
In Allene (\[{{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}\]), the type(s) of hybridization of the carbon atoms is (are)?
A sp and \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}\]
B sp and \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}\]
C only \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}\]
D \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}\]and \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}\]
Answer
601.8k+ views
Hint:
The atomic orbitals of an atom combine with each other to form a new set of hybrid orbitals, which are more prominent to bonding with upcoming elements. This process of forming new hybrid orbitals is called hybridization. Hybridization also defines the structure of the molecules. For a specific hybridization there is a specific structure of the molecules. Which is called molecular geometry.
Formula used: \[H = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {V + X - C + A} \right]\]
Complete step by step answer:
Allene is an organic compound ,where every carbon atom are bounded with another carbon atom with double bond. These compounds are also called cumulated dienes. The structure of the simplest allene is shown below.
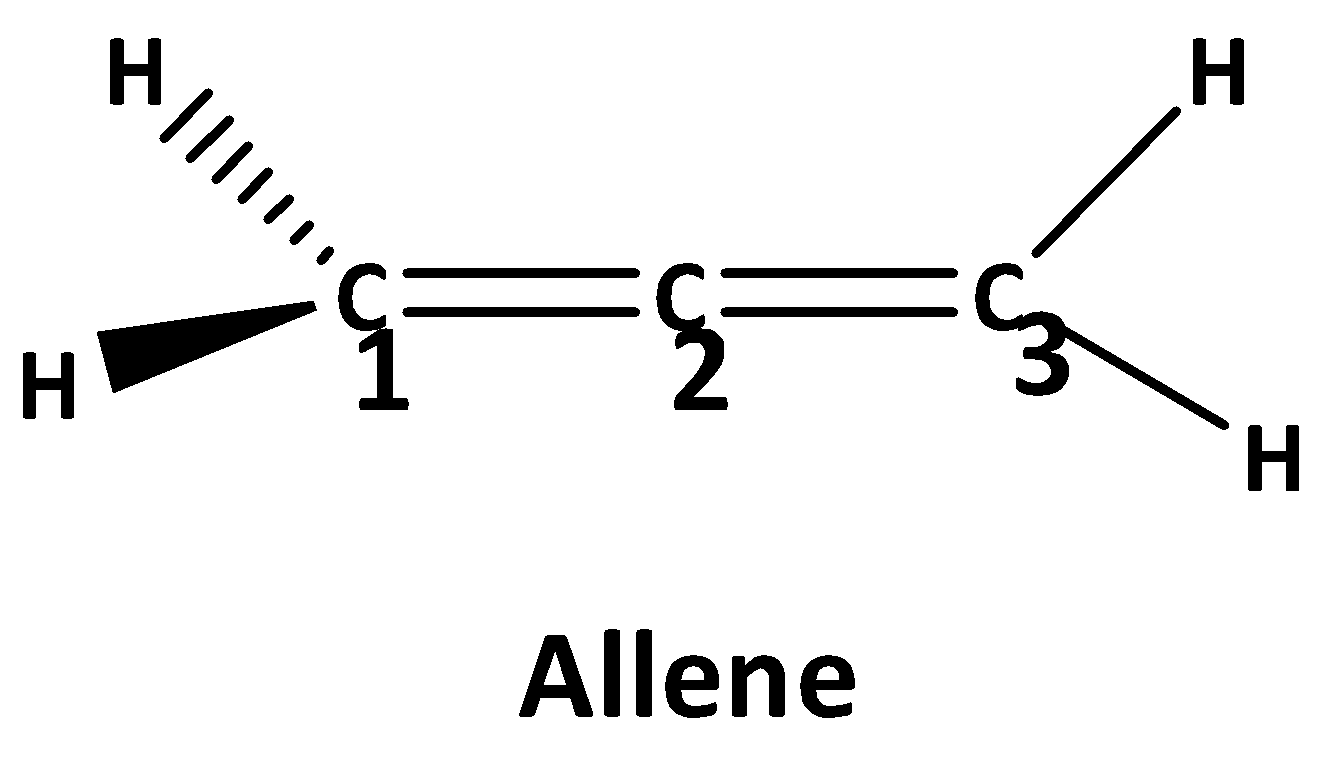
The formula to calculate the hybridization of the central molecule is, \[H = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {V + X - C + A} \right]\]. where V is the number of valence electrons of the central atom, X is the number of monovalent atoms attached to the central atom, C is the total cationic charge and A is the total anionic charge.
Now for allene \[{{\text{c}}_1}\] carbon hybridization is,
\[
H = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {V + X - C + A} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {4 + 2 - 0 + 0} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ 6 \right] \\
= 3 \\
\]
For H=3 hybridization is \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}\].
Now for allene \[{{\text{c}}_2}\] carbon hybridization is,
\[
H = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {V + X - C + A} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {4 + 0 - 0 + 0} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2} \times 4 \\
= 2 \\
\]
For H=2 hybridization is\[{\text{sp}}\].
Now for allene \[{{\text{c}}_3}\] carbon hybridization is,
\[
H = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {V + X - C + A} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {4 + 2 - 0 + 0} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ 6 \right] \\
= 3 \\
\]
For H=3 hybridization is \[s{p^2}\].
Therefore the hybridizations of allene is \[{\text{sp}}\] and \[s{p^2}\].
The correct option is, B.
Note: Atomic orbitals of an atom combine with each other to form a new set of hybrid orbitals, which are more prominent to bonding with upcoming elements. This process of forming new hybrid orbitals is called hybridization.
The atomic orbitals of an atom combine with each other to form a new set of hybrid orbitals, which are more prominent to bonding with upcoming elements. This process of forming new hybrid orbitals is called hybridization. Hybridization also defines the structure of the molecules. For a specific hybridization there is a specific structure of the molecules. Which is called molecular geometry.
Formula used: \[H = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {V + X - C + A} \right]\]
Complete step by step answer:
Allene is an organic compound ,where every carbon atom are bounded with another carbon atom with double bond. These compounds are also called cumulated dienes. The structure of the simplest allene is shown below.

The formula to calculate the hybridization of the central molecule is, \[H = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {V + X - C + A} \right]\]. where V is the number of valence electrons of the central atom, X is the number of monovalent atoms attached to the central atom, C is the total cationic charge and A is the total anionic charge.
Now for allene \[{{\text{c}}_1}\] carbon hybridization is,
\[
H = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {V + X - C + A} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {4 + 2 - 0 + 0} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ 6 \right] \\
= 3 \\
\]
For H=3 hybridization is \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}\].
Now for allene \[{{\text{c}}_2}\] carbon hybridization is,
\[
H = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {V + X - C + A} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {4 + 0 - 0 + 0} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2} \times 4 \\
= 2 \\
\]
For H=2 hybridization is\[{\text{sp}}\].
Now for allene \[{{\text{c}}_3}\] carbon hybridization is,
\[
H = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {V + X - C + A} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {4 + 2 - 0 + 0} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ 6 \right] \\
= 3 \\
\]
For H=3 hybridization is \[s{p^2}\].
Therefore the hybridizations of allene is \[{\text{sp}}\] and \[s{p^2}\].
The correct option is, B.
Note: Atomic orbitals of an atom combine with each other to form a new set of hybrid orbitals, which are more prominent to bonding with upcoming elements. This process of forming new hybrid orbitals is called hybridization.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




