
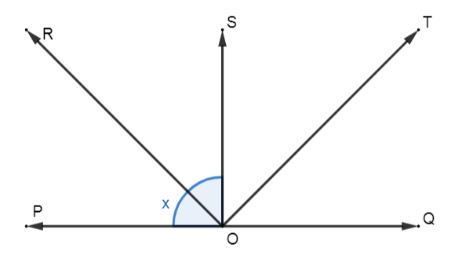
In fig., ray $OS$ stand on a line $POQ$. Ray $OR$ and ray $OT$ are angle bisectors of $\angle POS$ and $\angle SOQ$ respectively. If $\angle POS = x$, find $\angle ROT$.

Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: Use the given fact that ray $OR$ is the angle bisectors of $\angle POS$ to find the measure of the $\angle ROS$. It is given that $OQ$ stands on line $POQ$, therefore the measure of the $\angle POQ$ must be $180^\circ $, use it to find the measure of the angle $\angle SOQ$. After that use the given fact that, ray $OT$ is the angle bisector of $\angle SOQ$ to find the measure of the angle $\angle SOT$. Use these angles to get the desired result.
Complete answer:
We have given that:
$\angle POS = x$ and, ray $OR$ and ray $OT$ are angle bisectors of $\angle POS$ and $\angle SOQ$ respectively.
The goal of the problem is to find the measurement of the $\angle ROT$.
As OR is the angle bisector of $\angle POS$, then it gives that:
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle POR = \angle ROS = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {\angle POS} \right)$
Substitute the value $\angle POS = x$:
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle POR = \angle ROS = \dfrac{x}{2}$
From the above analysis, we have the conclusion that:
$ \Rightarrow $ $\angle ROS = \dfrac{x}{2}$
It is given that $POQ$ straight line, it means that $\angle POQ$ is a straight angle, and then the measure of the angle $\angle POQ$ is $180^\circ $.
The angle $\angle POQ$ can also be break in two angles as:
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle POQ = \angle POS + \angle SOQ$
Substitute the value of angle $\angle POQ$ as $180^\circ $, so the above equation is given as:
$ \Rightarrow $ $180^\circ = \angle POS + \angle SOQ$
The measure of the angle is given in the problem as $x$, so
$ \Rightarrow $ $180^\circ = x + \angle SOQ$
Solve the above equation and find the value of the angle $\angle SOQ$.
$ \Rightarrow $ $\angle SOQ = 180^\circ - x$
Now, it is given that $OT$ are angle bisectors of $\angle SOQ$, then it gives that:
$ \Rightarrow $ $\angle SOT = \angle TOQ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {\angle SOQ} \right)$
Substitute the value $\angle SOQ = 180^\circ - x$:
$ \Rightarrow $ $\angle SOT = \angle TOQ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {180^\circ - x} \right)$
From the above analysis, we have the conclusion that:
$ \Rightarrow $ $\angle SOT = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {180^\circ - x} \right)$
We have to find the measure of the angle $\angle ROT$ so first, we break this angle as:
$ \Rightarrow $ $\angle ROT = \angle ROS + \angle SOT$
Now, substitute the values $\angle ROS = \dfrac{x}{2}$and$\angle SOT = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {180^\circ - x} \right)$, then the above equation is given as:
$ \Rightarrow $ $\angle ROT = \dfrac{x}{2} + \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {180^\circ - x} \right)$
Simplify the above equation:
$ \Rightarrow $ \[\angle ROT = \frac{x}{2} + \frac{1}{2}\left( {180^\circ } \right) - \frac{x}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \angle ROT = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {180^\circ } \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \angle ROT = 90^\circ \]
Therefore, the measurement of the angle \[\angle ROT\] is $90^\circ $.
Note: It is given in the problem that Ray $OR$ and ray $OT$ are angle bisectors of $\angle POS$ and $\angle SOQ$ respectively. It means that the ray $OR$ bisects the angle $\angle POS$ into two equal angles. If the measure of the angle $\angle POS = x$, then its angle bisectors are:
$\angle POR = \angle ROS = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( x \right)$.
Complete answer:
We have given that:
$\angle POS = x$ and, ray $OR$ and ray $OT$ are angle bisectors of $\angle POS$ and $\angle SOQ$ respectively.
The goal of the problem is to find the measurement of the $\angle ROT$.
As OR is the angle bisector of $\angle POS$, then it gives that:
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle POR = \angle ROS = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {\angle POS} \right)$
Substitute the value $\angle POS = x$:
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle POR = \angle ROS = \dfrac{x}{2}$
From the above analysis, we have the conclusion that:
$ \Rightarrow $ $\angle ROS = \dfrac{x}{2}$
It is given that $POQ$ straight line, it means that $\angle POQ$ is a straight angle, and then the measure of the angle $\angle POQ$ is $180^\circ $.
The angle $\angle POQ$ can also be break in two angles as:
$ \Rightarrow $$\angle POQ = \angle POS + \angle SOQ$
Substitute the value of angle $\angle POQ$ as $180^\circ $, so the above equation is given as:
$ \Rightarrow $ $180^\circ = \angle POS + \angle SOQ$
The measure of the angle is given in the problem as $x$, so
$ \Rightarrow $ $180^\circ = x + \angle SOQ$
Solve the above equation and find the value of the angle $\angle SOQ$.
$ \Rightarrow $ $\angle SOQ = 180^\circ - x$
Now, it is given that $OT$ are angle bisectors of $\angle SOQ$, then it gives that:
$ \Rightarrow $ $\angle SOT = \angle TOQ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {\angle SOQ} \right)$
Substitute the value $\angle SOQ = 180^\circ - x$:
$ \Rightarrow $ $\angle SOT = \angle TOQ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {180^\circ - x} \right)$
From the above analysis, we have the conclusion that:
$ \Rightarrow $ $\angle SOT = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {180^\circ - x} \right)$
We have to find the measure of the angle $\angle ROT$ so first, we break this angle as:
$ \Rightarrow $ $\angle ROT = \angle ROS + \angle SOT$
Now, substitute the values $\angle ROS = \dfrac{x}{2}$and$\angle SOT = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {180^\circ - x} \right)$, then the above equation is given as:
$ \Rightarrow $ $\angle ROT = \dfrac{x}{2} + \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {180^\circ - x} \right)$
Simplify the above equation:
$ \Rightarrow $ \[\angle ROT = \frac{x}{2} + \frac{1}{2}\left( {180^\circ } \right) - \frac{x}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \angle ROT = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {180^\circ } \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \angle ROT = 90^\circ \]
Therefore, the measurement of the angle \[\angle ROT\] is $90^\circ $.
Note: It is given in the problem that Ray $OR$ and ray $OT$ are angle bisectors of $\angle POS$ and $\angle SOQ$ respectively. It means that the ray $OR$ bisects the angle $\angle POS$ into two equal angles. If the measure of the angle $\angle POS = x$, then its angle bisectors are:
$\angle POR = \angle ROS = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( x \right)$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




