
In citric acid cycle the step not using dehydrogenase enzyme is
A. Malic acid to oxaloacetate
B. Succinate to fumarate
C. Oxaloacetate to citric acid
D. Citric acid to ketoglutarate
Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint:-The tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle) is also known as the citric acid cycle or Krebs cycle (according to its discoverer Sir Hans Krebs). The TCA cycle, or The citric acid cycle is the center of cellular metabolism and the gateway to the aerobic metabolism of any molecule which can be converted into acetyl groups or dicarboxylic acids.
Complete Answer:-1. Pyruvate is first decarboxylated and converted to acetyl-CoA, which is the link between glycolysis and the TCA cycle and serves as a fuel for the TCA cycle. Acetyl-CoA is a two-carbon molecule that starts the TCA cycle and condenses with a four-carbon intermediate, oxaloacetate, to form citrate and initiate the six-carbon step.
2. Citrate is isomerized to give isocitrate which is then oxidized and decarboxylated twice to give α-ketoglutarate and then Succinyl-CoA. Meanwhile, two molecules of NADH are generated and two carbons are released from the cycle as CO2, and as a result, the four-carbon step begins.
3.Succinyl-CoA is finally converted to oxaloacetate through the formation of succinate, fumarate and L-malate.
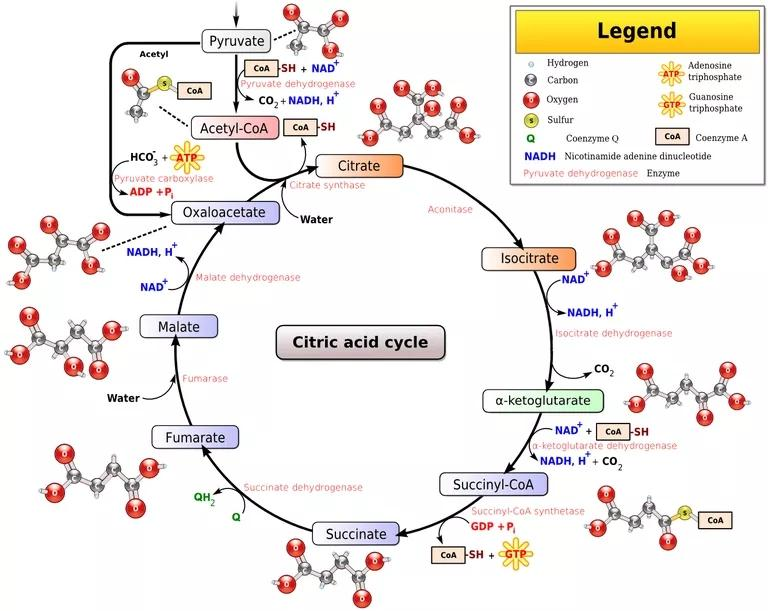
4. The 4 carbon step gives FADH2 (FAD = flavin adenine dinucleotide) and NADH (NAD = nicotinamide dinucleotide) during two oxidation steps: succinate to fumarate and L-malate to oxaloacetate. GTP (High Energy ATP Compatible Molecule) is also formed when Succinyl-CoA is converted to succinate. Finally, the oxaloacetate is regenerated and combined with the acetyl-CoA and you are ready to proceed.
From the given cycle it’s clear that the correct option is (C).
Note:- Products which are used for the biosynthesis of proteins, nucleic acids, etc. Thus the cycle has a dual purpose, on the one hand a catabolic role and on the other an anabolic role. Such dual target metabolic pathways are known as amphibolites.
Although the cycle gene, cholesterol rates a large amount of energy, its main function is to provide precursors not only for strong forms of fuel, but also for the building blocks of many other molecules such as cholesterol, amino acids and nucleotide bases.
Complete Answer:-1. Pyruvate is first decarboxylated and converted to acetyl-CoA, which is the link between glycolysis and the TCA cycle and serves as a fuel for the TCA cycle. Acetyl-CoA is a two-carbon molecule that starts the TCA cycle and condenses with a four-carbon intermediate, oxaloacetate, to form citrate and initiate the six-carbon step.
2. Citrate is isomerized to give isocitrate which is then oxidized and decarboxylated twice to give α-ketoglutarate and then Succinyl-CoA. Meanwhile, two molecules of NADH are generated and two carbons are released from the cycle as CO2, and as a result, the four-carbon step begins.
3.Succinyl-CoA is finally converted to oxaloacetate through the formation of succinate, fumarate and L-malate.

4. The 4 carbon step gives FADH2 (FAD = flavin adenine dinucleotide) and NADH (NAD = nicotinamide dinucleotide) during two oxidation steps: succinate to fumarate and L-malate to oxaloacetate. GTP (High Energy ATP Compatible Molecule) is also formed when Succinyl-CoA is converted to succinate. Finally, the oxaloacetate is regenerated and combined with the acetyl-CoA and you are ready to proceed.
From the given cycle it’s clear that the correct option is (C).
Note:- Products which are used for the biosynthesis of proteins, nucleic acids, etc. Thus the cycle has a dual purpose, on the one hand a catabolic role and on the other an anabolic role. Such dual target metabolic pathways are known as amphibolites.
Although the cycle gene, cholesterol rates a large amount of energy, its main function is to provide precursors not only for strong forms of fuel, but also for the building blocks of many other molecules such as cholesterol, amino acids and nucleotide bases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




