
In a triangle, the sum of lengths of two sides is x and the product of the lengths of the same two sides is y. If ${{x}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}=y$, where c is the length of the third side of the triangle, then the circumradius of the triangle is:
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: We start solving the problem by assuming the variable for the other two sides of the triangle and find the equations for x and y. We then substitute them in ${{x}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}=y$ and make necessary arrangements to resemble the formula of cosine rule $\cos C=\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}}{2ab}$. We then find the angle C and use the fact that the circumradius of the circle $R=\dfrac{a}{2\sin A}=\dfrac{b}{2\sin B}=\dfrac{c}{2\sin C}$ to find the required result.
Complete step-by-step answer:
According to the problem, we are given that the sum and product of the two sides of the triangle is x and y. We need to find the circumradius of the triangle If ${{x}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}=y$, where c is the length of the third side of the triangle.
Let us assume the other two sides of the triangle be a and b.
Let us draw the figure representing the given information.
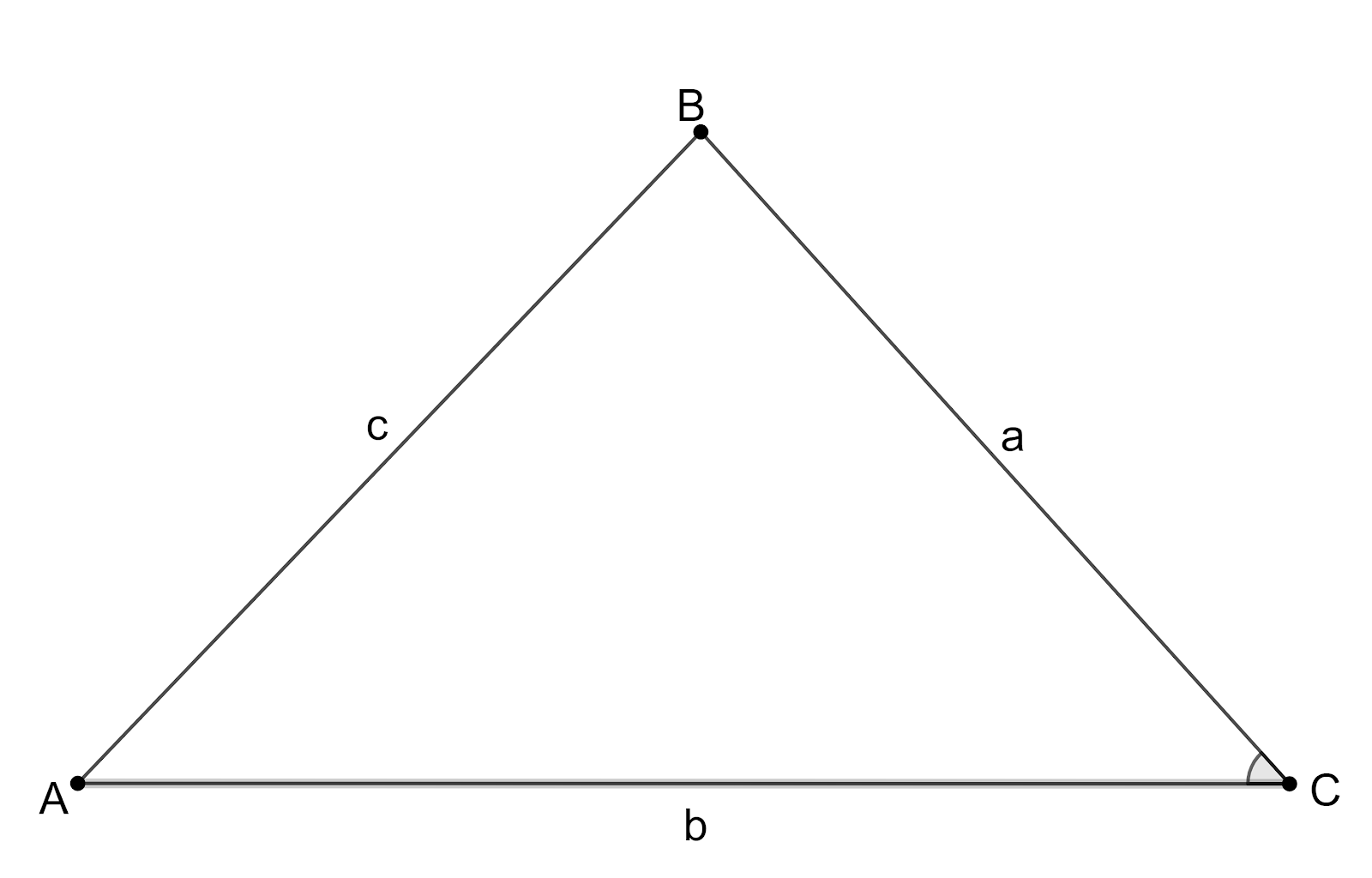
So, we have $x=a+b$ and $y=ab$.
