
In $\Delta PQR$ , right angled at Q, $PR+QR=25cm$ and $PQ=5cm$ . Determine the value of$\sin P,\cos P,\tan P$.
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: First of all find all the sides of the triangle. As PQ is given, PR + QR are also given so using Pythagoras theorem we can find the values of PR and QR. Now, using trigonometric ratios we can find $\sin P,\cos P,\tan P$ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
The below figure describes a$\Delta PQR$right angled at Q having 3 sides with $PQ=5cm$ .
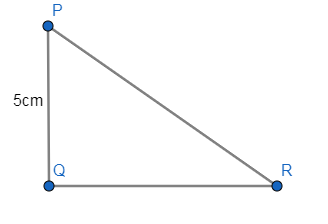
In the question, it is given that:
$PQ=5cm$
$PR+QR=25cm$ ………Eq. (2)
As PQR is a right triangle, so we can use Pythagoras theorem which states that:
$P{{R}^{2}}=P{{Q}^{2}}+Q{{R}^{2}}$ PR2 = PQ2 + QR2
From eq. (2) we can write $PR=25-QR$ and then substituting in the above equation will give: $\begin{align}
& {{\left( 25-QR \right)}^{2}}=P{{Q}^{2}}+Q{{R}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 625+Q{{R}^{2}}-50QR={{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}}+Q{{R}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 625-50QR=25 \\
& \Rightarrow 600=50QR \\
& \Rightarrow QR=12 \\
\end{align}$
From the above calculation we have got $QR=12cm$ .
Now, substituting this value of QR in eq. (1) we get,
$\begin{align}
& PR+QR=25cm \\
& PR=25-12 \\
& PR=13 \\
\end{align}$
From the above calculation we have got $PR=13cm$ .
Now, we know all the sides of the triangle.
PQ = 5cm, PR = 13cm and QR = 12cm
We are going to find the values of $\sin P,\cos P,\tan P$ .
We know that $\sin P=\dfrac{P}{H}$ where “P” stands for the perpendicular of the triangle with respect to angle P and “H” stands for the hypotenuse of the triangle with respect to angle P.
So, in the given triangle for $\sin P$ the perpendicular is QR and the hypotenuse is PR.
$\begin{align}
& \sin P=\dfrac{QR}{PR} \\
& \Rightarrow \sin P=\dfrac{12}{13} \\
\end{align}$
We know that $\cos P=\dfrac{B}{H}$ where “B” stands for the base of the triangle with respect to angle P and “H” stands for the hypotenuse of the triangle with respect to angle P.
So, in the given triangle for $\cos P$ the base (B) is QR and the hypotenuse (H) is PR.
$\begin{align}
& \cos P=\dfrac{PQ}{PR} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos P=\dfrac{5}{13} \\
\end{align}$
We know that $\tan P=\dfrac{P}{B}$ where “B” stands for the base of the triangle with respect to angle P and “P” stands for the perpendicular of the triangle with respect to angle P
So, in the given triangle for $\tan P$ the base (B) is QR and the perpendicular (P) is QR.
$\begin{align}
& \tan P=\dfrac{QR}{PQ} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan P=\dfrac{12}{5} \\
\end{align}$
From the above calculations, the values of $\sin P,\cos P,\tan P$ are as follows:
$\sin P=\dfrac{12}{13},\cos P=\dfrac{5}{13}\And \tan P=\dfrac{12}{5}$
Note: You can verify that the values of $\sin P,\cos P,\tan P$ are correct or not.
The values of $\sin P\text{ and }\cos P$ is:
$\sin P=\dfrac{12}{13}\And \cos P=\dfrac{5}{13}$
As you can see both the cosine and sine of P are less than 1 and we already know that the value of sine and cosine cannot exceed 1 so the answer that we are getting is correct.
The value of $\tan P$ is:
$\tan P=\dfrac{12}{5}$
The value of tan P from the above equation is greater than 1 and we know that tan of an angle can take any values from -∞ to ∞ so the answer that we are getting is correct.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The below figure describes a$\Delta PQR$right angled at Q having 3 sides with $PQ=5cm$ .

In the question, it is given that:
$PQ=5cm$
$PR+QR=25cm$ ………Eq. (2)
As PQR is a right triangle, so we can use Pythagoras theorem which states that:
$P{{R}^{2}}=P{{Q}^{2}}+Q{{R}^{2}}$ PR2 = PQ2 + QR2
From eq. (2) we can write $PR=25-QR$ and then substituting in the above equation will give: $\begin{align}
& {{\left( 25-QR \right)}^{2}}=P{{Q}^{2}}+Q{{R}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 625+Q{{R}^{2}}-50QR={{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}}+Q{{R}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 625-50QR=25 \\
& \Rightarrow 600=50QR \\
& \Rightarrow QR=12 \\
\end{align}$
From the above calculation we have got $QR=12cm$ .
Now, substituting this value of QR in eq. (1) we get,
$\begin{align}
& PR+QR=25cm \\
& PR=25-12 \\
& PR=13 \\
\end{align}$
From the above calculation we have got $PR=13cm$ .
Now, we know all the sides of the triangle.
PQ = 5cm, PR = 13cm and QR = 12cm
We are going to find the values of $\sin P,\cos P,\tan P$ .
We know that $\sin P=\dfrac{P}{H}$ where “P” stands for the perpendicular of the triangle with respect to angle P and “H” stands for the hypotenuse of the triangle with respect to angle P.
So, in the given triangle for $\sin P$ the perpendicular is QR and the hypotenuse is PR.
$\begin{align}
& \sin P=\dfrac{QR}{PR} \\
& \Rightarrow \sin P=\dfrac{12}{13} \\
\end{align}$
We know that $\cos P=\dfrac{B}{H}$ where “B” stands for the base of the triangle with respect to angle P and “H” stands for the hypotenuse of the triangle with respect to angle P.
So, in the given triangle for $\cos P$ the base (B) is QR and the hypotenuse (H) is PR.
$\begin{align}
& \cos P=\dfrac{PQ}{PR} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos P=\dfrac{5}{13} \\
\end{align}$
We know that $\tan P=\dfrac{P}{B}$ where “B” stands for the base of the triangle with respect to angle P and “P” stands for the perpendicular of the triangle with respect to angle P
So, in the given triangle for $\tan P$ the base (B) is QR and the perpendicular (P) is QR.
$\begin{align}
& \tan P=\dfrac{QR}{PQ} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan P=\dfrac{12}{5} \\
\end{align}$
From the above calculations, the values of $\sin P,\cos P,\tan P$ are as follows:
$\sin P=\dfrac{12}{13},\cos P=\dfrac{5}{13}\And \tan P=\dfrac{12}{5}$
Note: You can verify that the values of $\sin P,\cos P,\tan P$ are correct or not.
The values of $\sin P\text{ and }\cos P$ is:
$\sin P=\dfrac{12}{13}\And \cos P=\dfrac{5}{13}$
As you can see both the cosine and sine of P are less than 1 and we already know that the value of sine and cosine cannot exceed 1 so the answer that we are getting is correct.
The value of $\tan P$ is:
$\tan P=\dfrac{12}{5}$
The value of tan P from the above equation is greater than 1 and we know that tan of an angle can take any values from -∞ to ∞ so the answer that we are getting is correct.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




