
In an isosceles $\vartriangle ABC$, if $AC = BC$ and $A{B^2} = 2A{C^2}$, then $\angle C$ is equal to
A)${45^ \circ }$
B)${60^ \circ }$
C)${30^ \circ }$
D)${90^ \circ }$
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: Check the nature of triangle and you are given $AC = BC$ and $A{B^2} = 2A{C^2}$, then you can check whether the triangle is right angled triangle by checking Pythagoras theorem. You can apply this theorem and get your answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First of all, draw the sketch of $\vartriangle ABC$ and note down the condition given in the question.
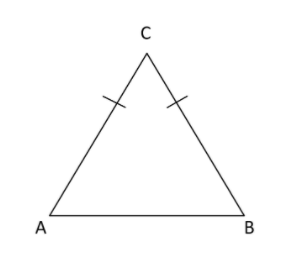
According to question, it is saying that sides $AC = BC$ (1)
And $A{B^2} = 2A{C^2}$ (2)
Now drop a perpendicular from C to AB that meets AB at D.
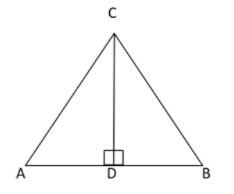
Hence, we draw perpendicular from C to AB and hence,
$\angle CDA = \angle CDB = {90^ \circ }$
Now you can check and compare the two triangles ,i.e., $\vartriangle ADC$ and $\vartriangle BDC$
We can check the congruence of both the triangles. So,
In $\vartriangle ADC$ and $\vartriangle BDC$
$AC = BC$ (As it is given in the question)
$\angle ADC = \angle BDC$ (Both are equal to ${90^ \circ }$as we drop the perpendicular from C to AB)
$CD = CD$ (Both are common for both the triangle)
Hence, both triangles are congruent by RHS congruence property.
$\vartriangle ADC \cong \vartriangle BDC$ (By RHS property)
Now from CPCT, (corresponding part of congruent triangle)
$AD = BD$ (3)
$\angle ACD = \angle BCD$ (4)
And $\angle CAD = \angle CBD$
(As we know, corresponding parts are equal for congruent triangle.)
Hence, we got $AD = BD$.
Hence, D is the mid point of AB.
So, we can write $AD = \dfrac{{AB}}{2}$ (5)
(As D bisects AB , so it is half of AB.)
Now lets see the $\vartriangle ADC$
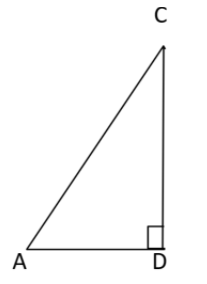
As we know, $\angle D = {90^ \circ }$hence it is right angled triangle , hence can use trigonometric properties, i.e., $\sin \theta = \dfrac{{Perpendicular}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}$
$\sin \angle ACD = \dfrac{{AD}}{{AC}}$
But we already proved that $AD = \dfrac{{AB}}{2}$
So,
$\sin \angle ACD = \dfrac{{AB}}{{2AC}}$ (6)
Now, in question, you are given condition
$A{B^2} = 2A{C^2}$
Taking square root on both side,
$AB = \sqrt 2 AC$
Now putting $AB = \sqrt 2 AC$ in equation (6)
$
\sin \angle ACD = \dfrac{{\sqrt 2 AC}}{{2AC}} \\
= \dfrac{{\sqrt 2 }}{2} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} \\
$
And this is known that $\sin {45^ \circ } = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
Hence, you will get $\angle ACD = {45^ \circ }$
Now we have proved in equation (4)
$\angle ACD = \angle BCD = {45^ \circ }$
So,
$
\angle C = \angle ACD + \angle BCD \\
= {45^ \circ } + {45^ \circ } \\
= {90^ \circ } \\
$
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: You may use an alternative method to find angle to save your time. You know $AC = BC$ and $A{B^2} = 2A{C^2}$, we know the formula
$\cos C = \dfrac{{A{C^2} + B{C^2} - A{B^2}}}{{2\left( {AC} \right)\left( {BC} \right)}}$
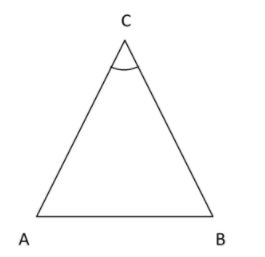
Now take
$
AC = BC = a \\
A{B^2} = 2{\left( {AC} \right)^2} = 2{a^2} \\
AB = \sqrt 2 a \\
\\
$
$
\cos C = \dfrac{{{a^2} + {a^2} - 2{a^2}}}{{2a \times a}} \\
\cos C = \dfrac{{2{a^2} - 2{a^2}}}{{2{a^2}}} \\
\cos C = 0 \\
C = {90^ \circ } \\
$
Complete step-by-step answer:
First of all, draw the sketch of $\vartriangle ABC$ and note down the condition given in the question.

