
In figure PS is the bisector of $\angle QPR$ of \[\Delta \text{PQR}\]. Prove that \[\dfrac{QS}{SR}=\dfrac{PQ}{PR}\]


Answer
591k+ views
Hint: In the given question, make an extra construction suitable to solve the problem. Extend the line QP up to T and meet points R and T such that \[\text{PS }||\text{ RT}\] then, apply basic proportionality theorem in triangle QRT. Apply some angle properties to prove some angles equal in both triangles \[\Delta \text{PQR}\] and \[\Delta \text{PTR}\] thus, give the required proof.
Complete step by step answer:
Given PS is the bisector of $\angle QPR$ in triangle PQR. Bisector divides any two given entities into two equal parts. Here, we have an angle bisector PS, which is dividing the angle $\angle QPR$ into two equal angles in triangle PQR.
We have to prove: \[\dfrac{QS}{SR}=\dfrac{PQ}{PR}\]

Now, we will extend QP up to T such that TR is parallel to PS, .

Now, observe $\angle QRT$ in triangle $\Delta QRT$, $TR\text{ }II\text{ }PS\text{ }\Rightarrow \text{ RT II SP}$ and PS intersects QT and QR at two distinct points P and S.
Now we will apply the basic proportionality theorem in $\Delta QRT$ which says: if a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle intersecting the other two sides in distinct points, then the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
Thus, we get
\[\dfrac{QS}{SR}=\dfrac{PQ}{PT}\text{ }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. (1)}\]
Now, we need to prove PT = PR
We have \[\text{RT II SP}\]. Now, let us mark angles in the figure.

In the above figure, we have alternate interior angles . It is shown below,
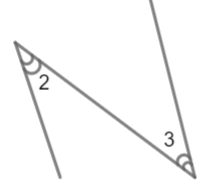
Therefore, we can say that \[\angle SPR=\angle PRT\]
$\begin{align}
& \therefore \angle 2=\angle 3.\text{ }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{.}\left( 2 \right) \\
& \angle SPR=\angle PRT \\
\end{align}$
And we can also write that \[\angle QPS=\angle PTR\] using the same concept.
\[\text{i}\text{.e}\text{. }\angle \text{1=}\angle \text{4 }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. (3)}\]
Now, by corresponding angles property, we have

Also, we have been given that PS is the bisector of $\angle QPR$. Therefore, we can write that
\[\begin{align}
& \therefore \angle QPS=\angle RPS \\
& \text{i}\text{.e}\text{. }\angle \text{1=}\angle \text{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, from equation (2) and (3), putting $\angle \text{1=}\angle 4\text{ and }\angle 2\text{=}\angle 3$, we get:
\[\begin{align}
& \angle 4\text{=}\angle 3 \\
& \text{i}\text{.e}\text{. }\angle \text{PTR=}\angle \text{PRT} \\
\end{align}\]
Since we have got $\angle \text{PTR=}\angle \text{PRT}$ , then we can write that PT = PR as we know that the sides opposite to equal angles of a triangle are equal.
Putting PT = PR in equation (1), we get,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{QS}{SR}=\dfrac{PQ}{PT} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{QS}{SR}=\dfrac{PQ}{PR} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, proved.
Note: This particular question is solved by creating an imaginary geometry by extending QP, students can also solve this question by assuming any other possible geometry/construction. Students must be aware of all the basic properties of angles and triangles to deal with geometry problems. The students must proceed in an order and use all the properties of angles, parallel lines and prove the result. The possible mistakes are equating the wrong angles, i.e instead of equating angles 1 and 4, there is a possibility that students might equate angles 2 and 4. So, such silly mistakes must be avoided as it will lead to wastage of time in exams.
Complete step by step answer:
Given PS is the bisector of $\angle QPR$ in triangle PQR. Bisector divides any two given entities into two equal parts. Here, we have an angle bisector PS, which is dividing the angle $\angle QPR$ into two equal angles in triangle PQR.
We have to prove: \[\dfrac{QS}{SR}=\dfrac{PQ}{PR}\]

Now, we will extend QP up to T such that TR is parallel to PS, .

Now, observe $\angle QRT$ in triangle $\Delta QRT$, $TR\text{ }II\text{ }PS\text{ }\Rightarrow \text{ RT II SP}$ and PS intersects QT and QR at two distinct points P and S.
Now we will apply the basic proportionality theorem in $\Delta QRT$ which says: if a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle intersecting the other two sides in distinct points, then the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
Thus, we get
\[\dfrac{QS}{SR}=\dfrac{PQ}{PT}\text{ }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. (1)}\]
Now, we need to prove PT = PR
We have \[\text{RT II SP}\]. Now, let us mark angles in the figure.

In the above figure, we have alternate interior angles . It is shown below,

Therefore, we can say that \[\angle SPR=\angle PRT\]
$\begin{align}
& \therefore \angle 2=\angle 3.\text{ }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{.}\left( 2 \right) \\
& \angle SPR=\angle PRT \\
\end{align}$
And we can also write that \[\angle QPS=\angle PTR\] using the same concept.
\[\text{i}\text{.e}\text{. }\angle \text{1=}\angle \text{4 }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. }\text{. (3)}\]
Now, by corresponding angles property, we have

Also, we have been given that PS is the bisector of $\angle QPR$. Therefore, we can write that
\[\begin{align}
& \therefore \angle QPS=\angle RPS \\
& \text{i}\text{.e}\text{. }\angle \text{1=}\angle \text{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, from equation (2) and (3), putting $\angle \text{1=}\angle 4\text{ and }\angle 2\text{=}\angle 3$, we get:
\[\begin{align}
& \angle 4\text{=}\angle 3 \\
& \text{i}\text{.e}\text{. }\angle \text{PTR=}\angle \text{PRT} \\
\end{align}\]
Since we have got $\angle \text{PTR=}\angle \text{PRT}$ , then we can write that PT = PR as we know that the sides opposite to equal angles of a triangle are equal.
Putting PT = PR in equation (1), we get,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{QS}{SR}=\dfrac{PQ}{PT} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{QS}{SR}=\dfrac{PQ}{PR} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, proved.
Note: This particular question is solved by creating an imaginary geometry by extending QP, students can also solve this question by assuming any other possible geometry/construction. Students must be aware of all the basic properties of angles and triangles to deal with geometry problems. The students must proceed in an order and use all the properties of angles, parallel lines and prove the result. The possible mistakes are equating the wrong angles, i.e instead of equating angles 1 and 4, there is a possibility that students might equate angles 2 and 4. So, such silly mistakes must be avoided as it will lead to wastage of time in exams.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




