
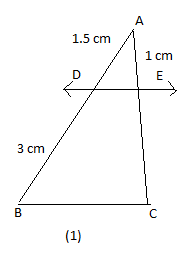
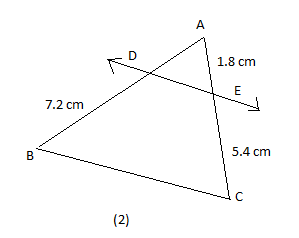
In figure (1) and (2), \[DE||BC\]. Find EC in (1) and AD in (2).


Answer
611.7k+ views
Hint: For the above question, we will use Thales theorem, which states that a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle, intersecting the other two sides in distinct parts, then the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been given the figure (1) as follows:
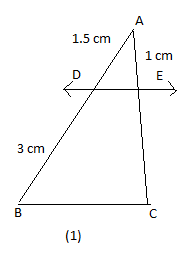
As we know that according to Thales theorem if a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle intersecting the other two sides at distinct points, then the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{AD}{BD}=\dfrac{AE}{EC} \\
& \dfrac{1.5}{3}=\dfrac{1}{EC} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, on cross multiplication, we will get the equation as follows:
\[\begin{align}
& 1.5(EC)=3 \\
& EC=2cm \\
\end{align}\]
We also have been given figure (2) as follows:
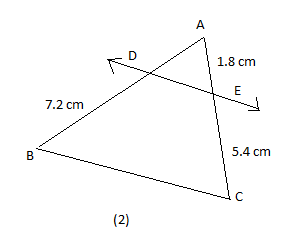
According to Thales theorem, we already know that,
\[\dfrac{AD}{BD}=\dfrac{AE}{EC}\]
Hence, on substituting the value of BD, AE and EC in the above expression, we will get the equation as follows:
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{AD}{7.2}=\dfrac{1.8}{5.4} \\
& \dfrac{AD}{7.2}=\dfrac{1}{3} \\
\end{align}\]
Then, on cross multiplication, we will get the equation as follows:
\[\begin{align}
& 3(AD)=7.2 \\
& AD=\dfrac{7.2}{3} \\
& AD=2.4cm \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the value of EC in figure (1) is equal to 2 cm and AD in figure (2) is equal to 2.4 cm.
Note: Thales theorem is also known as The Basic Proportionality Theorem. We have to be extremely careful while doing the cross multiplication of the terms in the above mentioned equations, as there is a slight chance that we might make a mistake here.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been given the figure (1) as follows:

As we know that according to Thales theorem if a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle intersecting the other two sides at distinct points, then the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{AD}{BD}=\dfrac{AE}{EC} \\
& \dfrac{1.5}{3}=\dfrac{1}{EC} \\
\end{align}\]
Hence, on cross multiplication, we will get the equation as follows:
\[\begin{align}
& 1.5(EC)=3 \\
& EC=2cm \\
\end{align}\]
We also have been given figure (2) as follows:

According to Thales theorem, we already know that,
\[\dfrac{AD}{BD}=\dfrac{AE}{EC}\]
Hence, on substituting the value of BD, AE and EC in the above expression, we will get the equation as follows:
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{AD}{7.2}=\dfrac{1.8}{5.4} \\
& \dfrac{AD}{7.2}=\dfrac{1}{3} \\
\end{align}\]
Then, on cross multiplication, we will get the equation as follows:
\[\begin{align}
& 3(AD)=7.2 \\
& AD=\dfrac{7.2}{3} \\
& AD=2.4cm \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the value of EC in figure (1) is equal to 2 cm and AD in figure (2) is equal to 2.4 cm.
Note: Thales theorem is also known as The Basic Proportionality Theorem. We have to be extremely careful while doing the cross multiplication of the terms in the above mentioned equations, as there is a slight chance that we might make a mistake here.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




