
In an equilateral triangle of side $ 2\sqrt{3} $ cm, the circum-radius is?
(a) 1 cm
(b) $ \sqrt{3} $ cm
(c) 2 cm
(d) $ 2\sqrt{3} $ cm
Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint: Here, we will draw the angular bisectors and then take any one of the triangles formed to find the circumradius of the given equilateral triangle. We will calculate the circumradius using the formula for the cosine of an angle, that is $ \cos \theta =\dfrac{base}{hypotenuse} $ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
The circumcircle is a triangle’s circumscribed circle, i.e., the unique circle that passes through each of the triangle’s three vertices. The centre of the circumcircle is called the circumcenter and the radius of the circle is called the circumradius.
So, first of all we will draw angular bisectors from each angle of the triangle, we will then observe that these bisectors meet at a point inside the triangle which is the circumcentre. These bisectors will cut the triangle into three equal triangles and each bisector will serve as the radius of the circumcircle. Then, by taking one of these triangles we can easily find the circumradius.
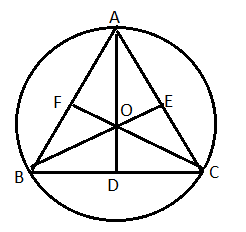
The angular bisectors of angles A, B and C are AD, BE and CF respectively. O is the circumcentre.
In an equilateral triangle, the angular bisector from any of the angles bisect the other side and is perpendicular to it.
So, we can say that AD bisects BC and $ \angle ADC={{90}^{0}} $ .
So, we have BD=DC
Since, $ BD+DC=BC=2\sqrt{3}\text{ cm} $
$ \begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 2DC=2\sqrt{3}\text{ cm} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{DC=}\sqrt{3}\text{ cm} \\
\end{align} $
Let us consider the triangle ODC.
Since, CF is the bisector of angle C, the angle OCD is equal to half of angle ACB, i.e., $ \angle OCD=\dfrac{1}{2}\angle ACB $
Since, each angle of the equilateral triangle is = $ {{60}^{0}} $
$ \Rightarrow \angle OCD=\dfrac{1}{2}\times {{60}^{0}}={{30}^{0}} $
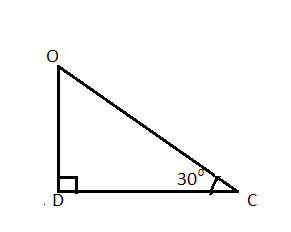
We have to find the length of OC, that is, the circumradius.
In triangle OCD:
$ \cos C=\dfrac{CD}{OC} $
Since, we have $ CD=\sqrt{3}\text{ cm} $ and $ \angle C={{30}^{0}} $ .
$ \begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cos {{30}^{0}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{OC} \\
& \Rightarrow OC=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{\cos {{30}^{0}}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)}=\sqrt{3}\times \dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}=2\text{ cm} \\
\end{align} $
Hence, option (c) is the correct answer.
Note: Students should observe that since in triangle ODC, we know the length of CD, so we will apply the formula for the cosine of an angle. If by mistake we use sine instead of cosine then it will give us the wrong result.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The circumcircle is a triangle’s circumscribed circle, i.e., the unique circle that passes through each of the triangle’s three vertices. The centre of the circumcircle is called the circumcenter and the radius of the circle is called the circumradius.
So, first of all we will draw angular bisectors from each angle of the triangle, we will then observe that these bisectors meet at a point inside the triangle which is the circumcentre. These bisectors will cut the triangle into three equal triangles and each bisector will serve as the radius of the circumcircle. Then, by taking one of these triangles we can easily find the circumradius.

The angular bisectors of angles A, B and C are AD, BE and CF respectively. O is the circumcentre.
In an equilateral triangle, the angular bisector from any of the angles bisect the other side and is perpendicular to it.
So, we can say that AD bisects BC and $ \angle ADC={{90}^{0}} $ .
So, we have BD=DC
Since, $ BD+DC=BC=2\sqrt{3}\text{ cm} $
$ \begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 2DC=2\sqrt{3}\text{ cm} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{DC=}\sqrt{3}\text{ cm} \\
\end{align} $
Let us consider the triangle ODC.
Since, CF is the bisector of angle C, the angle OCD is equal to half of angle ACB, i.e., $ \angle OCD=\dfrac{1}{2}\angle ACB $
Since, each angle of the equilateral triangle is = $ {{60}^{0}} $
$ \Rightarrow \angle OCD=\dfrac{1}{2}\times {{60}^{0}}={{30}^{0}} $

We have to find the length of OC, that is, the circumradius.
In triangle OCD:
$ \cos C=\dfrac{CD}{OC} $
Since, we have $ CD=\sqrt{3}\text{ cm} $ and $ \angle C={{30}^{0}} $ .
$ \begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cos {{30}^{0}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{OC} \\
& \Rightarrow OC=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{\cos {{30}^{0}}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)}=\sqrt{3}\times \dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}=2\text{ cm} \\
\end{align} $
Hence, option (c) is the correct answer.
Note: Students should observe that since in triangle ODC, we know the length of CD, so we will apply the formula for the cosine of an angle. If by mistake we use sine instead of cosine then it will give us the wrong result.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




