
In ECG, P-wave represents
A) Ventricular repolarization
B) Ventricular depolarization
C) Atrial depolarization
D) Atrial repolarization
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint:ECG stands for Electrocardiogram, which records the heart signals with the help of electrodes placed on the body of a patient.
Complete answer:
ECG:-
>It records the electrical signal from the heart in order to check heart condition.
>It is a painless test.
>It is a graphical representation showing waves
>Electrodes are placed on the chest of the patient to record his/her heart condition.
>The signals are shown in a monitor or computer attached with the ECG machine.
Waves of ECG:-
The ECG include:
1) P Wave
2) Q Wave
3) S Wave
4) R Wave
5) U Wave
6) T Wave
P- Wave:-
In ECG, the P-Wave represents Atrial depolarization. This Atrial depolarization results in atrial contraction or atrial systole.
Q- Wave:-
In ECG, the Q- Wave represents Ventricular depolarization. The Q Wave is an initially negative deflection of the QRS complex.
S- Wave:-
In ECG, the S-Wave signifies the Ventricular depolarization. The S wave is the first downward deflection of QRS complex occurs after the R wave.
R- Wave:-
In ECG, the R-Wave represents the Ventricular depolarization. It is the first positive wave of the QRS complex.
U- Wave:-
U wave represents the ventricular repolarization. This wave comes after the T wave.
T- Wave:-
T waves represent the ventricular repolarization. The T wave comes after the QRS complex.
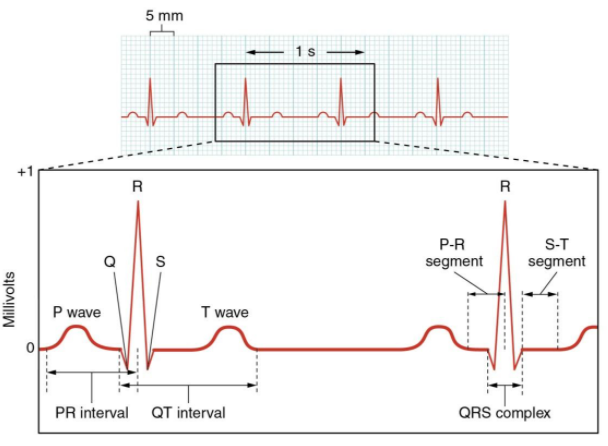
Therefore, from the above discussion it is clear that in ECG, the P- wave represents Atrial depolarization.
Hence option “C” is the correct answer.
Note:Remember to keep in mind that there is no distinct wave for atrial repolarization so don’t get confused with it. All the waves in the QRS complex show ventricular depolarization.
Complete answer:
ECG:-
>It records the electrical signal from the heart in order to check heart condition.
>It is a painless test.
>It is a graphical representation showing waves
>Electrodes are placed on the chest of the patient to record his/her heart condition.
>The signals are shown in a monitor or computer attached with the ECG machine.
Waves of ECG:-
The ECG include:
1) P Wave
2) Q Wave
3) S Wave
4) R Wave
5) U Wave
6) T Wave
P- Wave:-
In ECG, the P-Wave represents Atrial depolarization. This Atrial depolarization results in atrial contraction or atrial systole.
Q- Wave:-
In ECG, the Q- Wave represents Ventricular depolarization. The Q Wave is an initially negative deflection of the QRS complex.
S- Wave:-
In ECG, the S-Wave signifies the Ventricular depolarization. The S wave is the first downward deflection of QRS complex occurs after the R wave.
R- Wave:-
In ECG, the R-Wave represents the Ventricular depolarization. It is the first positive wave of the QRS complex.
U- Wave:-
U wave represents the ventricular repolarization. This wave comes after the T wave.
T- Wave:-
T waves represent the ventricular repolarization. The T wave comes after the QRS complex.

Therefore, from the above discussion it is clear that in ECG, the P- wave represents Atrial depolarization.
Hence option “C” is the correct answer.
Note:Remember to keep in mind that there is no distinct wave for atrial repolarization so don’t get confused with it. All the waves in the QRS complex show ventricular depolarization.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




