
In $\Delta PQR$, right angled at Q, PQ = 3cm and PR = 6cm. Determine $\angle QPR \And \angle PRQ$.
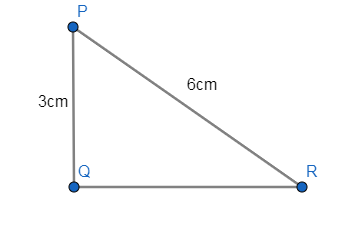

Answer
609k+ views
Hint: The given question contains a right angled $\Delta PQR$; two sides PQ and PR so from trigonometric ratios we can find the values of $\angle QPR\And \angle PRQ$. Let us assume $\angle PRQ=\theta $ and $\angle QPR=\alpha $ so $\sin \theta =\dfrac{PQ}{PR}$and from this ratio we can find $\angle PRQ$. We know that $\cos \alpha =\dfrac{PQ}{PR}$ so from this ratio we can find $\angle QPR$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The below figure shows a $\Delta PQR$ right angled at Q with two sides PQ and PR are given as 3cm and 6cm respectively.
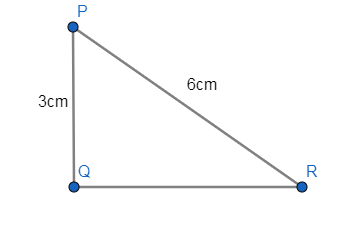
Let us assume that $\angle PRQ=\theta $ & $\angle QPR=\alpha $.
From the trigonometric ratios we know that,
$\sin \theta =\dfrac{P}{H}$
In the above equation, P stands for perpendicular or the side just opposite to angle θ and H stands for hypotenuse of the right $\Delta PQR$.
$\sin \theta =\dfrac{PQ}{PR}$
It is given that PQ = 3cm and PR = 6cm. Substituting these values in the above equation we get,
$\begin{align}
& \sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{6} \\
& \Rightarrow \sin \theta =\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}$
We know that when $\sin \theta =\dfrac{1}{2}$ then the value of θ is equal to 30°.
As we have assumed that $\angle PRQ=\theta $ so $\angle PRQ={{30}^{\circ }}$.
From the trigonometric ratios we know that,
$\cos \alpha =\dfrac{B}{H}$
In the above equation, B stands for the base of the triangle with respect to angle α and H stands for hypotenuse of the right $\Delta PQR$.
$\begin{align}
& \cos \alpha =\dfrac{PQ}{\operatorname{P}R} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \alpha =\dfrac{3}{6} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \alpha =\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}$
When $\cos \alpha =\dfrac{1}{2}$ then the value of angle α is 60°.
As we have assumed that $\angle QPR=\alpha $ so $\angle QPR={{60}^{\circ }}$.
Hence, we have calculated the value of $\angle PRQ={{30}^{\circ }}\And \angle QPR={{60}^{\circ }}$.
Note: You can check whether the angles that you are getting are correct or not. As angle Q is already given as 90°and we have calculated the values of $\angle QPR\And \angle PRQ$. And the sum of all the angles of a triangle is 180°.
$\angle PQR+\angle QPR+\angle PRQ={{180}^{\circ }}$
Adding L.H.S of the above equation will give:
$\begin{align}
& {{90}^{\circ }}+{{60}^{\circ }}+{{30}^{\circ }} \\
& ={{180}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
From the above calculation L.H.S = R.H.S so the angles that we have calculated are correct.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The below figure shows a $\Delta PQR$ right angled at Q with two sides PQ and PR are given as 3cm and 6cm respectively.

Let us assume that $\angle PRQ=\theta $ & $\angle QPR=\alpha $.
From the trigonometric ratios we know that,
$\sin \theta =\dfrac{P}{H}$
In the above equation, P stands for perpendicular or the side just opposite to angle θ and H stands for hypotenuse of the right $\Delta PQR$.
$\sin \theta =\dfrac{PQ}{PR}$
It is given that PQ = 3cm and PR = 6cm. Substituting these values in the above equation we get,
$\begin{align}
& \sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{6} \\
& \Rightarrow \sin \theta =\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}$
We know that when $\sin \theta =\dfrac{1}{2}$ then the value of θ is equal to 30°.
As we have assumed that $\angle PRQ=\theta $ so $\angle PRQ={{30}^{\circ }}$.
From the trigonometric ratios we know that,
$\cos \alpha =\dfrac{B}{H}$
In the above equation, B stands for the base of the triangle with respect to angle α and H stands for hypotenuse of the right $\Delta PQR$.
$\begin{align}
& \cos \alpha =\dfrac{PQ}{\operatorname{P}R} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \alpha =\dfrac{3}{6} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \alpha =\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}$
When $\cos \alpha =\dfrac{1}{2}$ then the value of angle α is 60°.
As we have assumed that $\angle QPR=\alpha $ so $\angle QPR={{60}^{\circ }}$.
Hence, we have calculated the value of $\angle PRQ={{30}^{\circ }}\And \angle QPR={{60}^{\circ }}$.
Note: You can check whether the angles that you are getting are correct or not. As angle Q is already given as 90°and we have calculated the values of $\angle QPR\And \angle PRQ$. And the sum of all the angles of a triangle is 180°.
$\angle PQR+\angle QPR+\angle PRQ={{180}^{\circ }}$
Adding L.H.S of the above equation will give:
$\begin{align}
& {{90}^{\circ }}+{{60}^{\circ }}+{{30}^{\circ }} \\
& ={{180}^{\circ }} \\
\end{align}$
From the above calculation L.H.S = R.H.S so the angles that we have calculated are correct.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What type of cell is found in the Seminiferous tub class 10 biology CBSE

What are the public facilities provided by the government? Also explain each facility




