
In a triangle ABC right angled at B, $\angle A=\angle C$, find the values of $\sin A\cos C+\cos A\sin C$.
Answer
606.6k+ views
Hint:We know that the sum of all the angles of a triangle is equal to $180{}^\circ $, so, $\angle A+\angle B+\angle C=180{}^\circ $. We will find the values of A and C and then we will put this value in the given relation, $\sin A\cos C+\cos A\sin C$ to get the value of the given trigonometric expression.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given in the question that ABC is a right angled triangle and $\angle B=90{}^\circ $. It is also given that angle A and angle C are equal and we have to find the value of the trigonometric expression, $\sin A\cos C+\cos A\sin C$. Now, we know that in a right angled triangle ABC, the sum of all the three angles of the triangle is equal to $180{}^\circ $. So, it means that,
$\angle A+\angle B+\angle C=180{}^\circ \ldots \ldots \ldots \left( i \right)$
It is also mentioned in the question that $\angle B=90{}^\circ $. So, we can draw the figure for the same as given below.
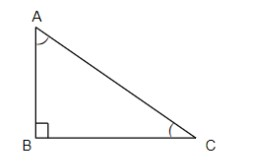
So, we can substitute the value of angle B, that is, $\angle B=90{}^\circ $ in equation (i). So, by doing the same, we get the equation as follows,
$\begin{align}
& \angle A+\angle C+90{}^\circ =180{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow \angle A+\angle C=180{}^\circ -90{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow \angle A+\angle C=90{}^\circ \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that, $\angle A=\angle C$, as it is given in the question. So, we can write the same. So, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \angle C+\angle C=90{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow 2\angle C=90{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow \angle C=\dfrac{90{}^\circ }{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \angle C=45{}^\circ \\
\end{align}$
So, since $\angle C=45{}^\circ $, $\angle A$ will also be equal to $45{}^\circ $. Now, we have the given relation as,
$\sin A\cos C+\cos A\sin C$
Let us write the standard trigonometric angles
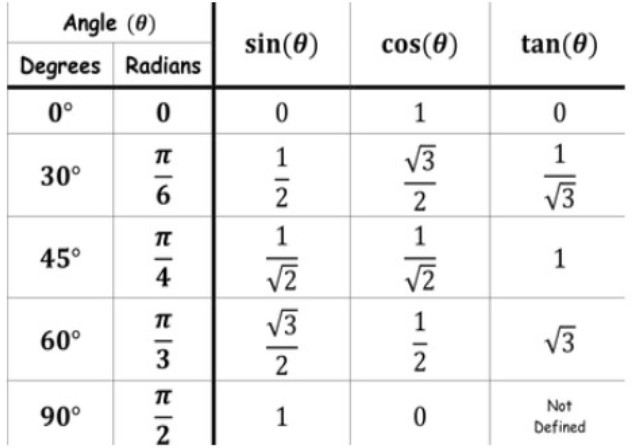
So, by substituting the values of $C=45{}^\circ $and $A=45{}^\circ $ in the above relation, we get,
$\sin 45{}^\circ \cos 45{}^\circ +\cos 45{}^\circ \sin 45{}^\circ $
We know that the value of $\sin 45{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$ and the value of $\cos 45{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$. So, by substituting these values in the above expression, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\times \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\times \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}=1 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the value of the given expression, $\sin A\cos C+\cos A\sin C$ is 1.
Note: There is a possibility of committing a calculation mistake in the last step. In a hurry, the students may write, $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\times \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\times \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\times \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$, which would change the answer completely. So, the students should be careful while substituting the values of the angles and they should remember a few of the trigonometric values of the standard angles.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given in the question that ABC is a right angled triangle and $\angle B=90{}^\circ $. It is also given that angle A and angle C are equal and we have to find the value of the trigonometric expression, $\sin A\cos C+\cos A\sin C$. Now, we know that in a right angled triangle ABC, the sum of all the three angles of the triangle is equal to $180{}^\circ $. So, it means that,
$\angle A+\angle B+\angle C=180{}^\circ \ldots \ldots \ldots \left( i \right)$
It is also mentioned in the question that $\angle B=90{}^\circ $. So, we can draw the figure for the same as given below.

So, we can substitute the value of angle B, that is, $\angle B=90{}^\circ $ in equation (i). So, by doing the same, we get the equation as follows,
$\begin{align}
& \angle A+\angle C+90{}^\circ =180{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow \angle A+\angle C=180{}^\circ -90{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow \angle A+\angle C=90{}^\circ \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that, $\angle A=\angle C$, as it is given in the question. So, we can write the same. So, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \angle C+\angle C=90{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow 2\angle C=90{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow \angle C=\dfrac{90{}^\circ }{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \angle C=45{}^\circ \\
\end{align}$
So, since $\angle C=45{}^\circ $, $\angle A$ will also be equal to $45{}^\circ $. Now, we have the given relation as,
$\sin A\cos C+\cos A\sin C$
Let us write the standard trigonometric angles

So, by substituting the values of $C=45{}^\circ $and $A=45{}^\circ $ in the above relation, we get,
$\sin 45{}^\circ \cos 45{}^\circ +\cos 45{}^\circ \sin 45{}^\circ $
We know that the value of $\sin 45{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$ and the value of $\cos 45{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$. So, by substituting these values in the above expression, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\times \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\times \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}=1 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the value of the given expression, $\sin A\cos C+\cos A\sin C$ is 1.
Note: There is a possibility of committing a calculation mistake in the last step. In a hurry, the students may write, $\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\times \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\times \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\times \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$, which would change the answer completely. So, the students should be careful while substituting the values of the angles and they should remember a few of the trigonometric values of the standard angles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




