
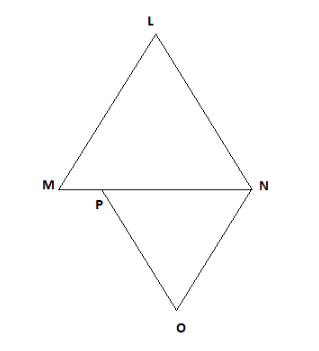
In figure, \[LM\parallel NQ\] and \[LN\parallel PQ\] . If \[MP = \dfrac{1}{3}MN\] , find the ratios of the areas of \[\Delta LMN\] and\[\Delta QNP\].

Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint: In this question given that the opposite lines of the two triangles are parallel so by using alternate interior triangle theorem of parallel line we will prove that the\[\Delta LMN\] and \[\Delta QNP\] are congruent and by using congruence theorem we will find the ratios of the areas of \[\Delta LMN\] and \[\Delta QNP\] .
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given
\[LM\parallel NQ\]
\[LN\parallel PQ\]
\[MP = \dfrac{1}{3}MN - - (i)\]
Now since the line \[LM\parallel NQ\], we can say
\[\angle LMN = \angle ONP\]
Since the two interior angles are cut by the transversal line MN so we can say interior angles are equal.
Now again since the line \[LN\parallel PQ\], we can say
\[\angle LNM = \angle OPN\]
Since the two interior angles are cut by the transversal line MN so we can say interior angles are equal.
Now since the \[\angle LMN = \angle ONP\]and \[\angle LNM = \angle OPN\], so by using the angle-angle criteria we can sa
\[\Delta LMN \sim \Delta NPQ\] [By AA criteria]
Now since the two triangles are congruent we can write the ratio of the area of the two triangles
\[\dfrac{{\Delta LMN}}{{\Delta NPQ}} = \dfrac{{M{N^2}}}{{N{P^2}}} - - (ii)\]
It is given that
\[MP = \dfrac{1}{3}MN - - (i)\]
So we can write
\[
\Rightarrow NP = 1 - MP \\
= 1 - \dfrac{1}{3}MN \\
= \dfrac{2}{3}MN \;
\]
Now substitute the value \[NP = \dfrac{2}{3}MN\], in the equation (ii), hence we get
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\Delta LMN}}{{\Delta NPQ}} = \dfrac{{M{N^2}}}{{N{P^2}}} \\
= \dfrac{{M{N^2}}}{{{{\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}MN} \right)}^2}}} \\
= \dfrac{{M{N^2}}}{{\dfrac{4}{9}M{N^2}}} \\
= \dfrac{9}{4} \;
\]
Hence the ratios of the areas of \[\Delta LMN\]and \[\Delta QNP\] will be equal to \[\dfrac{9}{4}\]
Note: From the properties of the parallel line if a transversal cuts any two parallel lines then the corresponding angles and vertically opposite angles are equal to each other. If a line passes through the two lines on the same plane then the line is called a transversal line and this makes the opposite interior angles to be equal.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given
\[LM\parallel NQ\]
\[LN\parallel PQ\]
\[MP = \dfrac{1}{3}MN - - (i)\]
Now since the line \[LM\parallel NQ\], we can say
\[\angle LMN = \angle ONP\]
Since the two interior angles are cut by the transversal line MN so we can say interior angles are equal.
Now again since the line \[LN\parallel PQ\], we can say
\[\angle LNM = \angle OPN\]
Since the two interior angles are cut by the transversal line MN so we can say interior angles are equal.
Now since the \[\angle LMN = \angle ONP\]and \[\angle LNM = \angle OPN\], so by using the angle-angle criteria we can sa
\[\Delta LMN \sim \Delta NPQ\] [By AA criteria]
Now since the two triangles are congruent we can write the ratio of the area of the two triangles
\[\dfrac{{\Delta LMN}}{{\Delta NPQ}} = \dfrac{{M{N^2}}}{{N{P^2}}} - - (ii)\]
It is given that
\[MP = \dfrac{1}{3}MN - - (i)\]
So we can write
\[
\Rightarrow NP = 1 - MP \\
= 1 - \dfrac{1}{3}MN \\
= \dfrac{2}{3}MN \;
\]
Now substitute the value \[NP = \dfrac{2}{3}MN\], in the equation (ii), hence we get
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{\Delta LMN}}{{\Delta NPQ}} = \dfrac{{M{N^2}}}{{N{P^2}}} \\
= \dfrac{{M{N^2}}}{{{{\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}MN} \right)}^2}}} \\
= \dfrac{{M{N^2}}}{{\dfrac{4}{9}M{N^2}}} \\
= \dfrac{9}{4} \;
\]
Hence the ratios of the areas of \[\Delta LMN\]and \[\Delta QNP\] will be equal to \[\dfrac{9}{4}\]
Note: From the properties of the parallel line if a transversal cuts any two parallel lines then the corresponding angles and vertically opposite angles are equal to each other. If a line passes through the two lines on the same plane then the line is called a transversal line and this makes the opposite interior angles to be equal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




