
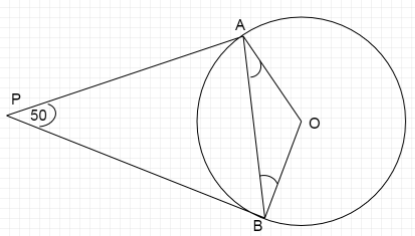
In figure IF \[PA,PB\] are the tangents to a circle with center \[O\] such that \[\angle APB = {50^ \circ }\] then \[\angle OAB\] is equal to
A. \[{25^ \circ }\]
B. \[{30^ \circ }\]
C. \[{40^ \circ }\]
D.\[{50^ \circ }\]

Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint:Here we use the property of tangents from one point to the circle being equal in length and then we have an isosceles triangle whose opposite sides and angles opposite to equal sides are equal. Later, we use the property of radius forming a right angle with the tangent to find the angles of the triangle \[AOB\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here from the above given figure, Point \[P\]lies outside the circle from which two tangents \[PA,PB\] to the circle are drawn.
Since, we know from the property that tangents drawn from one point to the circle are equal in length therefore, we can write \[PA = PB\]
Which gives us \[\vartriangle PAB\] as an isosceles triangle with sides \[PA = PB\]
Since, in an isosceles triangle, angles opposite to equal sides are equal
Therefore, \[\angle PBA = \angle PAB\]
Now since we know sum of all three angles in a triangle sums up to \[{180^ \circ }\]
Now in \[\vartriangle PAB\], Taking the sum of all three angles we can write
\[\angle PBA + \angle PAB + \angle APB = {180^ \circ }\]
Now we substitute the values of \[\angle PBA = \angle PAB,\angle APB = {50^ \circ }\]
\[\angle PAB + \angle PAB + {50^ \circ } = {180^ \circ }\]
Taking the degree values to RHS of the equation
\[
2\angle PAB = {180^ \circ } - {50^ \circ } \\
2\angle PAB = {130^ \circ } \\
\]
Dividing both sides of the equation by \[2\]
\[
\dfrac{{2\angle PAB}}{2} = \dfrac{{{{130}^ \circ }}}{2} \\
\angle PAB = {65^ \circ } \\
\]
Therefore, \[\angle PBA = \angle PAB = {65^ \circ }\]
Now, we know that the radius of the circle forms a right angle with the tangent at that point.
Therefore, \[\angle OAP = {90^ \circ }\]
We can write \[\angle OAP = \angle OAB + \angle PAB\]
Therefore, \[\angle OAB + \angle PAB = {90^ \circ }\]
Substitute the value of \[\angle PAB = {65^ \circ }\]
Therefore, \[
\angle OAB + {65^ \circ } = {90^ \circ } \\
\angle OAB = {90^ \circ } - {65^ \circ } = {25^ \circ } \\
\]
Thus, \[\angle OAB = {25^ \circ }\]
SO, option A is correct.
Note:Students can make mistakes while finding the angle in an isosceles triangle if they assume the wrong set of angles equal, always the angles opposite to equal sides are equal and the third angle is different. Students should always convert their answer from degree into radians if required using the formula \[1radian = {\left( {\dfrac{{180}}{\pi }} \right)^{^ \circ }}\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here from the above given figure, Point \[P\]lies outside the circle from which two tangents \[PA,PB\] to the circle are drawn.
Since, we know from the property that tangents drawn from one point to the circle are equal in length therefore, we can write \[PA = PB\]
Which gives us \[\vartriangle PAB\] as an isosceles triangle with sides \[PA = PB\]
Since, in an isosceles triangle, angles opposite to equal sides are equal
Therefore, \[\angle PBA = \angle PAB\]
Now since we know sum of all three angles in a triangle sums up to \[{180^ \circ }\]
Now in \[\vartriangle PAB\], Taking the sum of all three angles we can write
\[\angle PBA + \angle PAB + \angle APB = {180^ \circ }\]
Now we substitute the values of \[\angle PBA = \angle PAB,\angle APB = {50^ \circ }\]
\[\angle PAB + \angle PAB + {50^ \circ } = {180^ \circ }\]
Taking the degree values to RHS of the equation
\[
2\angle PAB = {180^ \circ } - {50^ \circ } \\
2\angle PAB = {130^ \circ } \\
\]
Dividing both sides of the equation by \[2\]
\[
\dfrac{{2\angle PAB}}{2} = \dfrac{{{{130}^ \circ }}}{2} \\
\angle PAB = {65^ \circ } \\
\]
Therefore, \[\angle PBA = \angle PAB = {65^ \circ }\]
Now, we know that the radius of the circle forms a right angle with the tangent at that point.
Therefore, \[\angle OAP = {90^ \circ }\]
We can write \[\angle OAP = \angle OAB + \angle PAB\]
Therefore, \[\angle OAB + \angle PAB = {90^ \circ }\]
Substitute the value of \[\angle PAB = {65^ \circ }\]
Therefore, \[
\angle OAB + {65^ \circ } = {90^ \circ } \\
\angle OAB = {90^ \circ } - {65^ \circ } = {25^ \circ } \\
\]
Thus, \[\angle OAB = {25^ \circ }\]
SO, option A is correct.
Note:Students can make mistakes while finding the angle in an isosceles triangle if they assume the wrong set of angles equal, always the angles opposite to equal sides are equal and the third angle is different. Students should always convert their answer from degree into radians if required using the formula \[1radian = {\left( {\dfrac{{180}}{\pi }} \right)^{^ \circ }}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE





