
In a crystal of diamond:
(i) How many carbon atoms are present per unit cell?
(ii) What type of lattice does diamond crystallize in?
(iii) How many carbon atoms surround each carbon atom?
(iv)How are they arranged?
Answer
531.4k+ views
Hint: We know that a unit is the smallest representation of a whole crystal. During a unit, an atom's coordination number is the number of atoms it's touching. The coordination number of face-centered cubic (FCC) is twelve and contains four atoms per unit. The coordination of the body-centered cubic (bcc) is eight and contains two atoms per unit.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we discuss the face centered cubic crystal lattice,
Face centered cubic (FCC):
There are the eight lattice points at each corner of the face centered crystal and there are additional lattice points at the middle of every face of the cube.
${\text{FCC}} = \dfrac{{{\text{Total number of edges}}}}{{{\text{Number of atoms share}}}} + \dfrac{{{\text{Number of corners}}}}{{{\text{Number of atoms shared}}}}$
(i) Diamond has face centered cubic unit structure made from atoms. This accounts for \[8 \times {\text{ }}1/8{\text{ }} + 6 \times {\text{ }}1/2 = 1 + 3 = 4\] Carbon atoms. Carbon atoms also are present in one half the tetrahedral voids. There are 8 tetrahedral voids in face centered cubic unit structure. This accounts for the remaining \[8 \times {\text{ }}1/2{\text{ }} = 4\] Carbon atoms. Thus, total \[4 + 4 = 8\] Carbon atoms are present per unit of diamond.
(ii) Diamond crystallizes in a face centered cubic unit lattice of carbon atoms.
(iii) Four carbon atoms surround each carbon atom.
(iv)Four carbon atoms are arranged tetrahedrally around each central carbon atom.
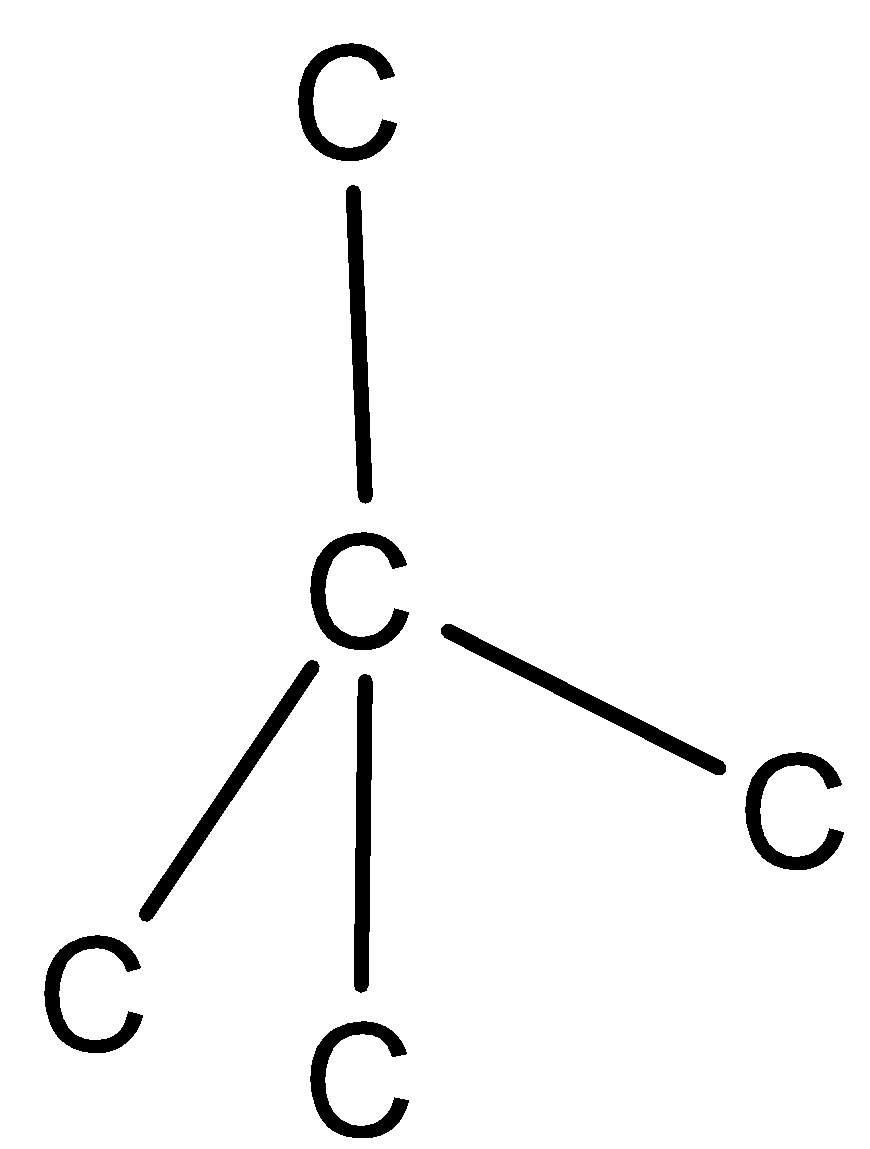
Note: We must remember that the diamond belongs to the class of the covalent network solid. In Diamond, the atoms are bonded covalently in a continuous, extended network. The strong binding forces that join all the adjacent atoms account for the extreme hardness of Diamond. They cannot be broken or abraded without breaking a large number of covalent chemical bonds. The high melting point nature of diamonds is due to the presence of strong intermolecular force.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we discuss the face centered cubic crystal lattice,
Face centered cubic (FCC):
There are the eight lattice points at each corner of the face centered crystal and there are additional lattice points at the middle of every face of the cube.
${\text{FCC}} = \dfrac{{{\text{Total number of edges}}}}{{{\text{Number of atoms share}}}} + \dfrac{{{\text{Number of corners}}}}{{{\text{Number of atoms shared}}}}$
(i) Diamond has face centered cubic unit structure made from atoms. This accounts for \[8 \times {\text{ }}1/8{\text{ }} + 6 \times {\text{ }}1/2 = 1 + 3 = 4\] Carbon atoms. Carbon atoms also are present in one half the tetrahedral voids. There are 8 tetrahedral voids in face centered cubic unit structure. This accounts for the remaining \[8 \times {\text{ }}1/2{\text{ }} = 4\] Carbon atoms. Thus, total \[4 + 4 = 8\] Carbon atoms are present per unit of diamond.
(ii) Diamond crystallizes in a face centered cubic unit lattice of carbon atoms.
(iii) Four carbon atoms surround each carbon atom.
(iv)Four carbon atoms are arranged tetrahedrally around each central carbon atom.

Note: We must remember that the diamond belongs to the class of the covalent network solid. In Diamond, the atoms are bonded covalently in a continuous, extended network. The strong binding forces that join all the adjacent atoms account for the extreme hardness of Diamond. They cannot be broken or abraded without breaking a large number of covalent chemical bonds. The high melting point nature of diamonds is due to the presence of strong intermolecular force.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




