
In each of the following, the carbonyl group is present except in:
A.$HCHO$
B.$C{H_3}COC{H_3}$
C.$HC{H_2}OH$
D.$C{H_3} - C = O - H$
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Carbonyl group is the functional group in which the carbon atom is bond to the oxygen atom by a double bond and is represented as $C=O$ and it is the part of many larger functional groups the organic reactions occur around this bond.
Complete answer:
The structure of the carbonyl group is shown below:
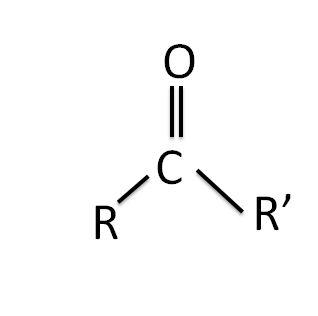
Where R is the alkyl group and R’ is another alkyl group, both R and R’ can be similar as well as different in nature.
Aldehydes are the group of compounds having the general formula of RCHO where R is the alkyl group and in CHO there is C=O thus it has the carbonyl group in it. Thus $$HCHO$$has the carbonyl group since it is an aldehyde molecule.
Similarly Ketones are the group of organic compounds having the general formula RC=O again the carbonyl group is present in the ketones as well and R is the alkyl group. Thus $C{H_3}COC{H_3}$has the carbonyl group in it as it is ether.
The compound $HCH_2OH$ is an alcohol where there is no double bond between the C
and the O atom in the molecule; the general formula of alcohols is R-OH. Thus $HC{H_2}OH$ has no carbonyl carbon atom in it.
As is evident from the structure there is a C=O in the structure of the molecule $C{H_3} - C = O - H$ and it contains the carbonyl group as well.
The reactivity of the carbonyl group is affected by the nature of the alkyl group attached with the molecule where oxygen is more electronegative than carbon atom. The bonds polarity is increased due to the electronegativity of the oxygen atom as compared to the carbon atom.
Thus option C is the correct answer.
Note:
This property of the C=O is utilised in the infrared spectroscopy where the unknown molecule is detected in a sample using the properties of C=O since it undergoes oxidation as well as reduction reactions which are very specific in nature.
Complete answer:
The structure of the carbonyl group is shown below:

Where R is the alkyl group and R’ is another alkyl group, both R and R’ can be similar as well as different in nature.
Aldehydes are the group of compounds having the general formula of RCHO where R is the alkyl group and in CHO there is C=O thus it has the carbonyl group in it. Thus $$HCHO$$has the carbonyl group since it is an aldehyde molecule.
Similarly Ketones are the group of organic compounds having the general formula RC=O again the carbonyl group is present in the ketones as well and R is the alkyl group. Thus $C{H_3}COC{H_3}$has the carbonyl group in it as it is ether.
The compound $HCH_2OH$ is an alcohol where there is no double bond between the C
and the O atom in the molecule; the general formula of alcohols is R-OH. Thus $HC{H_2}OH$ has no carbonyl carbon atom in it.
As is evident from the structure there is a C=O in the structure of the molecule $C{H_3} - C = O - H$ and it contains the carbonyl group as well.
The reactivity of the carbonyl group is affected by the nature of the alkyl group attached with the molecule where oxygen is more electronegative than carbon atom. The bonds polarity is increased due to the electronegativity of the oxygen atom as compared to the carbon atom.
Thus option C is the correct answer.
Note:
This property of the C=O is utilised in the infrared spectroscopy where the unknown molecule is detected in a sample using the properties of C=O since it undergoes oxidation as well as reduction reactions which are very specific in nature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




