
In $\Delta MGN,MP \bot GN$. If $MG = a$ units, $MN = b$ units, $GP = c$ units and $PN = d$ units.
Prove that $\left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right) = \left( {c + d} \right)\left( {c - d} \right)$.
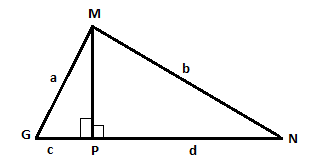

Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: We need to know the concepts of Pythagoras theorem & formulas of algebraic expressions. Here we will have to apply Pythagoras theorem in the given triangle first and then equalize the perpendicular $MP$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
$\left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right) = \left( {c + d} \right)\left( {c - d} \right)$
Using Pythagoras theorem ${a^2} = {b^2} + {c^2}$ in triangle $\Delta MGP$ and $\Delta MPN$we get –
$
{a^2} = M{P^2} + {C^2} \\
M{P^2} = {a^2} - {c^2}...........(i) \\
$
and,
$
{b^2} = M{P^2} + {d^2} \\
M{P^2} = {b^2} - {d^2}..........(ii) \\
$
$
\therefore {a^2} - {c^2} = {b^2} - {d^2} \\
{a^2} - {b^2} = {c^2} - {d^2} \\
$ [from equation $(i)$& $(ii)$]
By using formulae, ${a^2} - b{}^2 = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)$we get –
$\left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right) = \left( {c + d} \right)\left( {c - d} \right)$
Hence, proved.
Note: In this type of question by generating two equations with the help of Pythagoras theorem is must. After that we can easily prove the given equation. While equating the linear equation formed by the given conditions, calculations & applying of formulas should be done carefully to avoid silly mistakes instead of knowing the concepts & formulations to be applied.
Complete step-by-step answer:
$\left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right) = \left( {c + d} \right)\left( {c - d} \right)$
Using Pythagoras theorem ${a^2} = {b^2} + {c^2}$ in triangle $\Delta MGP$ and $\Delta MPN$we get –
$
{a^2} = M{P^2} + {C^2} \\
M{P^2} = {a^2} - {c^2}...........(i) \\
$
and,
$
{b^2} = M{P^2} + {d^2} \\
M{P^2} = {b^2} - {d^2}..........(ii) \\
$
$
\therefore {a^2} - {c^2} = {b^2} - {d^2} \\
{a^2} - {b^2} = {c^2} - {d^2} \\
$ [from equation $(i)$& $(ii)$]
By using formulae, ${a^2} - b{}^2 = \left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right)$we get –
$\left( {a + b} \right)\left( {a - b} \right) = \left( {c + d} \right)\left( {c - d} \right)$
Hence, proved.
Note: In this type of question by generating two equations with the help of Pythagoras theorem is must. After that we can easily prove the given equation. While equating the linear equation formed by the given conditions, calculations & applying of formulas should be done carefully to avoid silly mistakes instead of knowing the concepts & formulations to be applied.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What type of cell is found in the Seminiferous tub class 10 biology CBSE

What are the public facilities provided by the government? Also explain each facility




