
In how many ways can 4 girls and 3 boys be seated in a row so that no two boys are together?
Answer
607.5k+ views
Hint:For solving this question, first we will see the important concepts like the fundamental principle of multiplication from permutations and combinations. After that, we will make 4 girls to be seated alternatively in the row and arrange them in $4!$ ways. Then, we will make boys to be seated in the empty spaces between girls and use the formula ${}^{n}{{C}_{r}}=\dfrac{n!}{r!\left( n-r \right)!}$ to get the number of ways in which boys can be seated. Then, we will multiply both results to get the total number of ways possible.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given:
We have to find the number of ways in which 4 girls and 3 boys be seated in a row so that no two boys are together.
Now, before we proceed we should know the following important concept and formulas:
1. Fundamental Principle of Multiplication: If there are two jobs such that one of them can be completed in $m$ ways, and when it has been completed in any of these $m$ ways, the second job can be completed in $n$ ways. Then, two jobs in succession can be completed in $m\times n$ ways.
2. Number of ways to select $r$ objects from the $n$ distinct objects. The formula for the number of different possible ways is ${}^{n}{{C}_{r}}=\dfrac{n!}{r!\left( n-r \right)!}$ .
3. Number of linear arrangements of $r$ distinct objects will be equal to $r!$ .
Now, first, we will make 4 girls to be seated alternatively in the row. For more clarity, look at the figure given below:
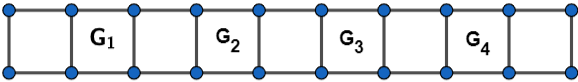
In the above figure ${{G}_{1}},{{G}_{2}},{{G}_{3}},{{G}_{4}}$ are the four girls. And we can arrange the four girls in a total $m=4!=24$ number of ways.
Now, if we make boys to be seated in the empty five spaces then, no two boys will be sitting together. And as we know that, we can select $r$ objects from $n$ distinct objects in ${}^{n}{{C}_{r}}=\dfrac{n!}{r!\left( n-r \right)!}$ the number of ways, then we can arrange the boys in $3!$ ways. Then,
Number of ways in which 3 boys can be seated $=n={}^{5}{{C}_{3}}\times 3!=\dfrac{5!}{3!\left( 5-3 \right)!}\times 3!=\dfrac{120}{2}=60$ ways.
Now, from the fundamental principle of multiplication, we can say that the number of ways in which 4 girls and 3 boys be seated in a row so that no two boys are together will be equal to $m\times n=24\times 60=1440$ ways.
Thus, the required number of ways will be $1440$ ways.
Note: Here, the student should first understand what is asked in the question and then proceed with the right approach to get the correct answer quickly. And in such questions of permutations and combinations,Apply the basic concepts and try to visualize the given event through figures. Moreover, for objective type problems, we could have used the formula $\dfrac{\left( g! \right)\left( g+1 \right)!}{\left( g+1-b \right)!}$ directly where $g$ is the number of girls and $b$ is the number of boys.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given:
We have to find the number of ways in which 4 girls and 3 boys be seated in a row so that no two boys are together.
Now, before we proceed we should know the following important concept and formulas:
1. Fundamental Principle of Multiplication: If there are two jobs such that one of them can be completed in $m$ ways, and when it has been completed in any of these $m$ ways, the second job can be completed in $n$ ways. Then, two jobs in succession can be completed in $m\times n$ ways.
2. Number of ways to select $r$ objects from the $n$ distinct objects. The formula for the number of different possible ways is ${}^{n}{{C}_{r}}=\dfrac{n!}{r!\left( n-r \right)!}$ .
3. Number of linear arrangements of $r$ distinct objects will be equal to $r!$ .
Now, first, we will make 4 girls to be seated alternatively in the row. For more clarity, look at the figure given below:

In the above figure ${{G}_{1}},{{G}_{2}},{{G}_{3}},{{G}_{4}}$ are the four girls. And we can arrange the four girls in a total $m=4!=24$ number of ways.
Now, if we make boys to be seated in the empty five spaces then, no two boys will be sitting together. And as we know that, we can select $r$ objects from $n$ distinct objects in ${}^{n}{{C}_{r}}=\dfrac{n!}{r!\left( n-r \right)!}$ the number of ways, then we can arrange the boys in $3!$ ways. Then,
Number of ways in which 3 boys can be seated $=n={}^{5}{{C}_{3}}\times 3!=\dfrac{5!}{3!\left( 5-3 \right)!}\times 3!=\dfrac{120}{2}=60$ ways.
Now, from the fundamental principle of multiplication, we can say that the number of ways in which 4 girls and 3 boys be seated in a row so that no two boys are together will be equal to $m\times n=24\times 60=1440$ ways.
Thus, the required number of ways will be $1440$ ways.
Note: Here, the student should first understand what is asked in the question and then proceed with the right approach to get the correct answer quickly. And in such questions of permutations and combinations,Apply the basic concepts and try to visualize the given event through figures. Moreover, for objective type problems, we could have used the formula $\dfrac{\left( g! \right)\left( g+1 \right)!}{\left( g+1-b \right)!}$ directly where $g$ is the number of girls and $b$ is the number of boys.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




