
In a quadrilateral ABCD, AB=CD and AD=BC. Prove that ABCD is a parallelogram.
Answer
612k+ views
Hint: Start by drawing the diagram, followed by proving that the opposite angles of the quadrilateral ABCD is equal using the properties of congruent triangles. If opposite angles of a quadrilateral are equal, then the quadrilateral is a parallelogram.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us start by drawing the diagram for a better visualisation of the situation given in the question.
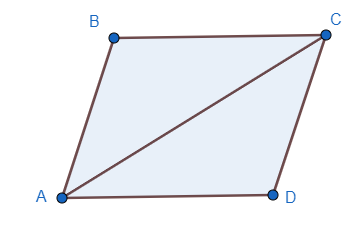
It is given that AB=CD and BC=AD. Also, we can see that AC is common in $\Delta ABC\text{ and }\Delta CDA$ . Therefore, as all three sides of $\Delta ABC$ are equal to corresponding sides of $\Delta CDA$ , we can say that both the triangles are congruent by SSS congruence rule.
Therefore, by using CPCT, we can say that:
$\begin{align}
& \angle ABC=\angle CDA \\
& \angle CAB=\angle ACD...........(i) \\
& \angle DAC=\angle BCA............(ii) \\
\end{align}$
Now if we add equation (i) and equation (ii), we get
$\angle CAB+\angle DAC=\angle ACD+\angle BCA$
Now from the figure, we can deduce that $\angle CAB+\angle DAC=\angle DAB$ and $\angle ACD+\angle BCA=\angle BCD$. Therefore, our equation becomes:
$\angle DAB=\angle BCD$
As the opposite angles of quadrilateral ABCD are equal, i.e., $\angle DAB=\angle BCD$ and $\angle ABC=\angle CDA$ , so we can say that quadrilateral ABCD is a parallelogram.
Note: It is prescribed to learn all the basic theorems related to congruence and similarity of triangles as they are used quite often. Also, learn the properties of parallelograms, including squares, as they might also be needed for solving such problems as we used in the above question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us start by drawing the diagram for a better visualisation of the situation given in the question.

It is given that AB=CD and BC=AD. Also, we can see that AC is common in $\Delta ABC\text{ and }\Delta CDA$ . Therefore, as all three sides of $\Delta ABC$ are equal to corresponding sides of $\Delta CDA$ , we can say that both the triangles are congruent by SSS congruence rule.
Therefore, by using CPCT, we can say that:
$\begin{align}
& \angle ABC=\angle CDA \\
& \angle CAB=\angle ACD...........(i) \\
& \angle DAC=\angle BCA............(ii) \\
\end{align}$
Now if we add equation (i) and equation (ii), we get
$\angle CAB+\angle DAC=\angle ACD+\angle BCA$
Now from the figure, we can deduce that $\angle CAB+\angle DAC=\angle DAB$ and $\angle ACD+\angle BCA=\angle BCD$. Therefore, our equation becomes:
$\angle DAB=\angle BCD$
As the opposite angles of quadrilateral ABCD are equal, i.e., $\angle DAB=\angle BCD$ and $\angle ABC=\angle CDA$ , so we can say that quadrilateral ABCD is a parallelogram.
Note: It is prescribed to learn all the basic theorems related to congruence and similarity of triangles as they are used quite often. Also, learn the properties of parallelograms, including squares, as they might also be needed for solving such problems as we used in the above question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




