
In a parallelogram $ ABCD, $ the bisector of angle $ ABC $ intersect $ AD $ at $ P. $ If $ PD = 5,BP = 6 $ and $ CP = 6 $ , find $ AB $
(A) $ 5 $
(B) $ 4 $
(C) $ 6 $
(D) $ 8 $
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: Use the properties of parallelogram and similarity of triangles to solve this question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Observe the diagram
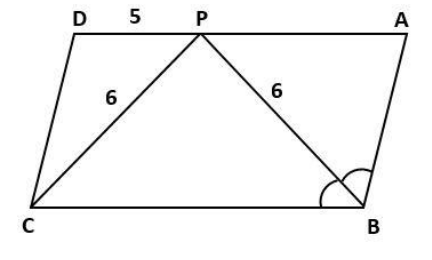
$ \Delta PBC $ is an isosceles triangle.
$ \because PB = CP = 6 $ (Given)
Also, $ \angle PBC = \angle APB $ (alternate interior angles) . . . (1)
$ \angle PBC = \angle ABP $ (Since, PB is angle bisector) . . . (2)
From equation (1) and (2), we get
$ \angle APB = \angle ABP $
$ \Rightarrow \Delta APB $ is an isosceles triangle.
$ \Rightarrow AP = AB $ (Sides opposite to equal angles of isosceles triangle)
In $ \Delta PCB $ and $ \Delta APB $
$ \angle PBC = \angle PBA $ (Since, PB is angle bisector) . . . (3)
From equation (3) and the fact that $ \Delta PCB $ and $ \Delta APB $ are isosceles triangle. We can say that
$ \angle PCB = \angle APB $ (Since their opposite angles are equal to each other)
Since, two angles of two triangles are equal, there third angle must be equal as well.
$ \Rightarrow \angle CPB = \angle PAB $
Therefore, by AAA criteria of similarity of triangles, we can write
$ \Delta PCB \approx \Delta APB $
Therefore, by the property of similar triangles, the ratio of corresponding sides of the two triangles is equal
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{PC}}{{AP}} = \dfrac{{CB}}{{PB}} = \dfrac{{PB}}{{AB}} $
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{CB}}{{PB}} = \dfrac{{PB}}{{AB}}\]
$ BC = AD $ (Opposite sides of a parallelogram)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AD}}{{PB}} = \dfrac{{PB}}{{AB}}\]
$ AD = AP + PD $
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AP + PD}}{{PB}} = \dfrac{{PB}}{{AB}}\]
$ AP = AB $ (Opposite sides to equal angles of $ \Delta APB $ )
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AB + PD}}{{PB}} = \dfrac{{PB}}{{AB}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AB + 5}}{6} = \dfrac{6}{{AB}}\] $ (\because PD = 5 $ and $ PB = 6) $
By cross multiplying, we get
$ A{B^2} + 5AB = 36 $
Let $ AB = x $
Then we get
$ {x^2} + 5x = 36 $
By rearranging it, we get
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 5x - 36 = 0 $
This is a quadratic equation. We will solve it by splitting the middle term
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 9x - 4x - 36 = 0 $
$ \Rightarrow x(x + 9) - 4(x + 9) = 0 $
$ \Rightarrow (x + 9)(x - 4) = 0 $
$ \Rightarrow x = - 9,4 $
But length cannot be negative.
Therefore $ x = 4 $
$ \therefore AB = AP = 4 $
Therefore, the value of $ AB = 4 $
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: In this question, less information was given directly. We had to find out the information we needed to solve this question using the properties of parallelogram, isosceles triangle and similarity of two triangles. From this question, we understand that properties of geometrical figures are very important.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Observe the diagram

$ \Delta PBC $ is an isosceles triangle.
$ \because PB = CP = 6 $ (Given)
Also, $ \angle PBC = \angle APB $ (alternate interior angles) . . . (1)
$ \angle PBC = \angle ABP $ (Since, PB is angle bisector) . . . (2)
From equation (1) and (2), we get
$ \angle APB = \angle ABP $
$ \Rightarrow \Delta APB $ is an isosceles triangle.
$ \Rightarrow AP = AB $ (Sides opposite to equal angles of isosceles triangle)
In $ \Delta PCB $ and $ \Delta APB $
$ \angle PBC = \angle PBA $ (Since, PB is angle bisector) . . . (3)
From equation (3) and the fact that $ \Delta PCB $ and $ \Delta APB $ are isosceles triangle. We can say that
$ \angle PCB = \angle APB $ (Since their opposite angles are equal to each other)
Since, two angles of two triangles are equal, there third angle must be equal as well.
$ \Rightarrow \angle CPB = \angle PAB $
Therefore, by AAA criteria of similarity of triangles, we can write
$ \Delta PCB \approx \Delta APB $
Therefore, by the property of similar triangles, the ratio of corresponding sides of the two triangles is equal
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{PC}}{{AP}} = \dfrac{{CB}}{{PB}} = \dfrac{{PB}}{{AB}} $
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{CB}}{{PB}} = \dfrac{{PB}}{{AB}}\]
$ BC = AD $ (Opposite sides of a parallelogram)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AD}}{{PB}} = \dfrac{{PB}}{{AB}}\]
$ AD = AP + PD $
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AP + PD}}{{PB}} = \dfrac{{PB}}{{AB}}\]
$ AP = AB $ (Opposite sides to equal angles of $ \Delta APB $ )
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AB + PD}}{{PB}} = \dfrac{{PB}}{{AB}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{AB + 5}}{6} = \dfrac{6}{{AB}}\] $ (\because PD = 5 $ and $ PB = 6) $
By cross multiplying, we get
$ A{B^2} + 5AB = 36 $
Let $ AB = x $
Then we get
$ {x^2} + 5x = 36 $
By rearranging it, we get
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 5x - 36 = 0 $
This is a quadratic equation. We will solve it by splitting the middle term
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + 9x - 4x - 36 = 0 $
$ \Rightarrow x(x + 9) - 4(x + 9) = 0 $
$ \Rightarrow (x + 9)(x - 4) = 0 $
$ \Rightarrow x = - 9,4 $
But length cannot be negative.
Therefore $ x = 4 $
$ \therefore AB = AP = 4 $
Therefore, the value of $ AB = 4 $
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: In this question, less information was given directly. We had to find out the information we needed to solve this question using the properties of parallelogram, isosceles triangle and similarity of two triangles. From this question, we understand that properties of geometrical figures are very important.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




