
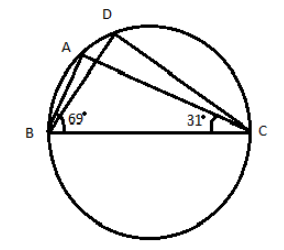
In figure, $\angle ABC = 69^\circ ,\,\angle ACB = 31^\circ ,\,$ find $\angle BDC$

Answer
597.9k+ views
Hint: In figure we can easily see a segment BADCB, $\angle BDC$ and $\angle BAC$ are angels in the same segment. So they must be equal. So to find $\angle BDC$ first we will find $\angle BAC$ and we can find $\angle BAC$ by applying the angle to some property of the triangle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given: $\angle ABC = 69^\circ $ is given and also $\angle ACB = 31^\circ $ is given also it is given in the figure that$\angle BDC$ are in the same segment.
As $\angle BDC$ and $\angle BAC$ are in the same segment BADCB therefore both the angles must be equal.
And by given angles we can easily find the $\angle BAC$ by applying the angle sum property of the triangle. Accordingly, the angle sum property of triangle sum of all the angles of the triangle is $180^\circ $ .
In triangle ABC we will apply the angle sum property of triangle $\angle ABC + \angle ACB + \angle BAC = 180^\circ $
$69^\circ + 31^\circ + \angle BAC = 180^\circ $
$\angle BAC = 80^\circ $
So we have found $\angle BAC$ and we have discussed earlier that $\angle BAC$ must be equal to $\angle BDC$ because of the same segment. So angle $\angle BDC$ will be $80^\circ $.
Note: Look at the figure and take a look at the segment BADCB. We can see that $\angle BAC$ and $\angle BDC$ are in the same segment and hence they must be equal. So we have found $\angle BAC$ here because we have given the value of two angles of the triangle ABC and it was easy for us to found the value of $\angle BAC$ by applying the angle sum property of triangle in the triangle ABC and then we equate the $\angle BAC$ to $\angle BDC$ and hence we have found the value of $\angle BDC$ is equal to $80^\circ $.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given: $\angle ABC = 69^\circ $ is given and also $\angle ACB = 31^\circ $ is given also it is given in the figure that$\angle BDC$ are in the same segment.
As $\angle BDC$ and $\angle BAC$ are in the same segment BADCB therefore both the angles must be equal.
And by given angles we can easily find the $\angle BAC$ by applying the angle sum property of the triangle. Accordingly, the angle sum property of triangle sum of all the angles of the triangle is $180^\circ $ .
In triangle ABC we will apply the angle sum property of triangle $\angle ABC + \angle ACB + \angle BAC = 180^\circ $
$69^\circ + 31^\circ + \angle BAC = 180^\circ $
$\angle BAC = 80^\circ $
So we have found $\angle BAC$ and we have discussed earlier that $\angle BAC$ must be equal to $\angle BDC$ because of the same segment. So angle $\angle BDC$ will be $80^\circ $.
Note: Look at the figure and take a look at the segment BADCB. We can see that $\angle BAC$ and $\angle BDC$ are in the same segment and hence they must be equal. So we have found $\angle BAC$ here because we have given the value of two angles of the triangle ABC and it was easy for us to found the value of $\angle BAC$ by applying the angle sum property of triangle in the triangle ABC and then we equate the $\angle BAC$ to $\angle BDC$ and hence we have found the value of $\angle BDC$ is equal to $80^\circ $.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