According to the problem, we are given ${{x}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}=y$.
So, we get ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}=ab$.
$\Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+2ab-{{c}^{2}}=ab$.
$\Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}=-ab$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}}{ab}=-1$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}}{2ab}=\dfrac{-1}{2}$.
From cosine rule of a triangle, we know that $\cos C=\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}}{2ab}$, where C is angle at the vertex C.
So, we have $\cos C=\dfrac{-1}{2}$.
$\Rightarrow C={{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{2} \right)$.
We know that the angles in a triangle lies between 0 and $\pi $.
$\Rightarrow C=\dfrac{2\pi }{3}$.
We know that the angles in a triangle lies between 0 and $\pi $.
So, we have found the angle at the vertex C as $\dfrac{2\pi }{3}$.
We know that the circumradius of the triangle ABC is defined as $R=\dfrac{a}{2\sin A}=\dfrac{b}{2\sin B}=\dfrac{c}{2\sin C}$.
We get circumradius as $R=\dfrac{c}{2\sin \left( \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)}$.
$\Rightarrow R=\dfrac{c}{2\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)}$.
$\Rightarrow R=\dfrac{c}{\sqrt{3}}$.
So, we have found the radius of the circumcircle as $\dfrac{c}{\sqrt{3}}$ units.
∴ The radius of the circumcircle is $\dfrac{c}{\sqrt{3}}$ units.
Note: Whenever we get this type of problems, we try to fit the given equations into the form which resembles with cosine or sine rule. We should keep in mind that the angles present in the triangle lies between \[{{0}^{\circ }}\] and ${{180}^{\circ }}$. We can also find the area of this triangle using the fact that the area of triangle ABC is $A=\dfrac{abc}{4R}$. Similarly, we can expect problems to find the perimeter of the triangle and inradius of the triangle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
According to the problem, we are given that the sum and product of the two sides of the triangle is x and y. We need to find the circumradius of the triangle If ${{x}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}=y$, where c is the length of the third side of the triangle.
Let us assume the other two sides of the triangle be a and b.
Let us draw the figure representing the given information.

So, we have $x=a+b$ and $y=ab$.
According to the problem, we are given ${{x}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}=y$.
So, we get ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}=ab$.
$\Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+2ab-{{c}^{2}}=ab$.
$\Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}=-ab$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}}{ab}=-1$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}}{2ab}=\dfrac{-1}{2}$.
From cosine rule of a triangle, we know that $\cos C=\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}}{2ab}$, where C is angle at the vertex C.
So, we have $\cos C=\dfrac{-1}{2}$.
$\Rightarrow C={{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{2} \right)$.
We know that the angles in a triangle lies between 0 and $\pi $.
$\Rightarrow C=\dfrac{2\pi }{3}$.
We know that the angles in a triangle lies between 0 and $\pi $.
So, we have found the angle at the vertex C as $\dfrac{2\pi }{3}$.
We know that the circumradius of the triangle ABC is defined as $R=\dfrac{a}{2\sin A}=\dfrac{b}{2\sin B}=\dfrac{c}{2\sin C}$.
We get circumradius as $R=\dfrac{c}{2\sin \left( \dfrac{2\pi }{3} \right)}$.
$\Rightarrow R=\dfrac{c}{2\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)}$.
$\Rightarrow R=\dfrac{c}{\sqrt{3}}$.
So, we have found the radius of the circumcircle as $\dfrac{c}{\sqrt{3}}$ units.
∴ The radius of the circumcircle is $\dfrac{c}{\sqrt{3}}$ units.
Note: Whenever we get this type of problems, we try to fit the given equations into the form which resembles with cosine or sine rule. We should keep in mind that the angles present in the triangle lies between \[{{0}^{\circ }}\] and ${{180}^{\circ }}$. We can also find the area of this triangle using the fact that the area of triangle ABC is $A=\dfrac{abc}{4R}$. Similarly, we can expect problems to find the perimeter of the triangle and inradius of the triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




