
In haloarene compounds, halogen combines with carbons having which hybridisation?
A. $s{p^2}$
B. $s{p^3}$
C. $sp$
D. $ds{p^2}$
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: As we all know that haloarenes are the aromatic hydrocarbon compounds in which one or more than one hydrogen atom that is directly bonded to the aromatic ring are replaced by the halogen atoms. Hybridisation is basically the chemical bonding which is used to explain the covalent bonds in organic molecules.
Complete step by step answer:
The Haloarenes are the aromatic hydrocarbons in which hydrogen atoms are replaced by halogen atoms and these halogens are directly attached to aromatic hydrocarbons like Chlorobenzene.
$sp$ hybridisation is the mixing of one s and one p orbital in the same shell and results in the formation of a new orbital called $sp$ orbital.
$s{p^2}$ hybridisation involves the mixing of one s and two p orbitals and the shape created by this mixing of orbitals is trigonal planar and the newly formed orbital is called $s{p^2}$ hybrid orbital.
$s{p^3}$ hybridisation is the mixing of one s and three p-orbitals resulting in the formation of four new equivalent orbitals giving the molecule a tetrahedral geometry.
$ds{p^2}$ hybridisation is the mixing of one d-orbital, one s and two p-orbitals giving the molecule a square planar geometry and the orbital formed is called the $ds{p^2}$ hybridised orbital.
For example- The carbon in chlorobenzene has three sigma-bonds and one pi-bond.
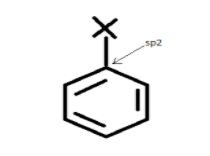
Generally, halogens combine with carbons in haloarenes which are $s{p^2}$ hybridized.
Therefore, the correct answer is (A) option.
Note:
The simplest way to identify the hybridization in the given compounds is to count the number of sigma and pi bonds because these bonds are basically what makes the orbitals and the halogen atom when attaches to the carbon atom next to the aromatic ring it is generally $s{p^3}$ hybridised.
Complete step by step answer:
The Haloarenes are the aromatic hydrocarbons in which hydrogen atoms are replaced by halogen atoms and these halogens are directly attached to aromatic hydrocarbons like Chlorobenzene.
$sp$ hybridisation is the mixing of one s and one p orbital in the same shell and results in the formation of a new orbital called $sp$ orbital.
$s{p^2}$ hybridisation involves the mixing of one s and two p orbitals and the shape created by this mixing of orbitals is trigonal planar and the newly formed orbital is called $s{p^2}$ hybrid orbital.
$s{p^3}$ hybridisation is the mixing of one s and three p-orbitals resulting in the formation of four new equivalent orbitals giving the molecule a tetrahedral geometry.
$ds{p^2}$ hybridisation is the mixing of one d-orbital, one s and two p-orbitals giving the molecule a square planar geometry and the orbital formed is called the $ds{p^2}$ hybridised orbital.
For example- The carbon in chlorobenzene has three sigma-bonds and one pi-bond.

Generally, halogens combine with carbons in haloarenes which are $s{p^2}$ hybridized.
Therefore, the correct answer is (A) option.
Note:
The simplest way to identify the hybridization in the given compounds is to count the number of sigma and pi bonds because these bonds are basically what makes the orbitals and the halogen atom when attaches to the carbon atom next to the aromatic ring it is generally $s{p^3}$ hybridised.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




