
In $\Delta PQR$, right-angled at Q, PR+QR = 25 cm and PQ = 5 cm. Determine the values of $\sin P,\cos P$ and $\tan P.$
Answer
597.9k+ views
Hint: In this question, the given triangle is a right –angled triangle, so first work out on the length of the unknown side of the triangle by using the Pythagoras theorem. Second work out on the values of $\sin P, \cos P$ and $\tan P$ using basic definition of sine, cosine and tangent functions respectively.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given that
$PR+QR=25$ cm and $PQ=5$ cm
Let us assume that $QR=x$
$\begin{align}
& PR+QR=25 \\
& PR=25-QR \\
& PR=25-x \\
\end{align}$
In right triangle POR, using Pythagoras theorem
\[{{\left( \text{Hypotenuse} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \text{Height} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \text{Base} \right)}^{2}}\]
${{\left( PR \right)}^{2}}={{\left( PQ \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( QR \right)}^{2}}$
Now put all the values in the above equation, we get
${{\left( 25-x \right)}^{2}}={{5}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}$
Expanding the term on the left side by using ${{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-2ab+{{b}^{2}}$ , we get
${{25}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}-2\times 25\times x=25+{{x}^{2}}$
Rearranging the terms, we get
$625+{{x}^{2}}-50x=25+{{x}^{2}}$
$625+{{x}^{2}}-50x-25-{{x}^{2}}=0$
Cancelling the term ${{x}^{2}}$ on the left side, we get
$-50x+600=0$
$-50x=-600$
Dividing both sides by -50, we get
$x=\dfrac{600}{50}=12$
Hence the required length of side QR $=x=12$cm
Therefore the length of side PR $=25-x=25-12=13$cm
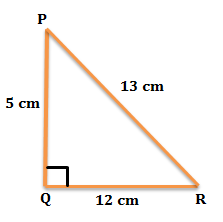
The basic definitions of the trigonometric functions are
The sine function of an angle is the ratio between the opposite side length to that of the hypotenuse.
$\sin P=\dfrac{\text{side opposite to angle P}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}=\dfrac{QR}{PR}=\dfrac{12}{13}$
The cosine function of an angle is the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse.
$\cos P=\dfrac{\text{side adjacent to angle P}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}=\dfrac{PQ}{PR}=\dfrac{5}{13}$
The tangent function is the ratio of the length of the opposite side to that of the adjacent side.
$\tan P=\dfrac{\text{side opposite to angle P}}{\text{side adjacent to angle P}}=\dfrac{QR}{PQ}=\dfrac{12}{5}$
Note: It should be noted that the tan can also be represented in terms of sine and cosine as their ratio. Hence $\tan P=\dfrac{\sin P}{\cos P}=\dfrac{\left( \dfrac{12}{13} \right)}{\left( \dfrac{5}{13} \right)}=\dfrac{12}{5}$ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given that
$PR+QR=25$ cm and $PQ=5$ cm
Let us assume that $QR=x$
$\begin{align}
& PR+QR=25 \\
& PR=25-QR \\
& PR=25-x \\
\end{align}$
In right triangle POR, using Pythagoras theorem
\[{{\left( \text{Hypotenuse} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \text{Height} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \text{Base} \right)}^{2}}\]
${{\left( PR \right)}^{2}}={{\left( PQ \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( QR \right)}^{2}}$
Now put all the values in the above equation, we get
${{\left( 25-x \right)}^{2}}={{5}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}$
Expanding the term on the left side by using ${{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-2ab+{{b}^{2}}$ , we get
${{25}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}-2\times 25\times x=25+{{x}^{2}}$
Rearranging the terms, we get
$625+{{x}^{2}}-50x=25+{{x}^{2}}$
$625+{{x}^{2}}-50x-25-{{x}^{2}}=0$
Cancelling the term ${{x}^{2}}$ on the left side, we get
$-50x+600=0$
$-50x=-600$
Dividing both sides by -50, we get
$x=\dfrac{600}{50}=12$
Hence the required length of side QR $=x=12$cm
Therefore the length of side PR $=25-x=25-12=13$cm

The basic definitions of the trigonometric functions are
The sine function of an angle is the ratio between the opposite side length to that of the hypotenuse.
$\sin P=\dfrac{\text{side opposite to angle P}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}=\dfrac{QR}{PR}=\dfrac{12}{13}$
The cosine function of an angle is the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse.
$\cos P=\dfrac{\text{side adjacent to angle P}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}=\dfrac{PQ}{PR}=\dfrac{5}{13}$
The tangent function is the ratio of the length of the opposite side to that of the adjacent side.
$\tan P=\dfrac{\text{side opposite to angle P}}{\text{side adjacent to angle P}}=\dfrac{QR}{PQ}=\dfrac{12}{5}$
Note: It should be noted that the tan can also be represented in terms of sine and cosine as their ratio. Hence $\tan P=\dfrac{\sin P}{\cos P}=\dfrac{\left( \dfrac{12}{13} \right)}{\left( \dfrac{5}{13} \right)}=\dfrac{12}{5}$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




