
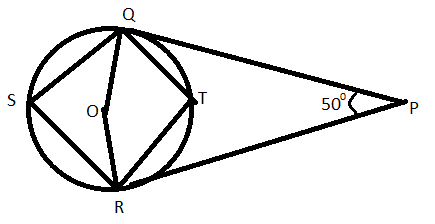
In figure find the value of \[\angle QSR\]

Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: Sum of all angles of a quadrilateral is equal to \[360^\circ \]. And we all know that the tangency point of the tangent of a circle is always perpendicular to the radius of the circle and by keeping this in mind we can easily solve this problem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we know that QO and OR are the radius of circle O.
So, we can say that the radius QO and OR is perpendicular to tangents QP and PR.
Now from the above we get that the \[\angle PQO = \angle PRO = 90^\circ \].
Sum of all angles of a quadrilateral is equal to \[360^\circ \]. So, we can say that the sum of all angles of a quadrilateral PQOR is \[360^\circ \].
It means that \[\angle PQO + \angle QOR + \angle ORP + \angle RPQ = 360^\circ \]
\[ \Rightarrow 90^\circ + \angle QOR + 90^\circ + 50^\circ = 360^\circ \]
\[ \Rightarrow \angle QOR = 360^\circ - (90^\circ + 90^\circ + 50^\circ )\]
\[ \Rightarrow \angle QOR = 360^\circ - 230^\circ = 130^\circ \]
And now in quadrilateral TQSR we know that \[\angle QSR = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \angle QOR\]
So, now \[\angle QSR = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 130^\circ = 65^\circ \]
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[\angle QSR = 65^\circ \]
Note : - whenever we come up with this type of problem then we must know all the properties and theorems of circle and quadrilateral only then we are able to apply the necessary theorem according to the question to get the answer. As such here we had applied the tangent – radius property of the circle to get the result.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we know that QO and OR are the radius of circle O.
So, we can say that the radius QO and OR is perpendicular to tangents QP and PR.
Now from the above we get that the \[\angle PQO = \angle PRO = 90^\circ \].
Sum of all angles of a quadrilateral is equal to \[360^\circ \]. So, we can say that the sum of all angles of a quadrilateral PQOR is \[360^\circ \].
It means that \[\angle PQO + \angle QOR + \angle ORP + \angle RPQ = 360^\circ \]
\[ \Rightarrow 90^\circ + \angle QOR + 90^\circ + 50^\circ = 360^\circ \]
\[ \Rightarrow \angle QOR = 360^\circ - (90^\circ + 90^\circ + 50^\circ )\]
\[ \Rightarrow \angle QOR = 360^\circ - 230^\circ = 130^\circ \]
And now in quadrilateral TQSR we know that \[\angle QSR = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \angle QOR\]
So, now \[\angle QSR = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 130^\circ = 65^\circ \]
\[ \Rightarrow \] \[\angle QSR = 65^\circ \]
Note : - whenever we come up with this type of problem then we must know all the properties and theorems of circle and quadrilateral only then we are able to apply the necessary theorem according to the question to get the answer. As such here we had applied the tangent – radius property of the circle to get the result.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




