
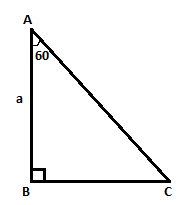
In given figure minimum distance to reach from point C to point A will be
A.\[{a^2}\]
B.\[\sqrt 2 \]
C.\[2\]
D.\[2a\]

Answer
576k+ views
Hint: Given is a right angled triangle. So use measurements of sides opposite to \[{60^ \circ }\] and \[{30^ \circ }\] remaining angles of triangles using \[{30^ \circ } - {60^ \circ } - {90^ \circ }\] triangle theorem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given figure is a right angled triangle.
One angle measures \[{60^ \circ }\] then remaining should be undoubtedly\[{30^ \circ }\] because the sum of all angles of a triangle is \[{180^ \circ }\].
From \[{30^ \circ } - {60^ \circ } - {90^ \circ }\] triangle theorem,
Side opposite to \[{30^ \circ }\]= \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times hypotenuse\]
Side opposite to \[{60^ \circ }\] =\[\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} \times hypotenuse\]
Thus the minimum distance to reach point A from point C is AC only that is hypotenuse of the figure. But we have no length given .But we have a side opposite to hypotenuse is given that is equal to a.
Now let’s use our formula.
Side opposite to \[{30^ \circ }\]= \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times hypotenuse\]
\[
\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{1}{2} \times hypotenuse \\
\Rightarrow hypotenuse = 2a \\
\]
This is the minimum distance \[2a\].
Thus, option D is correct.
Note: In a right angled triangle angles are\[{30^ \circ } - {60^ \circ } - {90^ \circ }\].
Two angles are already given and only need to find the remaining.
Sides opposite to respective angles have measures related with hypotenuse.
In a right angled triangle we generally use Pythagoras’s theorem to find hypotenuse unless measures of base and height of the triangle are given.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given figure is a right angled triangle.
One angle measures \[{60^ \circ }\] then remaining should be undoubtedly\[{30^ \circ }\] because the sum of all angles of a triangle is \[{180^ \circ }\].
From \[{30^ \circ } - {60^ \circ } - {90^ \circ }\] triangle theorem,
Side opposite to \[{30^ \circ }\]= \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times hypotenuse\]
Side opposite to \[{60^ \circ }\] =\[\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} \times hypotenuse\]
Thus the minimum distance to reach point A from point C is AC only that is hypotenuse of the figure. But we have no length given .But we have a side opposite to hypotenuse is given that is equal to a.
Now let’s use our formula.
Side opposite to \[{30^ \circ }\]= \[\dfrac{1}{2} \times hypotenuse\]
\[
\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{1}{2} \times hypotenuse \\
\Rightarrow hypotenuse = 2a \\
\]
This is the minimum distance \[2a\].
Thus, option D is correct.
Note: In a right angled triangle angles are\[{30^ \circ } - {60^ \circ } - {90^ \circ }\].
Two angles are already given and only need to find the remaining.
Sides opposite to respective angles have measures related with hypotenuse.
In a right angled triangle we generally use Pythagoras’s theorem to find hypotenuse unless measures of base and height of the triangle are given.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 7 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the factors of 100 class 7 maths CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

Convert 200 Million dollars in rupees class 7 maths CBSE

AIM To prepare stained temporary mount of onion peel class 7 biology CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of the national daily class 7 english CBSE

List of coprime numbers from 1 to 100 class 7 maths CBSE





