
In angiosperms, functional megaspore develops into
(a) Embryo sac
(b) Ovule
(c) Endosperm
(d) Pollen sac
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: In angiosperms, functional megaspore develops into a female gametophyte which is located in the nucellus. In plants, fertilization occurs in this location and forms the egg cell or nucleus developing into an embryo after fertilization.
Complete Step by Step Answer: The functional megaspore grows into an Embryo sac in angiosperms. An Embryo sac is a female gametophyte located in the nucleus and is formed from functional megaspore.
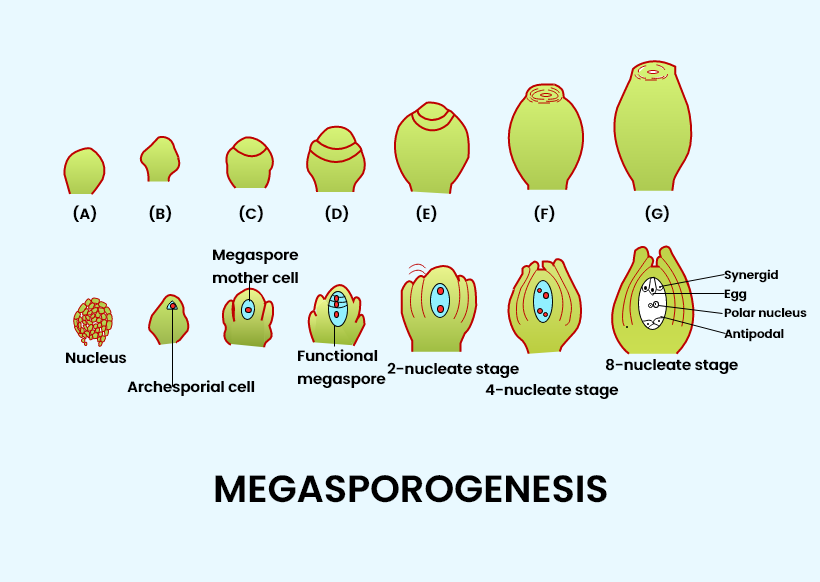 The nucleus of chalazal functional megaspore (fourth from micropyle) divides mitotically to form two nuclei which move to opposite poles, forming the 2 nucleate embryo sac. Two sequential mitotic nuclear divisions results in the formation of 4-nucleates and later the 8-nucleate stages of the embryo sac. One nucleus from each pole moves to the middle to form polar nuclei.
The nucleus of chalazal functional megaspore (fourth from micropyle) divides mitotically to form two nuclei which move to opposite poles, forming the 2 nucleate embryo sac. Two sequential mitotic nuclear divisions results in the formation of 4-nucleates and later the 8-nucleate stages of the embryo sac. One nucleus from each pole moves to the middle to form polar nuclei.
At this stage, the following changes occur - Three of the nuclei (n) get organized as the cells of the micropylar end forming egg apparatus. One is the egg cell (n) and two are the synergids (n). - three nuclei get organized as the antipodal cell (n) at the chalazal end. - Two nuclei in the center are called the polar nuclei (n). - This constitutes a 7-celled and 8-nucleated embryo sac.
So, the answer is “Embryo sac”.
Additional Information: The process of formation of megaspores from the megaspore mother cell (MMC) is called megasporogenesis. Ovules typically discern a single mother cell of the megaspore in the nucellus micropylar area.
The MMC undergoes meiosis and forms a four haploid megaspore linear tetrad. From which three degenerates (micropylar end) and three functional (chalazal end) remain.
Note: - MMC is a large cell containing dense cytoplasm and a prominent nucleus. - To ensure the formation of haploid female gametophyte before fertilization MMC undergoes meiosis. - These mitotic divisions are strictly free nuclear i.e.; nuclear divisions are not followed immediately by cell wall formation. - In the majority of angiosperms, one of the megaspores is functional while the three degenerates. Only the functional megaspore (n) develops into the female gametophyte. This process of embryo sac formation from a single megaspore is termed as Monosporic development. - Polygonum type of embryo sac is found in 80% of flowering plants. This development has been studied in Polygonum by Strasburger.
Complete Step by Step Answer: The functional megaspore grows into an Embryo sac in angiosperms. An Embryo sac is a female gametophyte located in the nucleus and is formed from functional megaspore.

At this stage, the following changes occur - Three of the nuclei (n) get organized as the cells of the micropylar end forming egg apparatus. One is the egg cell (n) and two are the synergids (n). - three nuclei get organized as the antipodal cell (n) at the chalazal end. - Two nuclei in the center are called the polar nuclei (n). - This constitutes a 7-celled and 8-nucleated embryo sac.
So, the answer is “Embryo sac”.
Additional Information: The process of formation of megaspores from the megaspore mother cell (MMC) is called megasporogenesis. Ovules typically discern a single mother cell of the megaspore in the nucellus micropylar area.
The MMC undergoes meiosis and forms a four haploid megaspore linear tetrad. From which three degenerates (micropylar end) and three functional (chalazal end) remain.
Note: - MMC is a large cell containing dense cytoplasm and a prominent nucleus. - To ensure the formation of haploid female gametophyte before fertilization MMC undergoes meiosis. - These mitotic divisions are strictly free nuclear i.e.; nuclear divisions are not followed immediately by cell wall formation. - In the majority of angiosperms, one of the megaspores is functional while the three degenerates. Only the functional megaspore (n) develops into the female gametophyte. This process of embryo sac formation from a single megaspore is termed as Monosporic development. - Polygonum type of embryo sac is found in 80% of flowering plants. This development has been studied in Polygonum by Strasburger.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




