
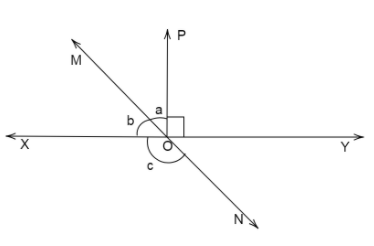
In figure, lines \[XY\]and \[MN\] intersect at \[O\]. If \[\angle POY = {90^ \circ }\]and \[a:b = 2:3\]. Find \[c\].
A. \[{106^ \circ }\]
B. \[{156^ \circ }\]
C. \[{126^ \circ }\]
D. \[{136^ \circ }\]

Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: Using the given angle \[\angle POY = {90^ \circ }\]and the set of supplementary angles \[\angle a,\angle b,\angle POY\] we calculate the sum of \[\angle a,\angle b\]. Then using the given ratio of angles \[a\] and \[b\] we find the value of one angle in terms of another, then substitute in the equation of supplementary angles to find the values of \[a\] and \[b\]. Using a set of supplementary angles on the line \[MN\]we calculate the value of \[c\].
* Supplementary angles are the set of angles which lie on a straight line and sum up to \[{180^ \circ }\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have lines \[XY\]and \[MN\] intersect at point \[O\].
Since, \[XY\] is a straight line.
Therefore all angles on the straight lines sum up to \[{180^ \circ }\]using the supplementary property.
Angles on the straight line \[XY\]are \[\angle XOM,\angle MOP,\angle POY\]
Therefore, we can say \[\angle XOM + \angle MOP + \angle POY = {180^ \circ }\]
Substituting the values of \[\angle XOM = b,\angle MOP = a,\angle POY = {90^ \circ }\] from the diagram, we get
\[b + a + {90^ \circ } = {180^ \circ }\]
Shifting all the constant terms in degrees to the right side of the equation
\[
a + b = {180^ \circ } - {90^ \circ } \\
a + b = {90^ \circ } \\
\] …(i)
Now we are given the ratio of angles \[a:b = 2:3\]
We can write the ratio in terms of fraction as \[\dfrac{a}{b} = \dfrac{2}{3}\]
Multiply both sides of the equation by \[b\] so we get the value of \[a\] in terms of \[b\]
\[
\dfrac{a}{b} \times b = \dfrac{2}{3} \times b \\
a = \dfrac{{2b}}{3} \\
\]
Now we substitute the value of \[a = \dfrac{{2b}}{3}\] in equation (i)
\[\dfrac{{2b}}{3} + b = {90^ \circ }\]
Take LCM on LHS of the equation
\[
\dfrac{{2b + 3b}}{3} = {90^ \circ } \\
\dfrac{{5b}}{3} = {90^ \circ } \\
\]
Multiply both sides of the equation by \[\dfrac{3}{5}\]
\[
\dfrac{{5b}}{3} \times \dfrac{3}{5} = {90^ \circ } \times \dfrac{3}{5} \\
b = 18 \times 3 = {54^ \circ } \\
\]
Now we substitute the value of \[b = {54^ \circ }\]in \[a + b = {90^ \circ }\]
\[a + {54^ \circ } = {90^ \circ }\]
Take all constant values in degree to one side
\[a = {90^ \circ } - {54^ \circ } = {36^ \circ }\]
So, we get the angles \[a = {36^ \circ },b = {54^ \circ }\]
Now looking at the line \[MN\]
Therefore all angles on the straight lines sum up to \[{180^ \circ }\]using the supplementary property.
Angles on the straight line \[MN\]are \[\angle XOM,\angle XON\]
Therefore, we can say \[\angle XOM + \angle XON = {180^ \circ }\]
Substituting the values of \[\angle XOM = b,\angle XON = c\] from the diagram, we get
\[b + c = {180^ \circ }\]
Substituting the value of in the equation.
\[{54^ \circ } + c = {180^ \circ }\]
Shift all the constant in degrees to one side of the equation
\[c = {180^ \circ } - {54^ \circ } = {126^ \circ }\]
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Students are likely to make mistakes in calculation while shifting the constants to the other side of the equation. Students should always change the sign from positive to negative and vice versa when shifting from one side of the equation to another.
* Supplementary angles are the set of angles which lie on a straight line and sum up to \[{180^ \circ }\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have lines \[XY\]and \[MN\] intersect at point \[O\].
Since, \[XY\] is a straight line.
Therefore all angles on the straight lines sum up to \[{180^ \circ }\]using the supplementary property.
Angles on the straight line \[XY\]are \[\angle XOM,\angle MOP,\angle POY\]
Therefore, we can say \[\angle XOM + \angle MOP + \angle POY = {180^ \circ }\]
Substituting the values of \[\angle XOM = b,\angle MOP = a,\angle POY = {90^ \circ }\] from the diagram, we get
\[b + a + {90^ \circ } = {180^ \circ }\]
Shifting all the constant terms in degrees to the right side of the equation
\[
a + b = {180^ \circ } - {90^ \circ } \\
a + b = {90^ \circ } \\
\] …(i)
Now we are given the ratio of angles \[a:b = 2:3\]
We can write the ratio in terms of fraction as \[\dfrac{a}{b} = \dfrac{2}{3}\]
Multiply both sides of the equation by \[b\] so we get the value of \[a\] in terms of \[b\]
\[
\dfrac{a}{b} \times b = \dfrac{2}{3} \times b \\
a = \dfrac{{2b}}{3} \\
\]
Now we substitute the value of \[a = \dfrac{{2b}}{3}\] in equation (i)
\[\dfrac{{2b}}{3} + b = {90^ \circ }\]
Take LCM on LHS of the equation
\[
\dfrac{{2b + 3b}}{3} = {90^ \circ } \\
\dfrac{{5b}}{3} = {90^ \circ } \\
\]
Multiply both sides of the equation by \[\dfrac{3}{5}\]
\[
\dfrac{{5b}}{3} \times \dfrac{3}{5} = {90^ \circ } \times \dfrac{3}{5} \\
b = 18 \times 3 = {54^ \circ } \\
\]
Now we substitute the value of \[b = {54^ \circ }\]in \[a + b = {90^ \circ }\]
\[a + {54^ \circ } = {90^ \circ }\]
Take all constant values in degree to one side
\[a = {90^ \circ } - {54^ \circ } = {36^ \circ }\]
So, we get the angles \[a = {36^ \circ },b = {54^ \circ }\]
Now looking at the line \[MN\]
Therefore all angles on the straight lines sum up to \[{180^ \circ }\]using the supplementary property.
Angles on the straight line \[MN\]are \[\angle XOM,\angle XON\]
Therefore, we can say \[\angle XOM + \angle XON = {180^ \circ }\]
Substituting the values of \[\angle XOM = b,\angle XON = c\] from the diagram, we get
\[b + c = {180^ \circ }\]
Substituting the value of in the equation.
\[{54^ \circ } + c = {180^ \circ }\]
Shift all the constant in degrees to one side of the equation
\[c = {180^ \circ } - {54^ \circ } = {126^ \circ }\]
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Students are likely to make mistakes in calculation while shifting the constants to the other side of the equation. Students should always change the sign from positive to negative and vice versa when shifting from one side of the equation to another.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE





