
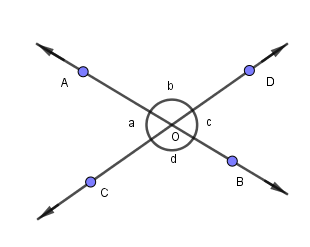
In figure, lines AB and CD intersect each other at point O. If $a:b = 4:5$, find a, b, c, and d.

Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: In this question we will keep in mind that a straight line forms an angle of ${180^ \circ }$. According to the given figure,$\angle AOC + \angle AOD = {180^ \circ}$.$\angle AOC = {80^ \circ }$$\angle AOC$ denotes $a$, $\angle AOD$ denotes $b$, $\angle BOD$ denotes $c$ and $\angle BOC$ denotes $d$.
Complete step by step solution:
Given,
$a:b = 4:5$
$\dfrac{a}{b} = \dfrac{4}{5}$
$ \Rightarrow 5a = 4b$
$ \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{4b}}{5}$
Now, we know that $\angle AOC$ is $a$ and $\angle AOD$ is $b$.
$\angle AOC + \angle AOD = {180^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow a + b = {180^ \circ }$
Putting the value of $a$ in the above equation, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{4b}}{5} + b = {180^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{9b}}{5} = {180^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow b = {180^ \circ } \times \dfrac{5}{9}$
$\therefore b = {100^ \circ }$ Or $\angle AOD$$ = {100^ \circ }$
Now we will find the value of $a$ by putting the value of $b$ in equation $a = \dfrac{{4b}}{5}$
$a = \dfrac{{4b}}{5}$
$ \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{4 \times {{100}^ \circ }}}{5}$
$\Rightarrow a = {80^ \circ }$Or $\angle AOC = {80^ \circ }$
We have already found the value of ‘a’ and ‘b’. Now, we will find the value of $c$ and $d$.
From the above figure we know that;
$\angle AOC + \angle COB = {180^ \circ }$ …. [Linear pair]
$ \Rightarrow {80^ \circ } + \angle COB = {180^ \circ }$
$\therefore \angle COB = {100^ \circ }$ Or d $ = {100^ \circ }$
Again, from the given figure we know that;
\[\angle COB + \angle DOB = {180^ \circ }\] [Linear pair]
\[ \Rightarrow {100^ \circ } + \angle DOB = {180^ \circ }\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle DOB = {80^ \circ }\]Or $c = {80^ \circ }$
$\therefore$ The required angles are: $a={80^\circ}$, ${b=100^\circ}$, $c={80^\circ}$ and $d={80^\circ}$.
Note:
In these types of questions we should apply a rule of straight line that a straight line always forms an angle of ${180^ \circ }$. If we add two angles that are $a$ and $b$ then it will be equal to ${180^ \circ }$. We can see this from the given figure that AB and CD are two straight lines intersecting each other at O. $\angle AOC + \angle AOD = {180^ \circ }$, \[\angle COB + \angle DOB = {180^ \circ }\], $\angle AOC + \angle COB = {180^ \circ }$ and $\angle AOD + \angle BOD = {180^ \circ }$. Ratios of two angles were also given in the question that is a : b is 4 : 5 through which we can find the angles at which line AB and CD intersect each other. So by applying these given information we can find the value of $\angle AOD$, $\angle AOC$, $\angle COB$ and \[\angle DOB\].
Alternatively, you can use the concept of transversal lines: When two lines intersect each other, opposite angles are equal.
Complete step by step solution:
Given,
$a:b = 4:5$
$\dfrac{a}{b} = \dfrac{4}{5}$
$ \Rightarrow 5a = 4b$
$ \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{4b}}{5}$
Now, we know that $\angle AOC$ is $a$ and $\angle AOD$ is $b$.
$\angle AOC + \angle AOD = {180^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow a + b = {180^ \circ }$
Putting the value of $a$ in the above equation, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{4b}}{5} + b = {180^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{9b}}{5} = {180^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow b = {180^ \circ } \times \dfrac{5}{9}$
$\therefore b = {100^ \circ }$ Or $\angle AOD$$ = {100^ \circ }$
Now we will find the value of $a$ by putting the value of $b$ in equation $a = \dfrac{{4b}}{5}$
$a = \dfrac{{4b}}{5}$
$ \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{4 \times {{100}^ \circ }}}{5}$
$\Rightarrow a = {80^ \circ }$Or $\angle AOC = {80^ \circ }$
We have already found the value of ‘a’ and ‘b’. Now, we will find the value of $c$ and $d$.
From the above figure we know that;
$\angle AOC + \angle COB = {180^ \circ }$ …. [Linear pair]
$ \Rightarrow {80^ \circ } + \angle COB = {180^ \circ }$
$\therefore \angle COB = {100^ \circ }$ Or d $ = {100^ \circ }$
Again, from the given figure we know that;
\[\angle COB + \angle DOB = {180^ \circ }\] [Linear pair]
\[ \Rightarrow {100^ \circ } + \angle DOB = {180^ \circ }\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle DOB = {80^ \circ }\]Or $c = {80^ \circ }$
$\therefore$ The required angles are: $a={80^\circ}$, ${b=100^\circ}$, $c={80^\circ}$ and $d={80^\circ}$.
Note:
In these types of questions we should apply a rule of straight line that a straight line always forms an angle of ${180^ \circ }$. If we add two angles that are $a$ and $b$ then it will be equal to ${180^ \circ }$. We can see this from the given figure that AB and CD are two straight lines intersecting each other at O. $\angle AOC + \angle AOD = {180^ \circ }$, \[\angle COB + \angle DOB = {180^ \circ }\], $\angle AOC + \angle COB = {180^ \circ }$ and $\angle AOD + \angle BOD = {180^ \circ }$. Ratios of two angles were also given in the question that is a : b is 4 : 5 through which we can find the angles at which line AB and CD intersect each other. So by applying these given information we can find the value of $\angle AOD$, $\angle AOC$, $\angle COB$ and \[\angle DOB\].
Alternatively, you can use the concept of transversal lines: When two lines intersect each other, opposite angles are equal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