According to question, it is saying that sides $AC = BC$ (1)
And $A{B^2} = 2A{C^2}$ (2)
Now drop a perpendicular from C to AB that meets AB at D.

Hence, we draw perpendicular from C to AB and hence,
$\angle CDA = \angle CDB = {90^ \circ }$
Now you can check and compare the two triangles ,i.e., $\vartriangle ADC$ and $\vartriangle BDC$
We can check the congruence of both the triangles. So,
In $\vartriangle ADC$ and $\vartriangle BDC$
$AC = BC$ (As it is given in the question)
$\angle ADC = \angle BDC$ (Both are equal to ${90^ \circ }$as we drop the perpendicular from C to AB)
$CD = CD$ (Both are common for both the triangle)
Hence, both triangles are congruent by RHS congruence property.
$\vartriangle ADC \cong \vartriangle BDC$ (By RHS property)
Now from CPCT, (corresponding part of congruent triangle)
$AD = BD$ (3)
$\angle ACD = \angle BCD$ (4)
And $\angle CAD = \angle CBD$
(As we know, corresponding parts are equal for congruent triangle.)
Hence, we got $AD = BD$.
Hence, D is the mid point of AB.
So, we can write $AD = \dfrac{{AB}}{2}$ (5)
(As D bisects AB , so it is half of AB.)
Now lets see the $\vartriangle ADC$

As we know, $\angle D = {90^ \circ }$hence it is right angled triangle , hence can use trigonometric properties, i.e., $\sin \theta = \dfrac{{Perpendicular}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}$
$\sin \angle ACD = \dfrac{{AD}}{{AC}}$
But we already proved that $AD = \dfrac{{AB}}{2}$
So,
$\sin \angle ACD = \dfrac{{AB}}{{2AC}}$ (6)
Now, in question, you are given condition
$A{B^2} = 2A{C^2}$
Taking square root on both side,
$AB = \sqrt 2 AC$
Now putting $AB = \sqrt 2 AC$ in equation (6)
$
\sin \angle ACD = \dfrac{{\sqrt 2 AC}}{{2AC}} \\
= \dfrac{{\sqrt 2 }}{2} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} \\
$
And this is known that $\sin {45^ \circ } = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
Hence, you will get $\angle ACD = {45^ \circ }$
Now we have proved in equation (4)
$\angle ACD = \angle BCD = {45^ \circ }$
So,
$
\angle C = \angle ACD + \angle BCD \\
= {45^ \circ } + {45^ \circ } \\
= {90^ \circ } \\
$
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: You may use an alternative method to find angle to save your time. You know $AC = BC$ and $A{B^2} = 2A{C^2}$, we know the formula
$\cos C = \dfrac{{A{C^2} + B{C^2} - A{B^2}}}{{2\left( {AC} \right)\left( {BC} \right)}}$

Now take
$
AC = BC = a \\
A{B^2} = 2{\left( {AC} \right)^2} = 2{a^2} \\
AB = \sqrt 2 a \\
\\
$
$
\cos C = \dfrac{{{a^2} + {a^2} - 2{a^2}}}{{2a \times a}} \\
\cos C = \dfrac{{2{a^2} - 2{a^2}}}{{2{a^2}}} \\
\cos C = 0 \\
C = {90^ \circ } \\
$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





