
In \[\Delta ABC\] , a=12, b=8, c=8, how do you find the cosine of each of the angles?
Answer
535.5k+ views
Hint: Law of cosines signifies the relation between the lengths of sides of a triangle with respect to the cosine of its angle. It is also called the cosine rule. If ABC is a triangle, then as per the statement of cosine law, we have sides of triangle i.e., a, b, c given, hence with respect to the given sides we need to find the cosine of each of the angles by applying formulas of it.
Formula used:
\[\cos A = \dfrac{{{b^2} + {c^2} - {a^2}}}{{2bc}}\]
\[\cos B = \dfrac{{{a^2} + {c^2} - {b^2}}}{{2ac}}\]
\[\cos C = \dfrac{{{a^2} + {b^2} - {c^2}}}{{2ab}}\]
In which, a, b, c are the sides of a given triangle ABC.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given,
In \[\Delta ABC\] , a=12, b=8, c=8.
We need to find the cosine of each of the angles, hence
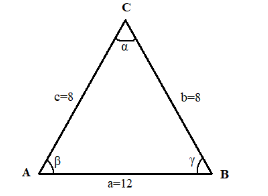
The law of cosines states that: \[{\gamma ^2} = {\alpha ^2} + {\beta ^2} - 2\alpha \beta \cos \Gamma \] , where \[\alpha ,\beta \] , and \[\gamma \] are the sides of a triangle and \[\Gamma \] is the angle opposite side \[\gamma \] (the angle between sides α and β).
This law can be rearranged to solve for the cosine of an angle instead of a side.
\[\cos \Gamma = \dfrac{{{\alpha ^2} + {\beta ^2} - {\gamma ^2}}}{{2\alpha \beta }}\]
Law of cosines signifies the relation between the lengths of sides of a triangle with respect to the cosine of its angle. Hence, for each angle, plug in the adjacent sides for α and β and the opposite side for \[\gamma \] :
\[\cos C = \dfrac{{{a^2} + {b^2} - {c^2}}}{{2ab}}\]
Now, substitute the values of a, b, c i.e., sides of triangle:
\[ = \dfrac{{{{12}^2} + {8^2} - {8^2}}}{{2 \cdot 12 \cdot 8}}\]
Evaluating the terms, we get:
\[ = \dfrac{{144 + 64 - 64}}{{192}} = \dfrac{{144}}{{192}} = \dfrac{3}{4}\]
Therefore, \[\cos C = \dfrac{3}{4}\] .
Now, for:
\[\cos B = \dfrac{{{a^2} + {c^2} - {b^2}}}{{2ac}}\]
Substitute the values of a, b, c i.e., sides of triangle:
\[ = \dfrac{{{{12}^2} + {8^2} - {8^2}}}{{2 \cdot 12 \cdot 8}}\]
Evaluating the terms, we get:
\[ = \dfrac{{144 + 64 - 64}}{{192}} = \dfrac{{144}}{{192}} = \dfrac{3}{4}\]
Therefore, \[\cos B = \dfrac{3}{4}\] .
And for,
\[\cos A = \dfrac{{{b^2} + {c^2} - {a^2}}}{{2bc}}\]
Substitute the values of a, b, c i.e., sides of triangle:
\[ = \dfrac{{{8^2} + {8^2} - {{12}^2}}}{{2 \cdot 8 \cdot 8}}\]
Evaluating the terms, we get:
\[ = \dfrac{{64 + 64 - 144}}{{128}} = \dfrac{{ - 16}}{{128}} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{8}\]
Therefore, \[\cos A = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{8}\] .
Therefore, the angles of triangle are:
\[\cos A = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{8},\cos B = \dfrac{3}{4},\cos C = \dfrac{3}{4}\]
So, the correct answer is “ \[\cos A = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{8},\cos B = \dfrac{3}{4},\cos C = \dfrac{3}{4}\] ”.
Note: We must note that, Cosine law is basically used to find unknown side of a triangle, when the length of the other two sides are given and the angle between the two known sides are given, but here we are asked to find the cosine angles with the given sides of triangle, hence we must know note all the formulas to find the angles.
Formula used:
\[\cos A = \dfrac{{{b^2} + {c^2} - {a^2}}}{{2bc}}\]
\[\cos B = \dfrac{{{a^2} + {c^2} - {b^2}}}{{2ac}}\]
\[\cos C = \dfrac{{{a^2} + {b^2} - {c^2}}}{{2ab}}\]
In which, a, b, c are the sides of a given triangle ABC.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given,
In \[\Delta ABC\] , a=12, b=8, c=8.
We need to find the cosine of each of the angles, hence

The law of cosines states that: \[{\gamma ^2} = {\alpha ^2} + {\beta ^2} - 2\alpha \beta \cos \Gamma \] , where \[\alpha ,\beta \] , and \[\gamma \] are the sides of a triangle and \[\Gamma \] is the angle opposite side \[\gamma \] (the angle between sides α and β).
This law can be rearranged to solve for the cosine of an angle instead of a side.
\[\cos \Gamma = \dfrac{{{\alpha ^2} + {\beta ^2} - {\gamma ^2}}}{{2\alpha \beta }}\]
Law of cosines signifies the relation between the lengths of sides of a triangle with respect to the cosine of its angle. Hence, for each angle, plug in the adjacent sides for α and β and the opposite side for \[\gamma \] :
\[\cos C = \dfrac{{{a^2} + {b^2} - {c^2}}}{{2ab}}\]
Now, substitute the values of a, b, c i.e., sides of triangle:
\[ = \dfrac{{{{12}^2} + {8^2} - {8^2}}}{{2 \cdot 12 \cdot 8}}\]
Evaluating the terms, we get:
\[ = \dfrac{{144 + 64 - 64}}{{192}} = \dfrac{{144}}{{192}} = \dfrac{3}{4}\]
Therefore, \[\cos C = \dfrac{3}{4}\] .
Now, for:
\[\cos B = \dfrac{{{a^2} + {c^2} - {b^2}}}{{2ac}}\]
Substitute the values of a, b, c i.e., sides of triangle:
\[ = \dfrac{{{{12}^2} + {8^2} - {8^2}}}{{2 \cdot 12 \cdot 8}}\]
Evaluating the terms, we get:
\[ = \dfrac{{144 + 64 - 64}}{{192}} = \dfrac{{144}}{{192}} = \dfrac{3}{4}\]
Therefore, \[\cos B = \dfrac{3}{4}\] .
And for,
\[\cos A = \dfrac{{{b^2} + {c^2} - {a^2}}}{{2bc}}\]
Substitute the values of a, b, c i.e., sides of triangle:
\[ = \dfrac{{{8^2} + {8^2} - {{12}^2}}}{{2 \cdot 8 \cdot 8}}\]
Evaluating the terms, we get:
\[ = \dfrac{{64 + 64 - 144}}{{128}} = \dfrac{{ - 16}}{{128}} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{8}\]
Therefore, \[\cos A = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{8}\] .
Therefore, the angles of triangle are:
\[\cos A = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{8},\cos B = \dfrac{3}{4},\cos C = \dfrac{3}{4}\]
So, the correct answer is “ \[\cos A = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{8},\cos B = \dfrac{3}{4},\cos C = \dfrac{3}{4}\] ”.
Note: We must note that, Cosine law is basically used to find unknown side of a triangle, when the length of the other two sides are given and the angle between the two known sides are given, but here we are asked to find the cosine angles with the given sides of triangle, hence we must know note all the formulas to find the angles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 11 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




