
In given figure,
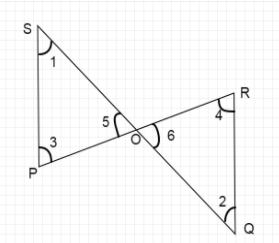
If \[\vartriangle POS \sim \vartriangle ROQ\]. Prove that \[PS\parallel QR\].

Answer
594.6k+ views
Hint: We prove two lines are parallel to each other by showing that alternate interior angles formed when two lines are cut by a transversal are equal.
* A transversal is a line that cuts or intersects any two lines in a plane.
*Alternate interior angles are the angles which are formed inside the two lines but on the opposite sides of the transversal.
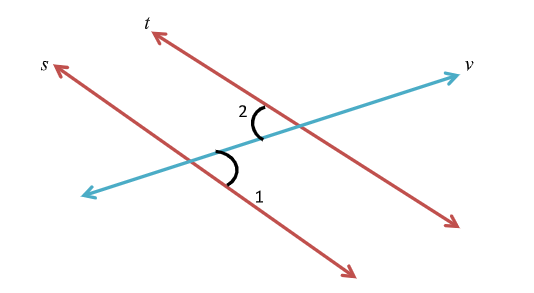
Here a set of two lines \[s\] and \[t\] are cut by a transversal \[v\]. Alternate interior angles are \[\angle 1\] and \[\angle 2\].
Complete step by step answer:
In the given diagram, \[\vartriangle POS \sim \vartriangle ROQ\]
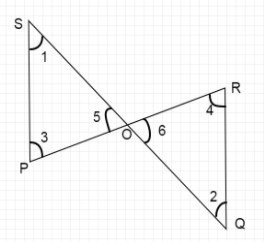
From the definition of similar triangles, the two triangles will have corresponding sides equal and corresponding angles equal.
Therefore, \[\angle 3 = \angle 4,\angle 1 = \angle 2,\angle 5 = \angle 6\]
Taking \[\angle 3 = \angle 4\]
Since, \[PS\] and \[QR\]are two lines intersected by a third line \[PR\] (called transversal) which makes angles \[\angle 3\] and \[\angle 4\] at the point of intersection.
\[\angle 3\] and \[\angle 4\] are the alternate interior angles made by the transversal.
Then from the property which states that when two lines are cut by a transversal and the alternate interior angles are congruent then the two lines are parallel, we can say the two lines \[PS\] and \[QR\] are parallel to each other.
Therefore, \[PS\parallel QR\].
Note:
Students should know in which direction when two triangles are given similar, then only they can make which angles are equal.
Alternative method:
Since, \[\vartriangle POS \sim \vartriangle ROQ\]
From the definition of similar triangles, the two triangles will have corresponding sides equal and corresponding angles equal.
Therefore, \[\angle 3 = \angle 4,\angle 1 = \angle 2,\angle 5 = \angle 6\]
Taking \[\angle 1 = \angle 2\]
Since, \[PS\] and \[QR\]are two lines intersected by a third line \[QS\] (called transversal) which makes angles \[\angle 1\] and \[\angle 2\] at the point of intersection.
\[\angle 1\] and \[\angle 2\] are the alternate interior angles made by the transversal.
Then from the property which states that when two lines are cut by a transversal and the alternate interior angles are congruent then the two lines are parallel, we can say the two lines \[PS\] and \[QR\] are parallel to each other.
Therefore, \[PS\parallel QR\].
* A transversal is a line that cuts or intersects any two lines in a plane.
*Alternate interior angles are the angles which are formed inside the two lines but on the opposite sides of the transversal.

Here a set of two lines \[s\] and \[t\] are cut by a transversal \[v\]. Alternate interior angles are \[\angle 1\] and \[\angle 2\].
Complete step by step answer:
In the given diagram, \[\vartriangle POS \sim \vartriangle ROQ\]

From the definition of similar triangles, the two triangles will have corresponding sides equal and corresponding angles equal.
Therefore, \[\angle 3 = \angle 4,\angle 1 = \angle 2,\angle 5 = \angle 6\]
Taking \[\angle 3 = \angle 4\]
Since, \[PS\] and \[QR\]are two lines intersected by a third line \[PR\] (called transversal) which makes angles \[\angle 3\] and \[\angle 4\] at the point of intersection.
\[\angle 3\] and \[\angle 4\] are the alternate interior angles made by the transversal.
Then from the property which states that when two lines are cut by a transversal and the alternate interior angles are congruent then the two lines are parallel, we can say the two lines \[PS\] and \[QR\] are parallel to each other.
Therefore, \[PS\parallel QR\].
Note:
Students should know in which direction when two triangles are given similar, then only they can make which angles are equal.
Alternative method:
Since, \[\vartriangle POS \sim \vartriangle ROQ\]
From the definition of similar triangles, the two triangles will have corresponding sides equal and corresponding angles equal.
Therefore, \[\angle 3 = \angle 4,\angle 1 = \angle 2,\angle 5 = \angle 6\]
Taking \[\angle 1 = \angle 2\]
Since, \[PS\] and \[QR\]are two lines intersected by a third line \[QS\] (called transversal) which makes angles \[\angle 1\] and \[\angle 2\] at the point of intersection.
\[\angle 1\] and \[\angle 2\] are the alternate interior angles made by the transversal.
Then from the property which states that when two lines are cut by a transversal and the alternate interior angles are congruent then the two lines are parallel, we can say the two lines \[PS\] and \[QR\] are parallel to each other.
Therefore, \[PS\parallel QR\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




