
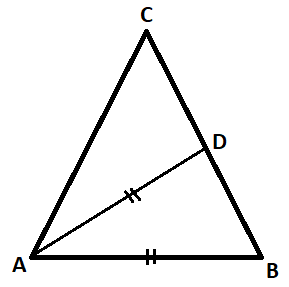
In an isosceles triangle $ABC,AC = BC,\angle BAC$ is bisected by AD where D lies on BC. It is found that AD = AB. Then $\angle ACB$ equals
A. ${72^ \circ }$
B. ${54^ \circ }$
C. ${36^ \circ }$
D. ${60^ \circ }$

Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: This is a simple problem, to solve this problem we have to know about some basic properties of triangles, such as properties of an isosceles triangle, which are any two sides of an isosceles triangle are equal and also the angles which are opposite to the equal sides are equal. One more important thing is that the sum of the angles in any triangle is equal to ${180^ \circ }.$
Complete step by step answer:
Here $\angle ACB = \angle C$ and
$\angle BAC = \angle A$
Given that the triangle ABC is an isosceles triangle. The sides AC is equal to BC, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow AC = BC$
Which means that the angles opposite to the sides AC and BC are also equal which is a property of an isosceles triangle.
$\therefore \angle A = \angle B$
Let $\angle A = \angle B = x$
Here given that the angle $\angle A$ is bisected by a line segment AD.
Now given that AD = AB, which means that now a new triangle ADB is formed which is also an isosceles triangle.
As the triangle ADB is an isosceles triangle, hence the angles opposite to the sides AD and AB are also equal, which are given below:
$ \Rightarrow \angle ADB = \angle B$
We know that $\angle B = x$
$\therefore \angle ADB = x$
Now given that the line segment AD bisects the angle $\angle A$, hence the angle $\angle DAB$ is given by:
$ \Rightarrow \angle DAB = \dfrac{{\angle A}}{2}$
$\because \angle A = x$
$\therefore \angle DAB = \dfrac{x}{2}$
Now every triangle should follow the property that the sum of the angles in a triangle should be equal to ${180^ \circ }$.
Consider the triangle ADB, the sum of angles in this triangle should sum up to give ${180^ \circ }$, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow \angle DAB + \angle B + \angle ADB = {180^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{2} + x + x = {180^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{5x}}{2} = {180^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow x = {72^ \circ }$
\[\therefore \angle A = \angle B = {72^ \circ }\]
Now consider the triangle ABC, the sum of all the angles in this triangle should be equal to ${180^ \circ }$.
$ \Rightarrow \angle A + \angle B + \angle C = {180^ \circ }$
\[ \Rightarrow {72^ \circ } + {72^ \circ } + \angle C = {180^ \circ }\]
\[ \Rightarrow \angle C = {180^ \circ } - {144^ \circ }\]
\[ \Rightarrow \angle C = {36^ \circ }\]
$\because \angle C = \angle ACB$
$\therefore \angle ACB = {36^ \circ }$
$\angle ACB$ equals ${36^ \circ }$.
Note: Here while solving this problem there is a slight chance of overlooking the given hint such as given that the sides AD and AB are equal in the triangle ADB. Here as it is given that AD and AB are equal, hence the angles opposite to the sides AD and AB are equal. This is an important and the most crucial step, as it leads to the rest of the process.
Complete step by step answer:
Here $\angle ACB = \angle C$ and
$\angle BAC = \angle A$
Given that the triangle ABC is an isosceles triangle. The sides AC is equal to BC, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow AC = BC$
Which means that the angles opposite to the sides AC and BC are also equal which is a property of an isosceles triangle.
$\therefore \angle A = \angle B$
Let $\angle A = \angle B = x$
Here given that the angle $\angle A$ is bisected by a line segment AD.
Now given that AD = AB, which means that now a new triangle ADB is formed which is also an isosceles triangle.
As the triangle ADB is an isosceles triangle, hence the angles opposite to the sides AD and AB are also equal, which are given below:
$ \Rightarrow \angle ADB = \angle B$
We know that $\angle B = x$
$\therefore \angle ADB = x$
Now given that the line segment AD bisects the angle $\angle A$, hence the angle $\angle DAB$ is given by:
$ \Rightarrow \angle DAB = \dfrac{{\angle A}}{2}$
$\because \angle A = x$
$\therefore \angle DAB = \dfrac{x}{2}$
Now every triangle should follow the property that the sum of the angles in a triangle should be equal to ${180^ \circ }$.
Consider the triangle ADB, the sum of angles in this triangle should sum up to give ${180^ \circ }$, as given below:
$ \Rightarrow \angle DAB + \angle B + \angle ADB = {180^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{2} + x + x = {180^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{5x}}{2} = {180^ \circ }$
$ \Rightarrow x = {72^ \circ }$
\[\therefore \angle A = \angle B = {72^ \circ }\]
Now consider the triangle ABC, the sum of all the angles in this triangle should be equal to ${180^ \circ }$.
$ \Rightarrow \angle A + \angle B + \angle C = {180^ \circ }$
\[ \Rightarrow {72^ \circ } + {72^ \circ } + \angle C = {180^ \circ }\]
\[ \Rightarrow \angle C = {180^ \circ } - {144^ \circ }\]
\[ \Rightarrow \angle C = {36^ \circ }\]
$\because \angle C = \angle ACB$
$\therefore \angle ACB = {36^ \circ }$
$\angle ACB$ equals ${36^ \circ }$.
Note: Here while solving this problem there is a slight chance of overlooking the given hint such as given that the sides AD and AB are equal in the triangle ADB. Here as it is given that AD and AB are equal, hence the angles opposite to the sides AD and AB are equal. This is an important and the most crucial step, as it leads to the rest of the process.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




