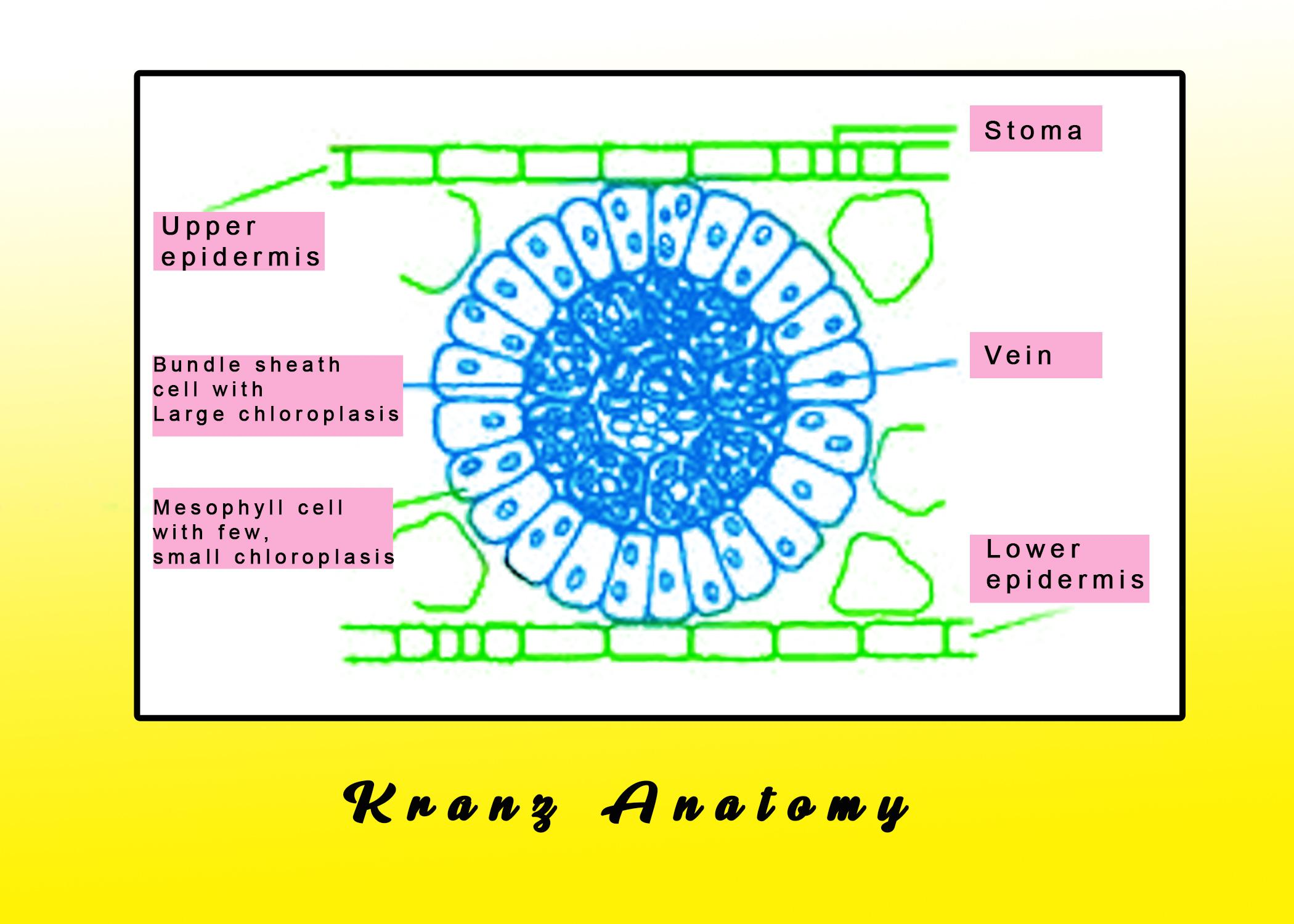
In the chloroplast of $C_4$ plants such as sugarcane, maize ( Zea mays), sorghum, etc., Kranz anatomy occurs. It has two photosynthetic cell types organized in a particular way. There are bundle sheath cells covering the vascular centers and mesophyll cells that surround the sheath cells of the bundle in turn. Rubisco is only found in internalized bundle sheath cells that assist in carbon dioxide fixation.
Kranz anatomy is a specialized structure in $C_4$ plants where the mesophyll cells are clustered in a ring-like fashion around the bundle-sheath cells. In the bundle sheath cells, the number of chloroplasts is more than that in the mesophyll cells. In $C_4$ grasses, such as maize and a few dicots, this is found.
Additional Information: In the $C_4$ plants, the light-dependent responses and the Calvin cycle are segregated. In the bundle sheath cells, the Calvin cycle happens and the mesophyll cells have light-dependent reactions.
Atmospheric oxygen is first fixed in the mesophyll cells to form the 4-carbon compound oxaloacetate, catalyzed by PEP carboxylase.
Oxaloacetate is converted into malate that is carried to the cells of the bundle-sheath.
In the bundle-sheath cells, malate dissociates to free carbon dioxide.
Carbon dioxide is fixed by Rubisco and converted into sugars.
So, the correct answer is ‘Thick walls, many intercellular spaces, and few chloroplasts’.
Note: In three separate steps, the Kranz anatomy is developed:
-Procambium initiation
-Bundle sheath and the specification of mesophyll cells.
-Creation of Chloroplast and integration of the $C_4$ cycle.
Complete answer:
In the chloroplast of $C_4$ plants such as sugarcane, maize ( Zea mays), sorghum, etc., Kranz anatomy occurs. It has two photosynthetic cell types organized in a particular way. There are bundle sheath cells covering the vascular centers and mesophyll cells that surround the sheath cells of the bundle in turn. Rubisco is only found in internalized bundle sheath cells that assist in carbon dioxide fixation.
Kranz anatomy is a specialized structure in $C_4$ plants where the mesophyll cells are clustered in a ring-like fashion around the bundle-sheath cells. In the bundle sheath cells, the number of chloroplasts is more than that in the mesophyll cells. In $C_4$ grasses, such as maize and a few dicots, this is found.
Additional Information: In the $C_4$ plants, the light-dependent responses and the Calvin cycle are segregated. In the bundle sheath cells, the Calvin cycle happens and the mesophyll cells have light-dependent reactions.
Atmospheric oxygen is first fixed in the mesophyll cells to form the 4-carbon compound oxaloacetate, catalyzed by PEP carboxylase.
Oxaloacetate is converted into malate that is carried to the cells of the bundle-sheath.
In the bundle-sheath cells, malate dissociates to free carbon dioxide.
Carbon dioxide is fixed by Rubisco and converted into sugars.
So, the correct answer is ‘Thick walls, many intercellular spaces, and few chloroplasts’.
Note: In three separate steps, the Kranz anatomy is developed:
-Procambium initiation
-Bundle sheath and the specification of mesophyll cells.
-Creation of Chloroplast and integration of the $C_4$ cycle.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




