
In a silicon diode, the reverse current increases from 10$\mu $A to 20$\mu $A when the reverse voltage changes from 2V to 4V. The reverse AC resistance of the diode is
A) $1 \times {10^5}\Omega $
B) $3 \times {10^5}\Omega $
C) $2 \times {10^5}\Omega $
D) $4 \times {10^5}\Omega $
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: Diode, an electrical component that allows the flow of current in only one direction. In the circuit diagrams, a diode is represented by a triangle with a line across one vertex. A diode works on a function of holes and electrons and hence with the reverse biasing the depletion layer will increase. By finding a change in voltage and current we can easily find resistance as $V=IR$.
Complete step by step answer:
The following diagram shows a PN junction diode with a depletion layer connected in reverse bias.
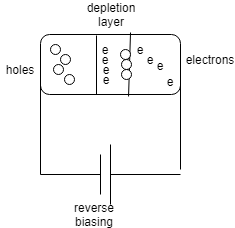
Reverse bias usually refers to how a diode is used in a circuit. If a diode is reverse biased, the voltage at the cathode is higher than that at the anode. Therefore, no current will flow until the electric field is so high that the diode breaks down.
The current here is known as drift current.
The voltage is changed from 4V to 2V
Change in voltage is $\Delta $V=4V-2V
We are also given the reverse current increases from 10$\mu $ A to 20$\mu $ A.
So change in current is $\Delta I$=20$\mu $ A.− 10$\mu $ A which is equal to 10$\mu $ A.
We know that $V=IR$
Putting values of $V$ and $I$, we will get
$R= 2 \times {10^5}\Omega $
Hence option C is correct.
Note:
A reverse-biased diode is said to be an open circuit. But when the diode is on, it acts as a short circuit. Ideally, the diode operates as an open nonlinear circuit with a fixed, constant voltage drop. This model is favored in the engineering field due to its simplicity. It is based on the concept that “forward conducting” has a minor fluctuating voltage drop from about 0.6-0.8 volts, with the assumption that the amount of voltage is constant at 0.7V.
Complete step by step answer:
The following diagram shows a PN junction diode with a depletion layer connected in reverse bias.

Reverse bias usually refers to how a diode is used in a circuit. If a diode is reverse biased, the voltage at the cathode is higher than that at the anode. Therefore, no current will flow until the electric field is so high that the diode breaks down.
The current here is known as drift current.
The voltage is changed from 4V to 2V
Change in voltage is $\Delta $V=4V-2V
We are also given the reverse current increases from 10$\mu $ A to 20$\mu $ A.
So change in current is $\Delta I$=20$\mu $ A.− 10$\mu $ A which is equal to 10$\mu $ A.
We know that $V=IR$
Putting values of $V$ and $I$, we will get
$R= 2 \times {10^5}\Omega $
Hence option C is correct.
Note:
A reverse-biased diode is said to be an open circuit. But when the diode is on, it acts as a short circuit. Ideally, the diode operates as an open nonlinear circuit with a fixed, constant voltage drop. This model is favored in the engineering field due to its simplicity. It is based on the concept that “forward conducting” has a minor fluctuating voltage drop from about 0.6-0.8 volts, with the assumption that the amount of voltage is constant at 0.7V.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




