
In a Wheatstone's bridge all the four arms have equal resistance R. If the resistance of the galvanometer arm is also R, the equivalent resistance of the combination is?
Answer
594k+ views
Hint-: We need to find the equivalent resistance using series and parallel combination series.
Complete step by step solution:
Given, In a Wheatstone's bridge all the four arms have equal resistance R. If the resistance of the galvanometer arm is also R.
In the balanced condition of Wheatstone's bridge there will be no current flowing through the arms.
As all the four arms have equal resistance R so it is a balanced $\left( {\dfrac{P}{Q} = \dfrac{R}{S}} \right)$ Wheatstone bridge circuit. Thus, as per condition no current flows in the galvanometer arm and its resistance will not work. Let us find the equivalent resistance.
The equivalent resistance is
$\eqalign{
& {R_{AB}} = \dfrac{{(R + R) + (R + R)}}{{(R + R) + (R + R)}} \cr
& \;\;\;\;\;\;{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{4{R^2}}}{{4R}} \cr
& \;\;\;\;\;\; = R \cr} $
The diagram below shows the equivalent resistance,
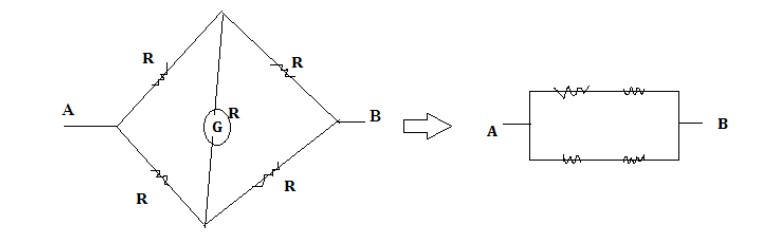
Additional information:
A Wheatstone bridge is an electrical circuit that is used to measure an unknown electrical resistance by balancing the two legs of a bridge circuit, one leg of which includes the unknown component.
The Wheatstone bridge is in balanced condition when no current flows through the coil and the potential difference across the galvanometer is zero. This condition occurs when the potential difference across the a to b and a to d are equal, and the potential differences across the b to c and c to d remain the same.
Note: A student needs to remember that in the balanced condition of Wheatstone's bridge there will be no current flowing.
Complete step by step solution:
Given, In a Wheatstone's bridge all the four arms have equal resistance R. If the resistance of the galvanometer arm is also R.
In the balanced condition of Wheatstone's bridge there will be no current flowing through the arms.
As all the four arms have equal resistance R so it is a balanced $\left( {\dfrac{P}{Q} = \dfrac{R}{S}} \right)$ Wheatstone bridge circuit. Thus, as per condition no current flows in the galvanometer arm and its resistance will not work. Let us find the equivalent resistance.
The equivalent resistance is
$\eqalign{
& {R_{AB}} = \dfrac{{(R + R) + (R + R)}}{{(R + R) + (R + R)}} \cr
& \;\;\;\;\;\;{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{4{R^2}}}{{4R}} \cr
& \;\;\;\;\;\; = R \cr} $
The diagram below shows the equivalent resistance,

Additional information:
A Wheatstone bridge is an electrical circuit that is used to measure an unknown electrical resistance by balancing the two legs of a bridge circuit, one leg of which includes the unknown component.
The Wheatstone bridge is in balanced condition when no current flows through the coil and the potential difference across the galvanometer is zero. This condition occurs when the potential difference across the a to b and a to d are equal, and the potential differences across the b to c and c to d remain the same.
Note: A student needs to remember that in the balanced condition of Wheatstone's bridge there will be no current flowing.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




