
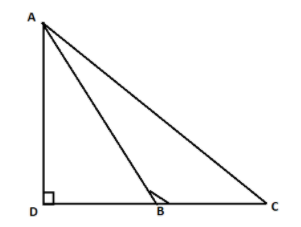
In fig. ABC is a triangle in which $\angle ABC > {90^\circ}$and $AD \bot CB$ are produced. Prove that $A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2} + 2BC.BD$

Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: According to given in the question we have to prove that $A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2} + 2BC.BD$ when ABC is a triangle in which $\angle ABC > {90^\circ}$ and $AD \bot CB$. So, first of all we have to use Pythagoras theorem for the right angled triangle ADB and for the right angled triangle ADC, then we compare both equations obtained from Pythagoras theorem to obtain the desired answer. So, now we have to know about the Pythagoras theorem that is mentioned below.
Pythagoras theorem: It states that in a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse sider is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides.
So, now we have to use the Pythagoras theorem in the triangle ADE which is right angled at D means $\angle D = {90^\circ}$.
Now, we have to apply the Pythagoras theorem for the right angled triangle ADC in which it is right angled at D.
Formula used: $ \Rightarrow {(a + b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab...................(A)$
Now, we have to substitute the expression obtained in another expression to obtain the required expression which we have to prove.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Step 1: First of all we have to use the Pythagoras theorem which is as explained in the solution hint in the triangle ADB in which AB is the hypotenuse and right angled at D. Hence,
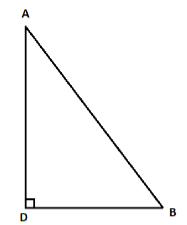
$ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = A{D^2} + B{D^2}................(1)$
Step 2: Now, same as the solution step 1 we have to apply Pythagoras theorem in the triangle ADC which is right angled at D and AC is the hypotenuse. Hence,
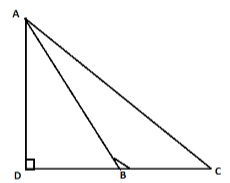
$ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = A{D^2} + C{D^2}................(2)$
Step 3: Now, in the triangle ADC as we know that:
$ \Rightarrow CD = BD + BC$
Hence, substituting this in the expression (2) as obtained in the solution step 2.
$ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = A{D^2} + {(BD + BC)^2}................(3)$
Step 4: Now, to solve the expression (3) as obtained in the solution step 3 we have to use the formula (A) as mentioned in the solution hint. Hence,
$ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = A{D^2} + B{D^2} + B{C^2} + 2BD.BC..................(4)$
Step 5: Now, to obtain the required expression we have to use the expression (1) which is as obtained in the solution step 1. Hence,
$ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2} + 2BD.BC$
Hence, with the help of the formula (A) for the given triangle ADC we have proved that $A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2} + 2BD.BC$.
Note: If the given triangle is a right angle triangle then we can apply the Pythagoras theorem for the given right angled triangle according to which sum of the square of its two sides is always equal to the square of hypotenuse of the triangle.
Pythagoras theorem: It states that in a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse sider is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides.
So, now we have to use the Pythagoras theorem in the triangle ADE which is right angled at D means $\angle D = {90^\circ}$.
Now, we have to apply the Pythagoras theorem for the right angled triangle ADC in which it is right angled at D.
Formula used: $ \Rightarrow {(a + b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab...................(A)$
Now, we have to substitute the expression obtained in another expression to obtain the required expression which we have to prove.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Step 1: First of all we have to use the Pythagoras theorem which is as explained in the solution hint in the triangle ADB in which AB is the hypotenuse and right angled at D. Hence,

$ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = A{D^2} + B{D^2}................(1)$
Step 2: Now, same as the solution step 1 we have to apply Pythagoras theorem in the triangle ADC which is right angled at D and AC is the hypotenuse. Hence,

$ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = A{D^2} + C{D^2}................(2)$
Step 3: Now, in the triangle ADC as we know that:
$ \Rightarrow CD = BD + BC$
Hence, substituting this in the expression (2) as obtained in the solution step 2.
$ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = A{D^2} + {(BD + BC)^2}................(3)$
Step 4: Now, to solve the expression (3) as obtained in the solution step 3 we have to use the formula (A) as mentioned in the solution hint. Hence,
$ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = A{D^2} + B{D^2} + B{C^2} + 2BD.BC..................(4)$
Step 5: Now, to obtain the required expression we have to use the expression (1) which is as obtained in the solution step 1. Hence,
$ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2} + 2BD.BC$
Hence, with the help of the formula (A) for the given triangle ADC we have proved that $A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2} + 2BD.BC$.
Note: If the given triangle is a right angle triangle then we can apply the Pythagoras theorem for the given right angled triangle according to which sum of the square of its two sides is always equal to the square of hypotenuse of the triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




