
In a \[\vartriangle ABC\] AD is perpendicular to BC. And \[A{D^2} = BD \times CD\]. Prove that \[\vartriangle ABC\] is a right triangle.
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: To prove this situation, we will draw a triangle and will show the conditions given in it. Then we will use Pythagoras theorem to prove that the given triangle is a right angle at vertex A such that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of the two sides of the same triangle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
To prove: \[\vartriangle ABC\] is a right angle triangle.
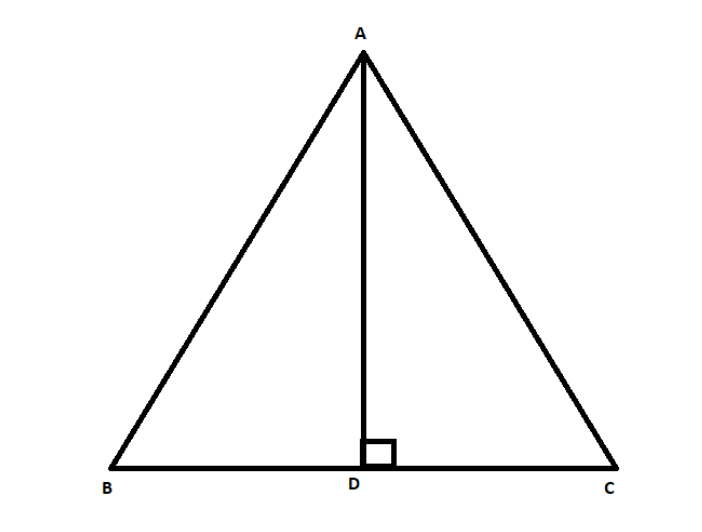
Consider the triangle drawn above. As per the given data AD is perpendicular to BC at D.
Now we will start to prove the statement that the given triangle is right at vertex A.
Consider \[\vartriangle ADB\& \vartriangle ADC\],
Using the given data that AD is perpendicular to BC at D we can use the Pythagoras theorem for the two triangles above.
\[A{B^2} = A{D^2} + B{D^2}\] …..equation1
\[A{C^2} = A{D^2} + C{D^2}\] …..equation2
On adding the equation we get,
\[A{B^2} + A{C^2} = A{D^2} + A{D^2} + B{D^2} + C{D^2}\]
Add the same terms,
\[A{B^2} + A{C^2} = 2A{D^2} + B{D^2} + C{D^2}\]
But it is given that \[A{D^2} = BD \times CD\]
So replacing the value of AD in the equation above,
\[A{B^2} + A{C^2} = 2\left( {BD \times CD} \right) + B{D^2} + C{D^2}\]
Now we can observe the above terms on RHS as,
\[A{B^2} + A{C^2} = B{D^2} + 2\left( {BD \times CD} \right) + C{D^2}\]
It is a perfect square,
\[A{B^2} + A{C^2} = {\left( {BD + CD} \right)^2}\]
And from the diagram above we can say that \[BD + CD = BC\]
So we will substitute this value and then,
\[A{B^2} + A{C^2} = B{C^2}\]
And thus this states that the square of one side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides. And thus the given triangle is a right angle triangle.
Note: Here note that the theorem that is related closely to right angles and right-angle triangles is used as the method to solve it. In a right angle we can say that Pythagora's theorem definitely fits. So just use it!
Complete step-by-step answer:
To prove: \[\vartriangle ABC\] is a right angle triangle.

Consider the triangle drawn above. As per the given data AD is perpendicular to BC at D.
Now we will start to prove the statement that the given triangle is right at vertex A.
Consider \[\vartriangle ADB\& \vartriangle ADC\],
Using the given data that AD is perpendicular to BC at D we can use the Pythagoras theorem for the two triangles above.
\[A{B^2} = A{D^2} + B{D^2}\] …..equation1
\[A{C^2} = A{D^2} + C{D^2}\] …..equation2
On adding the equation we get,
\[A{B^2} + A{C^2} = A{D^2} + A{D^2} + B{D^2} + C{D^2}\]
Add the same terms,
\[A{B^2} + A{C^2} = 2A{D^2} + B{D^2} + C{D^2}\]
But it is given that \[A{D^2} = BD \times CD\]
So replacing the value of AD in the equation above,
\[A{B^2} + A{C^2} = 2\left( {BD \times CD} \right) + B{D^2} + C{D^2}\]
Now we can observe the above terms on RHS as,
\[A{B^2} + A{C^2} = B{D^2} + 2\left( {BD \times CD} \right) + C{D^2}\]
It is a perfect square,
\[A{B^2} + A{C^2} = {\left( {BD + CD} \right)^2}\]
And from the diagram above we can say that \[BD + CD = BC\]
So we will substitute this value and then,
\[A{B^2} + A{C^2} = B{C^2}\]
And thus this states that the square of one side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides. And thus the given triangle is a right angle triangle.
Note: Here note that the theorem that is related closely to right angles and right-angle triangles is used as the method to solve it. In a right angle we can say that Pythagora's theorem definitely fits. So just use it!
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




