
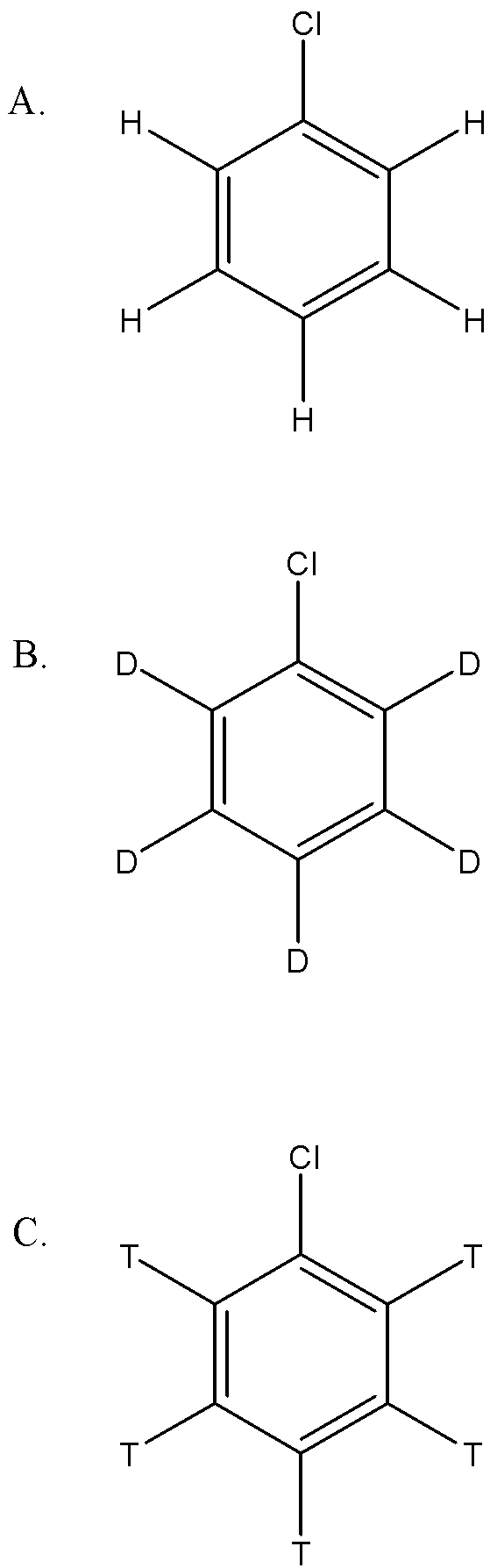
In Dow’s process haloarene is converted to phenol with fused ${NaOH}$ .The most reactive compound towards the reaction is:

