
In an elevator moving vertically up with an acceleration ‘ $ g $ ’, the force exerted on the floor by a passenger of mass $ M $ is-
A. $ Mg $
B. $ \dfrac{1}{2}Mg $
C. zero
D. $ 2Mg $
Answer
497.7k+ views
Hint: Apply Newton’s Third law of Motion- Every action has an equal and opposite reaction. In a system, if the weight of the object acts downward a Normal Reaction force acts on the object in the opposite direction (upwards) with the same magnitude. Normal reaction force acts perpendicularly into two surfaces when they are in contact.
Complete step by step answer:
Free Body Diagram- It is a diagrammatic representation used to visualize the applied forces, acceleration and resulting reaction force on a body in a given situation.
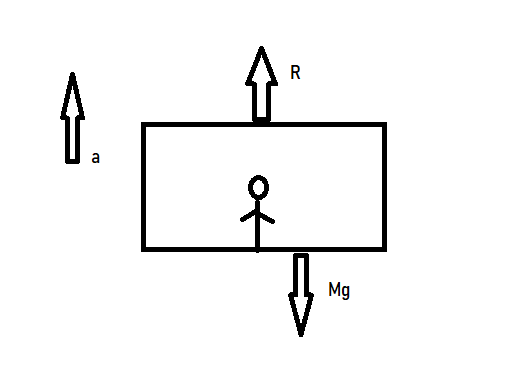
$ R = $ Normal Reaction force exerted by elevator floor which acts upward.
$ a = $ acceleration with which the elevator is moving in an upward direction.
$ Mg = $ weight of the passenger. $ M $ is the mass of the passenger and $ g $ is the acceleration due to gravity. The weight of the passenger acts in the downward direction.
Using Newton’s Second Law- rate of change of momentum of a body is directly proportional to the force applied on it.
We get,
$ {F_{net}} = Ma $
$ R - Mg = Ma $
Given the acceleration $ a = g $ ,
$ R - Mg = Mg $
$ \Rightarrow R = 2Mg $
Option D. $ 2Mg $ is correct.
Note:
The mass of the elevator is not taken into account here. If the elevator moves upwards the passenger feels heavier, if the elevator moves downwards the passenger feels lighter and if the cable of the elevator breaks down the passenger feels weightless since both the passenger and elevator will move downwards with same acceleration.
Complete step by step answer:
Free Body Diagram- It is a diagrammatic representation used to visualize the applied forces, acceleration and resulting reaction force on a body in a given situation.

$ R = $ Normal Reaction force exerted by elevator floor which acts upward.
$ a = $ acceleration with which the elevator is moving in an upward direction.
$ Mg = $ weight of the passenger. $ M $ is the mass of the passenger and $ g $ is the acceleration due to gravity. The weight of the passenger acts in the downward direction.
Using Newton’s Second Law- rate of change of momentum of a body is directly proportional to the force applied on it.
We get,
$ {F_{net}} = Ma $
$ R - Mg = Ma $
Given the acceleration $ a = g $ ,
$ R - Mg = Mg $
$ \Rightarrow R = 2Mg $
Option D. $ 2Mg $ is correct.
Note:
The mass of the elevator is not taken into account here. If the elevator moves upwards the passenger feels heavier, if the elevator moves downwards the passenger feels lighter and if the cable of the elevator breaks down the passenger feels weightless since both the passenger and elevator will move downwards with same acceleration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




