
In an experiment on photoelectric effect the frequency $v$ of the incident light is plotted against the stopping potential ${V_o}$. Work function of the photoelectric surface is given by(whereas e is electric charge)
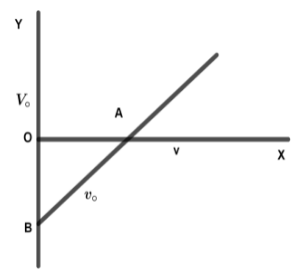
A. $OB \times e$ in $eV$
B. $OB$ in volt
C. $OA$ in $eV$
D. The slope of the line $AB$

Answer
521.7k+ views
Hint: Photoelectric impact is that the emission of electrons. Electronic devices specialised for light detection. For example, when light shines on a metal, electrons can be ejected from the surface of the metal in development.
Complete step by step answer:
From photoelectric impact,
${V_o} = \dfrac{{hv}}{e} - \dfrac{w}{e}$
Assume, $y = mx + c$
Here the worth of c is, $c = - \dfrac{w}{e}$
If c intersects in OB then,
$ - OB = - \dfrac{w}{e}$
Then we have tendency to get, the work operate
$\therefore w = OB \times e$ in volt
Hence the given operation of the electric potential surface is evidenced.
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Additional information: Photoelectric impact was first determined in 1887 by scientist Heinrich Hertz. Once continuous analysis during this field, Albert Einstein gave its palmy clarification. Photo emission is the instantaneous process. Most mechanical energy doesn't rely on the intensity of light. In 1905 Einstein extended planck's hypothesis to clarify the photoelectric effect. Photoelectric current is proportional to the intensity of light. Energy of a photon is equal to work function and maximum kinetic energy of the electron.
Note: In photoelectric impact ejected electrons are a unit known as photoelectrons. The kinetic energy of light remains constant once light amplitude will increases. Some options were explained by the classic theory of magnetic force waves. In the photoelectric equation, E is a work function and h is Planck's constant. Once it’s light by monochromatic radiation, then the target material serves as anode.
Complete step by step answer:
From photoelectric impact,
${V_o} = \dfrac{{hv}}{e} - \dfrac{w}{e}$
Assume, $y = mx + c$
Here the worth of c is, $c = - \dfrac{w}{e}$
If c intersects in OB then,
$ - OB = - \dfrac{w}{e}$
Then we have tendency to get, the work operate
$\therefore w = OB \times e$ in volt
Hence the given operation of the electric potential surface is evidenced.
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Additional information: Photoelectric impact was first determined in 1887 by scientist Heinrich Hertz. Once continuous analysis during this field, Albert Einstein gave its palmy clarification. Photo emission is the instantaneous process. Most mechanical energy doesn't rely on the intensity of light. In 1905 Einstein extended planck's hypothesis to clarify the photoelectric effect. Photoelectric current is proportional to the intensity of light. Energy of a photon is equal to work function and maximum kinetic energy of the electron.
Note: In photoelectric impact ejected electrons are a unit known as photoelectrons. The kinetic energy of light remains constant once light amplitude will increases. Some options were explained by the classic theory of magnetic force waves. In the photoelectric equation, E is a work function and h is Planck's constant. Once it’s light by monochromatic radiation, then the target material serves as anode.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




