
In $ BrF_3 $ , expected geometry is trigonal bipyramidal and actual geometry is T-shaped. True or False.
Answer
531.9k+ views
Hint :Hybridization is the idea that atomic orbitals fuse to form newly hybridized orbitals, which in turn, influences molecular geometry and bonding properties. Hybridization is also an expansion of the valence bond theory.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
To determine the hybridization of bromine trifluoride we will first take the bromine atom which is the central atom and look at its electron configuration. It is represented as;
$ 1{s^2}\;2{s^2}2{p^6}\;3{s^2}3{p^6}3{d^{10}}4{s^2}4{p^5} $
However, in order to form bonds with the fluorine atom some electrons in Bromine are shifted to 4d-orbitals. Besides, fluorine has a higher oxidative capacity and therefore it forces bromine to promote electrons to the said level. Now, bromine can use the d-orbitals for hybridization.
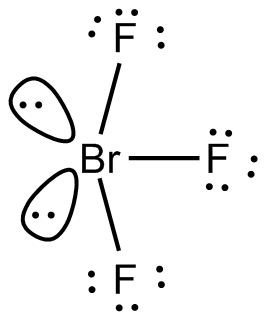
$ Br{F_3} $ Will consist of seven electrons in its outermost shell. After the bond formation, it will further have two lone pairs and $ \;3{\text{ }}Br--F $ covalent bonds. As the hybridization value or the electron pair is equal to five it gives rise to $ s{p^3}d $ hybrid orbitals.
$ Br{F_3} $ Is $ A{X_5} $ type of molecule with two lone pairs and three bond pairs of electrons. The central $ Br $ atom undergoes $ s{p^3}d $ hybridization. The expected geometry is trigonal bipyramidal and the actual geometry is T-shaped since two of the orbitals are occupied by lone pairs.
Note :
Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule. It includes the general shape of the molecule as well as bond lengths, bond angles, torsional angles, and any other geometrical parameters that determine the position of each atom.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
To determine the hybridization of bromine trifluoride we will first take the bromine atom which is the central atom and look at its electron configuration. It is represented as;
$ 1{s^2}\;2{s^2}2{p^6}\;3{s^2}3{p^6}3{d^{10}}4{s^2}4{p^5} $
However, in order to form bonds with the fluorine atom some electrons in Bromine are shifted to 4d-orbitals. Besides, fluorine has a higher oxidative capacity and therefore it forces bromine to promote electrons to the said level. Now, bromine can use the d-orbitals for hybridization.
$ Br{F_3} $ Will consist of seven electrons in its outermost shell. After the bond formation, it will further have two lone pairs and $ \;3{\text{ }}Br--F $ covalent bonds. As the hybridization value or the electron pair is equal to five it gives rise to $ s{p^3}d $ hybrid orbitals.
$ Br{F_3} $ Is $ A{X_5} $ type of molecule with two lone pairs and three bond pairs of electrons. The central $ Br $ atom undergoes $ s{p^3}d $ hybridization. The expected geometry is trigonal bipyramidal and the actual geometry is T-shaped since two of the orbitals are occupied by lone pairs.

Note :
Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule. It includes the general shape of the molecule as well as bond lengths, bond angles, torsional angles, and any other geometrical parameters that determine the position of each atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




