
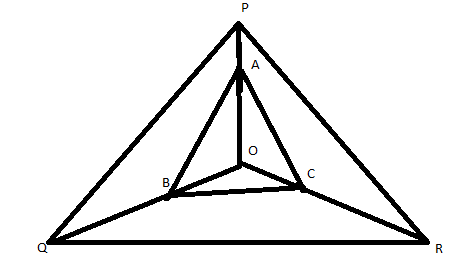
In a given figure, \[A,B\] and \[C\] are points on \[OP\], \[OQ\] and \[OR\] respectively such that \[AB\parallel PQ\] and \[AC\parallel PR\]. Show that \[BC\parallel QR\].

Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: To solve this geometry, use a similar triangle concept. Similar triangles, two figures having the same shape (but not necessarily the same size) are called similar figures.
The first part of the solution is important, for that, we use one of the theorems of a similar triangle that is, if a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
The second part of the solution is done by using “if a line divides any two sides of a triangle in the same ratio, the line is parallel to the third side”.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given: \[AB\parallel PQ\] and \[AC\parallel PR\]
To show that: \[BC\parallel QR\]
In a\[\Delta OPQ\],
\[AB\parallel PQ\]
Here, by the theorem, in a \[\Delta OPQ\] the line \[AB\] which is parallel to \[PQ\] intersects the other two sides in distinct points, so it divides the other two side in same ratio
The ratio is, \[\dfrac{{OA}}{{AP}} = \dfrac{{OB}}{{BQ}}...\left( 1 \right)\]
Similarly,
\[\Delta OPR\]
\[AC\parallel PR\]
Here, by the theorem, in a \[\Delta OPR\] the line \[AC\] which is parallel to \[PR\] intersects the other two sides in distinct points, so it divides the other two side in same ratio
The ratio is, \[\dfrac{{OC}}{{CR}} = \dfrac{{OA}}{{AP}}....\left( 2 \right)\]
The ratio of \[(1)\& (2)\] shows the two \[\Delta OPQ\] and \[\Delta OPR\], \[BC\parallel QR\] also corresponding sides are same ratio \[\dfrac{{OA}}{{AP}} = \dfrac{{OB}}{{BQ}}\]=\[\dfrac{{OC}}{{CR}} = \dfrac{{OA}}{{AP}}\]
Thus,
\[\dfrac{{OB}}{{BQ}} = \dfrac{{OC}}{{CR}}\]
Hence proved.
Now, we can say that the triangle is a similar triangle.
To show that the side is parallel, we use the second part of the hint
In a \[\Delta OQR\],
\[\dfrac{{OC}}{{CR}} = \dfrac{{OB}}{{BQ}}\]
That is, line \[BC\]divides the triangle \[\Delta OQR\] in the same ratio
Therefore, \[BC\parallel QR\]
Hence proved.
Note: The theorem, we state the first part and second part is called basic proportionality theorem.
Two triangles are said to be similar, if their corresponding angles are equal and their corresponding sides are in the same ratio proportion.
The first part of the solution is important, for that, we use one of the theorems of a similar triangle that is, if a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
The second part of the solution is done by using “if a line divides any two sides of a triangle in the same ratio, the line is parallel to the third side”.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given: \[AB\parallel PQ\] and \[AC\parallel PR\]
To show that: \[BC\parallel QR\]
In a\[\Delta OPQ\],
\[AB\parallel PQ\]
Here, by the theorem, in a \[\Delta OPQ\] the line \[AB\] which is parallel to \[PQ\] intersects the other two sides in distinct points, so it divides the other two side in same ratio
The ratio is, \[\dfrac{{OA}}{{AP}} = \dfrac{{OB}}{{BQ}}...\left( 1 \right)\]
Similarly,
\[\Delta OPR\]
\[AC\parallel PR\]
Here, by the theorem, in a \[\Delta OPR\] the line \[AC\] which is parallel to \[PR\] intersects the other two sides in distinct points, so it divides the other two side in same ratio
The ratio is, \[\dfrac{{OC}}{{CR}} = \dfrac{{OA}}{{AP}}....\left( 2 \right)\]
The ratio of \[(1)\& (2)\] shows the two \[\Delta OPQ\] and \[\Delta OPR\], \[BC\parallel QR\] also corresponding sides are same ratio \[\dfrac{{OA}}{{AP}} = \dfrac{{OB}}{{BQ}}\]=\[\dfrac{{OC}}{{CR}} = \dfrac{{OA}}{{AP}}\]
Thus,
\[\dfrac{{OB}}{{BQ}} = \dfrac{{OC}}{{CR}}\]
Hence proved.
Now, we can say that the triangle is a similar triangle.
To show that the side is parallel, we use the second part of the hint
In a \[\Delta OQR\],
\[\dfrac{{OC}}{{CR}} = \dfrac{{OB}}{{BQ}}\]
That is, line \[BC\]divides the triangle \[\Delta OQR\] in the same ratio
Therefore, \[BC\parallel QR\]
Hence proved.
Note: The theorem, we state the first part and second part is called basic proportionality theorem.
Two triangles are said to be similar, if their corresponding angles are equal and their corresponding sides are in the same ratio proportion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