Answer
609.3k+ views
Hint: Dow’s process is a method by which phenol is prepared by reacting it with molten sodium hydroxide at extreme temperature conditions. The mechanism involved is called Benzyne mechanism since it involves the formation of the reactive intermediate Benzyne.
Complete step by step answer:
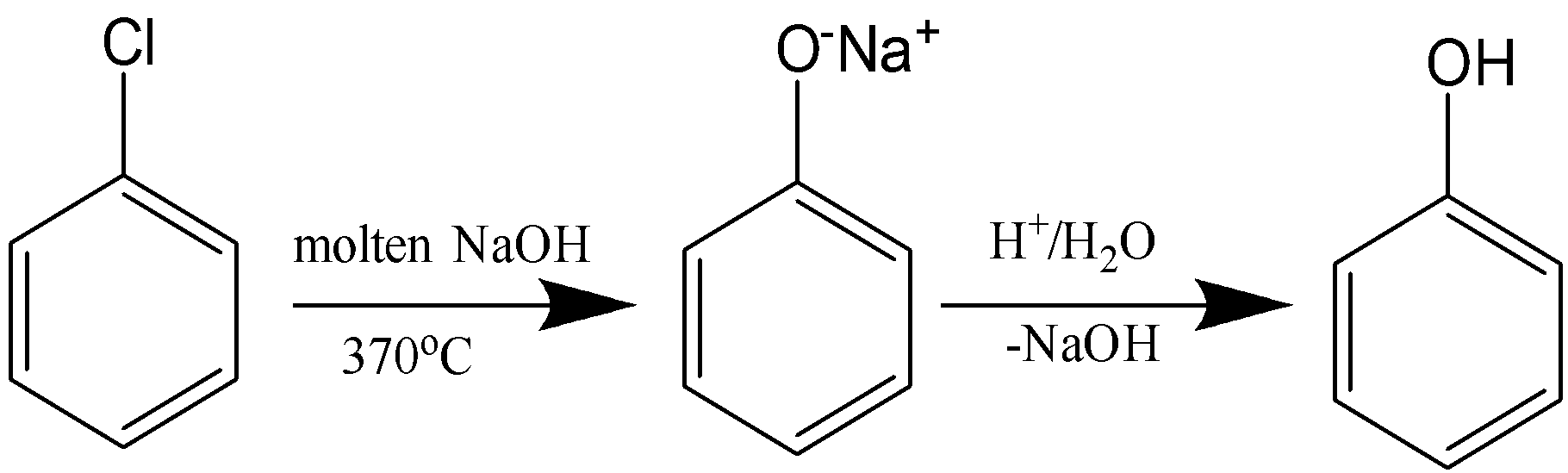
In Dow’s process, Phenol is produced from chlorobenzene by fusing it with molten sodium hydroxide at 350oC to convert it to sodium phenoxide which upon acidification gives phenol. The reaction occurs via elimination-addition mechanism that involves a benzyne intermediate.
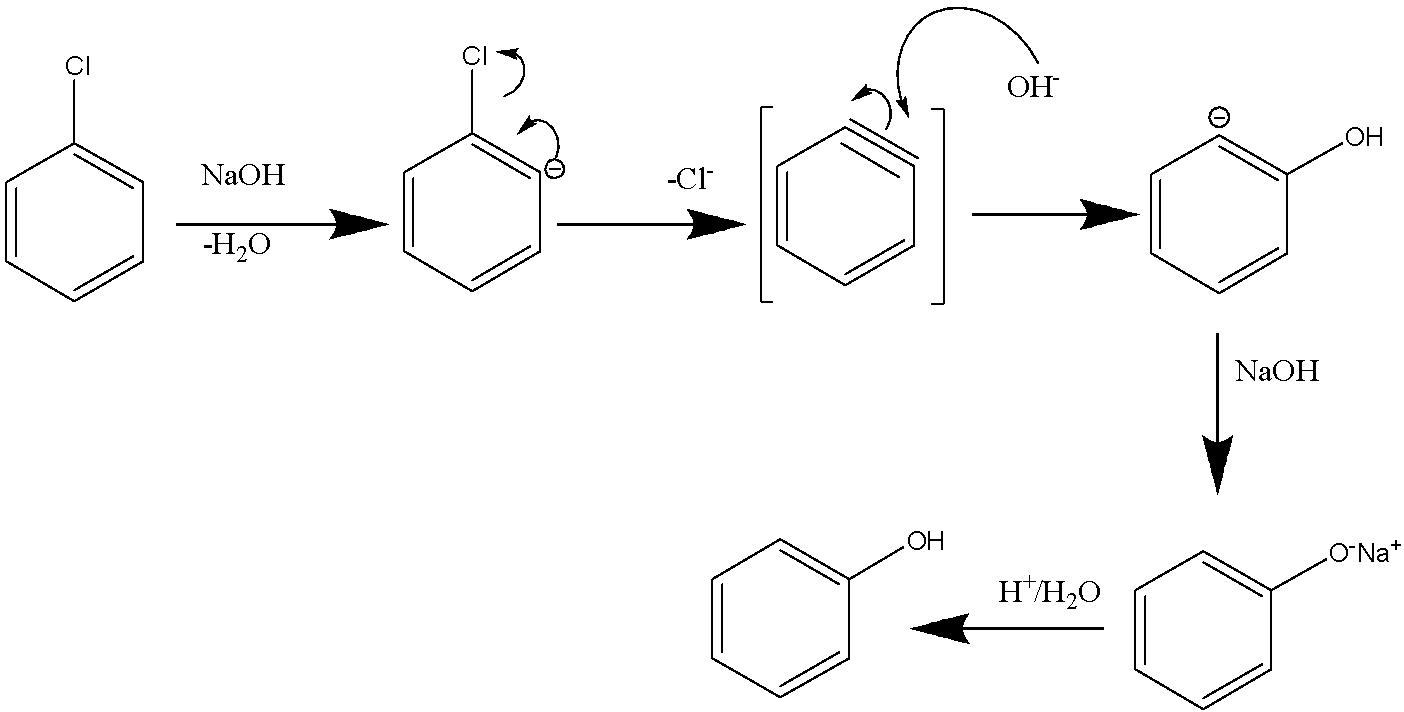
Mechanism:
The first step hydroxide ion removes the proton from carbon adjacent to the carbon bonded to chlorine. This leads to the elimination of a water molecule followed by the formation of the short lived benzyne intermediate. In the second step, the hydroxide ion attacks the benzyne intermediate to give the sodium phenoxide which on acidification gives phenol.
Since the first step involves the abstraction proton, this suggests that if the bond can be easily broken, that reactant will be more reactive. Since the order of bond strength is: ${C-T}$>${C-D}$>${C-H}$
therefore A. will be more reactive.
Hence answer A. correct.
Note: In the Benzyne mechanism the regioselectivity is important. If the haloarene is substituted, then special care must be taken while predicting the product. The mesomeric effect of the said substituents will not matter since in the Benzyne intermediate the triple bond is perpendicular to the benzene ring’s pi electrons. But, the inductive effect will matter and will determine the regioselectivity in the product. “When an electron withdrawing group is present, the intermediate where the negative charge is the closest to the electron withdrawing group will be favoured”.
Complete step by step answer:
In Dow’s process, Phenol is produced from chlorobenzene by fusing it with molten sodium hydroxide at 350oC to convert it to sodium phenoxide which upon acidification gives phenol. The reaction occurs via elimination-addition mechanism that involves a benzyne intermediate.

Mechanism:
The first step hydroxide ion removes the proton from carbon adjacent to the carbon bonded to chlorine. This leads to the elimination of a water molecule followed by the formation of the short lived benzyne intermediate. In the second step, the hydroxide ion attacks the benzyne intermediate to give the sodium phenoxide which on acidification gives phenol.

Since the first step involves the abstraction proton, this suggests that if the bond can be easily broken, that reactant will be more reactive. Since the order of bond strength is: ${C-T}$>${C-D}$>${C-H}$
therefore A. will be more reactive.

Hence answer A. correct.
Note: In the Benzyne mechanism the regioselectivity is important. If the haloarene is substituted, then special care must be taken while predicting the product. The mesomeric effect of the said substituents will not matter since in the Benzyne intermediate the triple bond is perpendicular to the benzene ring’s pi electrons. But, the inductive effect will matter and will determine the regioselectivity in the product. “When an electron withdrawing group is present, the intermediate where the negative charge is the closest to the electron withdrawing group will be favoured”.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




