
In column I some circuits are given. In all the circuits except in (i), switch S remains closed for a long time and then it is opened at t=0; while for (i), the situation is reversed. Column II tells something about the quantities. Match the entries of column I with the entries of column II.
List I List II
A. Induced e.m.f can be greater than E
B. Induced e.m.f would be less than E
C. Finally energy stored in inductor is zero
D. Finally energy stored in the inductor is non zero.
| List I | List II |

| A. Induced e.m.f can be greater than E |

| B. Induced e.m.f would be less than E |

| C. Finally energy stored in inductor is zero |

| D. Finally energy stored in the inductor is non zero. |
Answer
524.1k+ views
Hint: As a very first step, you could read the question well and hence understand the situation properly. Now, you could analyse each circuit one by one and hence find the required quantity as per the list II given on the side. Thereby, you will be able to do the matching easily.
Complete answer:
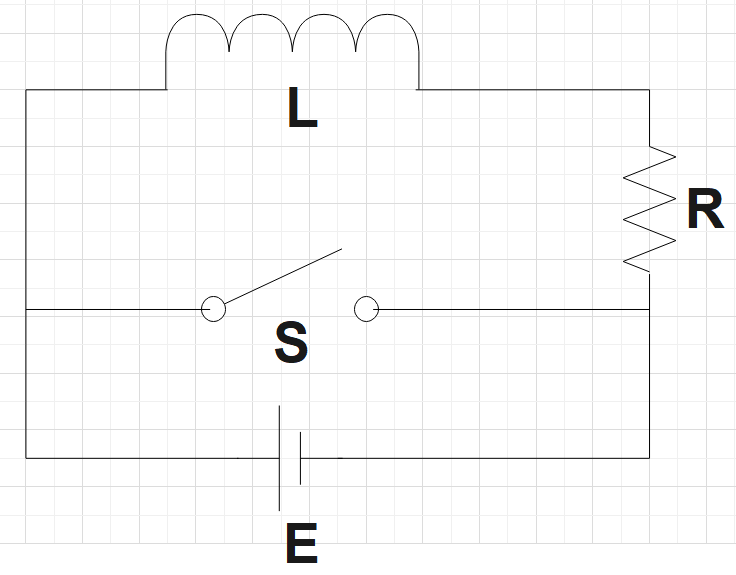
For first circuit in List I, current in the inductor present in the circuit when the switch is kept open is given by,
${{I}_{0}}=\dfrac{E}{R}$
We could say that initially the induced end is E and finally it becomes zero. Hence, the energy stored in the inductor would also be zero. So the first circuit matches C.
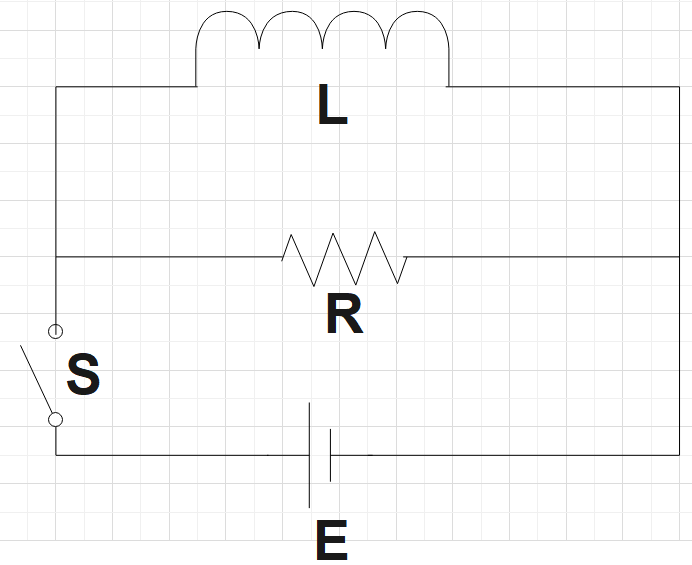
For the second circuit, the energy is lost through a resistor in the form of heat. Finally,
I become equal to 0 and so will the energy. The second circuit also matches C.
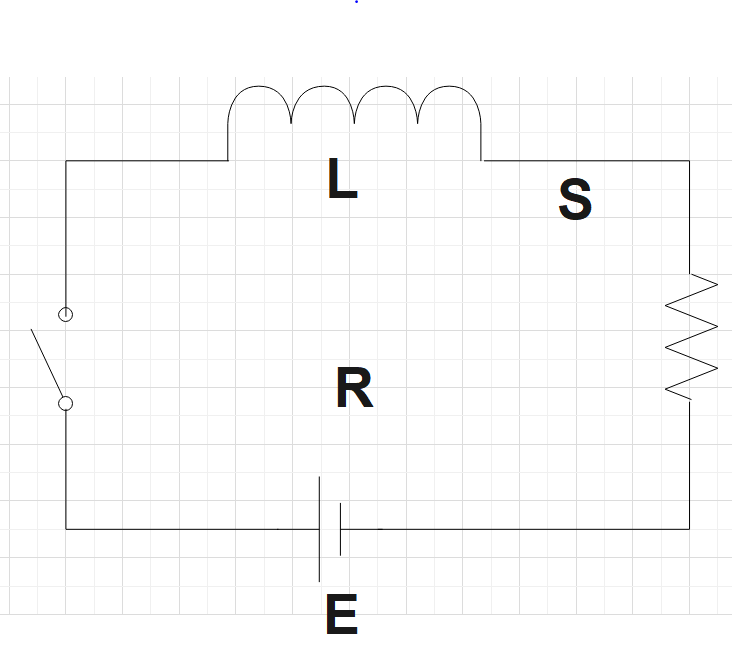
Now for the third circuit, the current suddenly becomes zero. Also, energy is dissipated in R and finally becomes zero. Along with this the flux change is also found to be very fast and hence the induced emf is found to be greater than E. So, the third circuit could be matched to A and C.
