
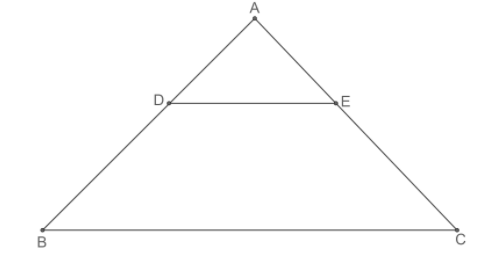
In \[\Delta ABC\], DE is parallel to base BC, with D on AB and on AC. If $\dfrac{AD}{DB}=\dfrac{2}{3}$, then find the value of $\dfrac{BC}{DE}$?

Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: We start solving the problem by using the property that corresponding angles are equal for the angles $\angle CBA$, $\angle EDA$ and $\angle ACB$, $\angle AED$. We then find the equal angles in both the triangles $\Delta ADE$ and $\Delta ABC$ to check the similarity between them. We then use the proportion of sides to sides between the triangles $\Delta ADE$ and $\Delta ABC$, and make necessary calculations to get the required result.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the problem, we are given that in \[\Delta ABC\], DE is parallel to base BC, with D on AB and on AC as shown in figure. We need to find the value of $\dfrac{BC}{DE}$ if it is given $\dfrac{AD}{DB}=\dfrac{2}{3}$.
Let us redraw the figure.
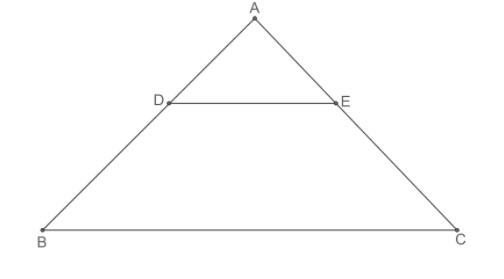
As the sides DE and BC are parallel to each other, we get that $\angle CBA=\angle EDA$ and $\angle ACB=\angle AED$ as these angles are corresponding angles. We know that the corresponding angles are equal.
Let us consider the triangles $\Delta ADE$ and $\Delta ABC$.
We have $\angle DAE=\angle BAC$ (common angle).
$\Rightarrow \angle CBA=\angle EDA$ (corresponding angles are equal).
$\Rightarrow \angle ACB=\angle AED$ (corresponding angles are equal).
We know that if three interior angles of two triangles are equal, then those triangles are similar to each other.
So, we get triangles $\Delta ADE$ and $\Delta ABC$ as similar triangles.
We know that the sides are proportionately equal to each other in similar triangles.
So, we get $\dfrac{AB}{AD}=\dfrac{AC}{AE}=\dfrac{BC}{DE}$ ---(1).
According to the problem, we are given $\dfrac{AD}{DB}=\dfrac{2}{3}$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{DB}{AD}=\dfrac{3}{2}$.
$\Rightarrow 1+\dfrac{DB}{AD}=1+\dfrac{3}{2}$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{AD+DB}{AD}=\dfrac{2+3}{2}$.
From the figure we can see that $AD+DB=AB$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{AB}{AD}=\dfrac{5}{2}$ ---(2).
Let us substitute equation (2) in equation (1).
So, we get $\dfrac{AB}{AD}=\dfrac{AC}{AE}=\dfrac{BC}{DE}=\dfrac{5}{2}$.
We have found the value of $\dfrac{BC}{DE}$ as $\dfrac{5}{2}$.
Note: We cannot make use of other properties like SAS, ASA in this case as we can see that there is no similar side present in both the triangles. Whenever we get this type of problem, we should try to make use of the similarity of triangles as this will lead us to the required solution comfortably. We should remember that proportionality of sides can only be used if both the triangles are proved to be similar. Similarly, we can expect problems to find the angles and length of the sides of the triangle.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the problem, we are given that in \[\Delta ABC\], DE is parallel to base BC, with D on AB and on AC as shown in figure. We need to find the value of $\dfrac{BC}{DE}$ if it is given $\dfrac{AD}{DB}=\dfrac{2}{3}$.
Let us redraw the figure.

As the sides DE and BC are parallel to each other, we get that $\angle CBA=\angle EDA$ and $\angle ACB=\angle AED$ as these angles are corresponding angles. We know that the corresponding angles are equal.
Let us consider the triangles $\Delta ADE$ and $\Delta ABC$.
We have $\angle DAE=\angle BAC$ (common angle).
$\Rightarrow \angle CBA=\angle EDA$ (corresponding angles are equal).
$\Rightarrow \angle ACB=\angle AED$ (corresponding angles are equal).
We know that if three interior angles of two triangles are equal, then those triangles are similar to each other.
So, we get triangles $\Delta ADE$ and $\Delta ABC$ as similar triangles.
We know that the sides are proportionately equal to each other in similar triangles.
So, we get $\dfrac{AB}{AD}=\dfrac{AC}{AE}=\dfrac{BC}{DE}$ ---(1).
According to the problem, we are given $\dfrac{AD}{DB}=\dfrac{2}{3}$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{DB}{AD}=\dfrac{3}{2}$.
$\Rightarrow 1+\dfrac{DB}{AD}=1+\dfrac{3}{2}$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{AD+DB}{AD}=\dfrac{2+3}{2}$.
From the figure we can see that $AD+DB=AB$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{AB}{AD}=\dfrac{5}{2}$ ---(2).
Let us substitute equation (2) in equation (1).
So, we get $\dfrac{AB}{AD}=\dfrac{AC}{AE}=\dfrac{BC}{DE}=\dfrac{5}{2}$.
We have found the value of $\dfrac{BC}{DE}$ as $\dfrac{5}{2}$.
Note: We cannot make use of other properties like SAS, ASA in this case as we can see that there is no similar side present in both the triangles. Whenever we get this type of problem, we should try to make use of the similarity of triangles as this will lead us to the required solution comfortably. We should remember that proportionality of sides can only be used if both the triangles are proved to be similar. Similarly, we can expect problems to find the angles and length of the sides of the triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?

Draw the diagram of the sectional view of the human class 10 biology CBSE




