
In $\Delta ABC$, if$M$is the midpoint of side BC, then$A{B^2} + A{C^2} = 2A{M^2} + 2B{M^2}$
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Since the question is given in terms of squares of sides, it would be better to approach this question by Pythagoras theorem. We need to have a right angled triangle to use Pythagoras theorem. So we will construct a perpendicular to make the question easy.
Complete step by step solution:
We have to prove
$A{B^2} + A{C^2} = 2A{M^2} + 2B{M^2}$
As explained in the hint, draw a perpendicular from A on BC
$ \Rightarrow AD \bot BC$
In$\Delta ABC$, it is also given that, $M$is the midpoint of side$BC$
$ \Rightarrow BM = MC$
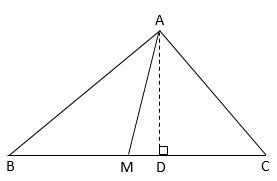
By Pythagoras theorem, in $\Delta ABC$
$A{B^2} = A{D^2} + B{D^2}$ and $A{C^2} = A{D^2} + D{C^2}$
Adding the two equations above, we get
$A{B^2} + A{C^2} = A{D^2} + B{D^2} + A{D^2} + D{C^2}$ . . . (1)
Now we will rearrange the above equation in such a way that we could substitute the terms that our proof requires.
For that, use
$BD = BM + MD$ and $DC = MC - MD$
Hence, equation (1) becomes
$A{B^2} + A{C^2} = A{D^2} + {(BM + MD)^2} + A{D^2} + {(MC - MD)^2}$
By using the formula ${(a + b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab$ and ${(a - b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab,$we can simplify the above equation as
$A{B^2} + A{C^2} = A{D^2} + B{M^2} + M{D^2} + 2BM \times MD + A{D^2} + M{C^2} + M{D^2} - 2MC \times MD$
Rearranging the above equation, we get
$A{B^2} + A{C^2} = A{D^2} + M{D^2} + B{M^2} + 2BM \times MD + A{D^2} + M{D^2} + M{C^2} - 2MC \times MD$
Now, in $\Delta ADM,$by Pythagoras theorem, we get
$A{D^2} + M{D^2} = A{M^2}$
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} + A{C^2} = A{M^2} + B{M^2} + 2BM \times MD + A{M^2} + M{C^2} - 2MC \times MD\]
Now, since, $BM = MC$, we can rearrange the above equation as
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} + A{C^2} = 2A{M^2} + B{M^2} + 2BM \times MD + B{M^2} - 2BM \times MD\]
Simplifying it, we get
\[A{B^2} + A{C^2} = 2A{M^2} + 2B{M^2}\]
Hence, it is proved that \[A{B^2} + A{C^2} = 2A{M^2} + 2B{M^2}\]
Additional information:
According to Pythagoras theorem, in a right angled triangle, the sum of squares of two adjacent sides is equal to the square of the hypotenuse.
Mathematically, in a right angle triangle, ABC, right angled at B.
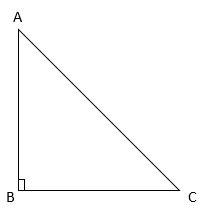
$A{B^2} + B{C^2} = A{C^2}$
Note: Simplest way to solve such a question is to use an approach that uses the information given in the question. This way, it becomes easy to reach the solution in less time. Having a foresight of using a proper construction whenever required can be very helpful in the long run.
Complete step by step solution:
We have to prove
$A{B^2} + A{C^2} = 2A{M^2} + 2B{M^2}$
As explained in the hint, draw a perpendicular from A on BC
$ \Rightarrow AD \bot BC$
In$\Delta ABC$, it is also given that, $M$is the midpoint of side$BC$
$ \Rightarrow BM = MC$

By Pythagoras theorem, in $\Delta ABC$
$A{B^2} = A{D^2} + B{D^2}$ and $A{C^2} = A{D^2} + D{C^2}$
Adding the two equations above, we get
$A{B^2} + A{C^2} = A{D^2} + B{D^2} + A{D^2} + D{C^2}$ . . . (1)
Now we will rearrange the above equation in such a way that we could substitute the terms that our proof requires.
For that, use
$BD = BM + MD$ and $DC = MC - MD$
Hence, equation (1) becomes
$A{B^2} + A{C^2} = A{D^2} + {(BM + MD)^2} + A{D^2} + {(MC - MD)^2}$
By using the formula ${(a + b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab$ and ${(a - b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab,$we can simplify the above equation as
$A{B^2} + A{C^2} = A{D^2} + B{M^2} + M{D^2} + 2BM \times MD + A{D^2} + M{C^2} + M{D^2} - 2MC \times MD$
Rearranging the above equation, we get
$A{B^2} + A{C^2} = A{D^2} + M{D^2} + B{M^2} + 2BM \times MD + A{D^2} + M{D^2} + M{C^2} - 2MC \times MD$
Now, in $\Delta ADM,$by Pythagoras theorem, we get
$A{D^2} + M{D^2} = A{M^2}$
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} + A{C^2} = A{M^2} + B{M^2} + 2BM \times MD + A{M^2} + M{C^2} - 2MC \times MD\]
Now, since, $BM = MC$, we can rearrange the above equation as
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} + A{C^2} = 2A{M^2} + B{M^2} + 2BM \times MD + B{M^2} - 2BM \times MD\]
Simplifying it, we get
\[A{B^2} + A{C^2} = 2A{M^2} + 2B{M^2}\]
Hence, it is proved that \[A{B^2} + A{C^2} = 2A{M^2} + 2B{M^2}\]
Additional information:
According to Pythagoras theorem, in a right angled triangle, the sum of squares of two adjacent sides is equal to the square of the hypotenuse.
Mathematically, in a right angle triangle, ABC, right angled at B.

$A{B^2} + B{C^2} = A{C^2}$
Note: Simplest way to solve such a question is to use an approach that uses the information given in the question. This way, it becomes easy to reach the solution in less time. Having a foresight of using a proper construction whenever required can be very helpful in the long run.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




