
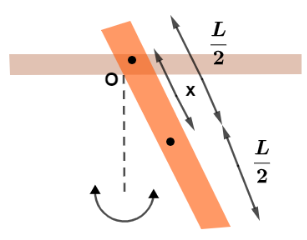
In above figure, a stick of length $L = 1.85\,m$ oscillates as a physical pendulum. (a) What value of distance $x$ between the stick's center of mass and pivot point O gives the least period? (b) What is the least period?

Answer
499.8k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question we need to understand center of mass. Center of mass is a position of a system where all the mass can be concentrated and the system could be analyzed at one point. Here, we will use the general formula of time period for compound pendulum and using the concept of moment of inertia in different cases for a given situation of stick, we will determine the value of x and the least time period of stick.
Complete step by step answer:
Here the rod can be treated as a compound pendulum, so we apply the compound pendulum formula to get the time period of the rod.Let $m$ be the mass of the rod and “l” be its length of rod.Also let the angular velocity of rod be $\omega $.So from the compound pendulum formula we know, $\omega = \sqrt {\dfrac{{mgx}}{I}} $. Here, $I$ is the moment of inertia of rod about the pivot point and “x” is distance of COM from pivot point O.
(a) So the time period of rod is given as, $T = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }$
Putting values we get, $T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{I}{{mgx}}} $
Since “I” is the moment of inertia of rod about pivot point O, so it is given from parallel axis theorem as, $I = {I_{COM}} + {I_x}$
Here, ${I_{COM}}$ is the moment of inertia of rod about center of mass and it is given as, ${I_{COM}} = \dfrac{{m{l^2}}}{{12}}$
And ${I_x}$ is the moment of inertia of rod due to length “x” of COM from pivot point O and is given as, ${I_x} = m{x^2}$
Putting values we get, $I = \dfrac{{m{l^2}}}{{12}} + m{x^2}$
Putting value of $I$ in time period we get, $T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{{m(\dfrac{{{l^2}}}{{12}} + {x^2})}}{{mgx}}} $
$T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{{({l^2} + 12{x^2})}}{{12gx}}} \to (i)$
Now to minimize T we need to differentiate it w.r.t “x” and put it equal to zero, but it is difficult to differentiate $T$ so we differentiate ${T^2}$ in order to minimize T.
So ${T^2} = {(2\pi )^2}\dfrac{{{{({l^2} + 12{x^2})}^2}}}{{{{(12g)}^2}{x^2}}}$
Let ${T^2} = P$ so $P = {(2\pi )^2}\dfrac{{{{({l^2} + 12{x^2})}^2}}}{{{{(12g)}^2}{x^2}}}$
So differentiating P with respect to “x” we get, $\dfrac{{dP}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{{{(2\pi )}^2}}}{{{{(12g)}^2}}}\dfrac{d}{{dx}}(\dfrac{{{{({l^2} + 12{x^2})}^2}}}{{{x^2}}}$
Using Differentiation rule of $(\dfrac{u}{v})' = \dfrac{{vu' - uv'}}{{{v^2}}}$ where u, v are the functions to be differentiated.
$\dfrac{{dP}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{{{(2\pi )}^2}}}{{{{(12g)}^2}}}[\dfrac{{\{ {x^2}(24x) \times 2 \times ({l^2} + 12{x^2})\} - \{ ({l^2} + 12{x^2}) \times 2x\} }}{{{x^4}}}]$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dP}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{{{(2\pi )}^2}}}{{{{(12g)}^2}}}\dfrac{{2x({l^2} + 12{x^2})\{ 24{x^2} - ({l^2} + 12{x^2})\} }}{{{x^4}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dP}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{{{(2\pi )}^2}}}{{{{(12g)}^2}}}\dfrac{{2({l^2} + 12{x^2})\{ 12{x^2} - {l^2}\} }}{{{x^3}}}$
Now to minimize this function we need to put it equal to zero we get,
$\dfrac{{dP}}{{dx}} = 0$
Putting value we get,
$\dfrac{{{{(2\pi )}^2}}}{{{{(12g)}^2}}}\dfrac{{2({l^2} + 12{x^2})\{ 12{x^2} - {l^2}\} }}{{{x^3}}} = 0$
Since denominator and constant both cannot be zero so,
$12{x^2} - {l^2} = 0$
$\Rightarrow {x^2} = \dfrac{{{l^2}}}{{12}}$
$\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{l}{{\sqrt {12} }}$
$\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{1.85}}{{\sqrt {12} }}$
$\Rightarrow x = 0.53\,m$
Therefore, the minimum value of “x” is, $x = 0.53\,m$.
(b) we put the minimum value of “x” in equation (i) to get minimum value of T we get,
$T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{{({{\{ 1.85\} }^2} + 12{{\{ 0.53\} }^2})}}{{12(9.8)(0.53)}}} $
Here, $l = 1.85m$
$x = 0.53m$ And $g = 9.8m{s^{ - 2}}$
So time period is $T = 2\pi \times 0.3301\sec $
$\therefore T = 2.074\sec $
So minimum time period required is, $T = 2.074\sec $.
