
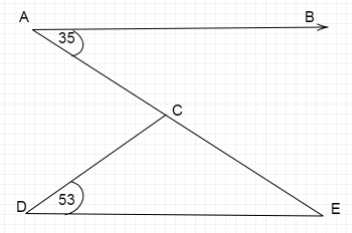
In figure, \[AB\parallel DE\] , \[\angle BAC = {35^ \circ },\angle CDE = {53^ \circ }\]. Find \[\angle DCE\]

Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint:Here we use the concept of two parallel lines being cut by a transversal makes equal alternate interior angles. So we find the third angle of the triangle and use the sum of angles of the triangle equal to \[{180^ \circ }\]and find \[\angle DCE\].
* Two lines are said to be parallel if they have the same distance between them at all points, also, the set of parallel lines never intersect. And a transversal is a line that cuts a set of any two lines be it a parallel set of lines or not.
* In a \[\vartriangle ABC\] , having three sides \[AB,BC,CA\], and angles \[\angle A,\angle B,\angle C\]
Then property of sum of triangles says \[\angle A + \angle B + \angle C = {180^ \circ }\]
* Alternate interior angles are the angles which are inside the two parallel lines but lie on the opposite side of the transversal.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the figure shown above, \[AB\parallel DE\], let us assume \[AE\] as a transversal that cuts both the lines at points \[A,E\].
Since we know the property when a transversal cuts parallel lines, then alternate interior angles are equal.
Here alternate interior angles are \[\angle BAE,\angle DEA\].
And we are given that \[\angle BAC = {35^ \circ }\]
Therefore, \[\angle BAE = \angle DEA = {35^ \circ }\]
Now we have values of two angles of a triangle \[\vartriangle CDE\]
Therefore using the property that sum of all three angles of a triangle is equal to \[{180^ \circ }\]
We can write
\[\angle CDE + \angle DEC + \angle DCE = {180^ \circ }\]
Substituting the values for \[\angle CDE = {53^ \circ },\angle DEC = {35^ \circ }\] ( since \[\angle DEC = \angle DEA\])
\[
{53^ \circ } + {35^ \circ } + \angle DCE = {180^ \circ } \\
{88^ \circ } + \angle DCE = {180^ \circ } \\
\]
Shifting the degree values to the right ride of the equation
\[\angle DCE = {(180 - 88)^ \circ } = {92^ \circ }\]
Therefore, value of \[\angle DCE = {92^ \circ }\]
Note:Students should always keep the angle measures in same unit throughout, if angles are given in radians convert it into degree using the formula \[1radian = {\left( {\dfrac{{180}}{\pi }} \right)^{^ \circ }}\]. Students should not be confused with alternate interior angles and corresponding angles as corresponding angles lie on the matching corner ( they are also equal when parallel lines are cut by transversal).
* Two lines are said to be parallel if they have the same distance between them at all points, also, the set of parallel lines never intersect. And a transversal is a line that cuts a set of any two lines be it a parallel set of lines or not.
* In a \[\vartriangle ABC\] , having three sides \[AB,BC,CA\], and angles \[\angle A,\angle B,\angle C\]
Then property of sum of triangles says \[\angle A + \angle B + \angle C = {180^ \circ }\]
* Alternate interior angles are the angles which are inside the two parallel lines but lie on the opposite side of the transversal.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the figure shown above, \[AB\parallel DE\], let us assume \[AE\] as a transversal that cuts both the lines at points \[A,E\].
Since we know the property when a transversal cuts parallel lines, then alternate interior angles are equal.
Here alternate interior angles are \[\angle BAE,\angle DEA\].
And we are given that \[\angle BAC = {35^ \circ }\]
Therefore, \[\angle BAE = \angle DEA = {35^ \circ }\]
Now we have values of two angles of a triangle \[\vartriangle CDE\]
Therefore using the property that sum of all three angles of a triangle is equal to \[{180^ \circ }\]
We can write
\[\angle CDE + \angle DEC + \angle DCE = {180^ \circ }\]
Substituting the values for \[\angle CDE = {53^ \circ },\angle DEC = {35^ \circ }\] ( since \[\angle DEC = \angle DEA\])
\[
{53^ \circ } + {35^ \circ } + \angle DCE = {180^ \circ } \\
{88^ \circ } + \angle DCE = {180^ \circ } \\
\]
Shifting the degree values to the right ride of the equation
\[\angle DCE = {(180 - 88)^ \circ } = {92^ \circ }\]
Therefore, value of \[\angle DCE = {92^ \circ }\]
Note:Students should always keep the angle measures in same unit throughout, if angles are given in radians convert it into degree using the formula \[1radian = {\left( {\dfrac{{180}}{\pi }} \right)^{^ \circ }}\]. Students should not be confused with alternate interior angles and corresponding angles as corresponding angles lie on the matching corner ( they are also equal when parallel lines are cut by transversal).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE