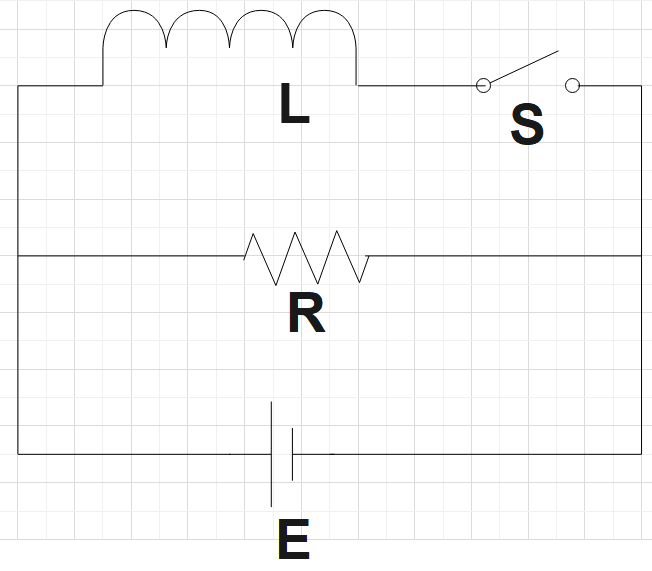
For the fourth circuit it's the same as the third circuit but as the switch is kept open, energy loss isn’t through Resistor.
Note:
So, basically in questions like this that involve matching two lists, one could deal with each option in the list one by one. This is done so as to avoid confusion. Also, what we require in solving this question is the basic idea of analysing a circuit. If you are good at it, it’s pretty much easy to solve.
Complete answer:
For first circuit in List I, current in the inductor present in the circuit when the switch is kept open is given by,
${{I}_{0}}=\dfrac{E}{R}$
We could say that initially the induced end is E and finally it becomes zero. Hence, the energy stored in the inductor would also be zero. So the first circuit matches C.
For the second circuit, the energy is lost through a resistor in the form of heat. Finally,
I become equal to 0 and so will the energy. The second circuit also matches C.
Now for the third circuit, the current suddenly becomes zero. Also, energy is dissipated in R and finally becomes zero. Along with this the flux change is also found to be very fast and hence the induced emf is found to be greater than E. So, the third circuit could be matched to A and C.
For the fourth circuit it's the same as the third circuit but as the switch is kept open, energy loss isn’t through Resistor.
Note:
So, basically in questions like this that involve matching two lists, one could deal with each option in the list one by one. This is done so as to avoid confusion. Also, what we require in solving this question is the basic idea of analysing a circuit. If you are good at it, it’s pretty much easy to solve.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