Note: It should be remembered that moment of inertia is defined as the product of mass and square of distance from the axis of rotation. And compound pendulums are such pendulums in which mass is distributed in length, surface area or volume of object. So here you see that center of mass is useful in identifying the locus of objects and its motion.
Complete step by step answer:
Here the rod can be treated as a compound pendulum, so we apply the compound pendulum formula to get the time period of the rod.Let $m$ be the mass of the rod and “l” be its length of rod.Also let the angular velocity of rod be $\omega $.So from the compound pendulum formula we know, $\omega = \sqrt {\dfrac{{mgx}}{I}} $. Here, $I$ is the moment of inertia of rod about the pivot point and “x” is distance of COM from pivot point O.
(a) So the time period of rod is given as, $T = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }$
Putting values we get, $T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{I}{{mgx}}} $
Since “I” is the moment of inertia of rod about pivot point O, so it is given from parallel axis theorem as, $I = {I_{COM}} + {I_x}$
Here, ${I_{COM}}$ is the moment of inertia of rod about center of mass and it is given as, ${I_{COM}} = \dfrac{{m{l^2}}}{{12}}$
And ${I_x}$ is the moment of inertia of rod due to length “x” of COM from pivot point O and is given as, ${I_x} = m{x^2}$
Putting values we get, $I = \dfrac{{m{l^2}}}{{12}} + m{x^2}$
Putting value of $I$ in time period we get, $T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{{m(\dfrac{{{l^2}}}{{12}} + {x^2})}}{{mgx}}} $
$T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{{({l^2} + 12{x^2})}}{{12gx}}} \to (i)$
Now to minimize T we need to differentiate it w.r.t “x” and put it equal to zero, but it is difficult to differentiate $T$ so we differentiate ${T^2}$ in order to minimize T.
So ${T^2} = {(2\pi )^2}\dfrac{{{{({l^2} + 12{x^2})}^2}}}{{{{(12g)}^2}{x^2}}}$
Let ${T^2} = P$ so $P = {(2\pi )^2}\dfrac{{{{({l^2} + 12{x^2})}^2}}}{{{{(12g)}^2}{x^2}}}$
So differentiating P with respect to “x” we get, $\dfrac{{dP}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{{{(2\pi )}^2}}}{{{{(12g)}^2}}}\dfrac{d}{{dx}}(\dfrac{{{{({l^2} + 12{x^2})}^2}}}{{{x^2}}}$
Using Differentiation rule of $(\dfrac{u}{v})' = \dfrac{{vu' - uv'}}{{{v^2}}}$ where u, v are the functions to be differentiated.
$\dfrac{{dP}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{{{(2\pi )}^2}}}{{{{(12g)}^2}}}[\dfrac{{\{ {x^2}(24x) \times 2 \times ({l^2} + 12{x^2})\} - \{ ({l^2} + 12{x^2}) \times 2x\} }}{{{x^4}}}]$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dP}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{{{(2\pi )}^2}}}{{{{(12g)}^2}}}\dfrac{{2x({l^2} + 12{x^2})\{ 24{x^2} - ({l^2} + 12{x^2})\} }}{{{x^4}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{dP}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{{{{(2\pi )}^2}}}{{{{(12g)}^2}}}\dfrac{{2({l^2} + 12{x^2})\{ 12{x^2} - {l^2}\} }}{{{x^3}}}$
Now to minimize this function we need to put it equal to zero we get,
$\dfrac{{dP}}{{dx}} = 0$
Putting value we get,
$\dfrac{{{{(2\pi )}^2}}}{{{{(12g)}^2}}}\dfrac{{2({l^2} + 12{x^2})\{ 12{x^2} - {l^2}\} }}{{{x^3}}} = 0$
Since denominator and constant both cannot be zero so,
$12{x^2} - {l^2} = 0$
$\Rightarrow {x^2} = \dfrac{{{l^2}}}{{12}}$
$\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{l}{{\sqrt {12} }}$
$\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{1.85}}{{\sqrt {12} }}$
$\Rightarrow x = 0.53\,m$
Therefore, the minimum value of “x” is, $x = 0.53\,m$.
(b) we put the minimum value of “x” in equation (i) to get minimum value of T we get,
$T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{{({{\{ 1.85\} }^2} + 12{{\{ 0.53\} }^2})}}{{12(9.8)(0.53)}}} $
Here, $l = 1.85m$
$x = 0.53m$ And $g = 9.8m{s^{ - 2}}$
So time period is $T = 2\pi \times 0.3301\sec $
$\therefore T = 2.074\sec $
So minimum time period required is, $T = 2.074\sec $.
Note: It should be remembered that moment of inertia is defined as the product of mass and square of distance from the axis of rotation. And compound pendulums are such pendulums in which mass is distributed in length, surface area or volume of object. So here you see that center of mass is useful in identifying the locus of objects and its motion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




